| 4-ピロン[1]
|

|
|
|
|
|
| 識別情報
|
| CAS登録番号
|
108-97-4 
|
| PubChem
|
7968
|
| ChemSpider
|
7680 
|
| ChEBI
|
|
C1=COC=CC1=O O=C\1/C=C\O/C=C/1
|
InChI=1S/C5H4O2/c6-5-1-3-7-4-2-5/h1-4H  Key: CVQUWLDCFXOXEN-UHFFFAOYSA-N  InChI=1/C5H4O2/c6-5-1-3-7-4-2-5/h1-4H Key: CVQUWLDCFXOXEN-UHFFFAOYAG
|
| 特性
|
| 化学式
|
C5H4O2
|
| モル質量
|
96.08
|
| 融点
|
32 - 34 °C, 271 K, 3 °F
|
| 沸点
|
210 - 215 °C, 268 K, -145 °F
|
| 危険性
|
| 引火点
|
101 °C (214 °F; 374 K)
|
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。
|
4-ピロン(4-Pyrone)またはγ-ピロン(γ-Pyrone)は、分子式C5H4O2の不飽和複素環式化合物である。2-ピロンの異性体である。
生成と反応
4-ピロン-2,6-ジカルボン酸の加熱による脱炭酸によって生成される[2]。プロトン性溶媒中でアミンと反応し、4-ピリドンを生成する[2][3][4]。
誘導体
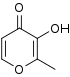
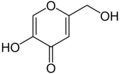
4-ピロンは、マルトールやコウジ酸等のいくつかの天然化合物の中心構造を形成し、フラボンの重要な一分類になっている。
|
|
| マルトール
|
コウジ酸
|
関連項目
出典
- ^ 4H-Pyran-4-one at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ a b Weygand, Conrad (1972). Hilgetag, G.; Martini, A.. eds. Weygand/Hilgetag Preparative Organic Chemistry (4th ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.. pp. 533-534, & 1009. ISBN 0471937495
- ^ Van Allan, J. A.; Reynolds, G. A.; Alessi, J. T.; Chie Chang, S.; C. Joines, R. (1971). “Reactions of 4‐pyrones with primary amines. A new class of ionic associates”. Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 8 (6): 919–922. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570080606.
- ^ Cook, Denys (1963). “The Preparation, Properties, and Structure of 2,6-bis-(Alkyamino)-2,5-heptadien-4-ones”. Canadian Journal of Chemistry 41 (6): 1435-1440. doi:10.1139/v63-195.