|
Suxibuzone
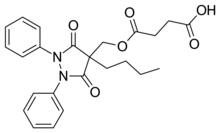
Suxibuzone is an analgesic used for joint and muscular pain. It is a prodrug of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) phenylbutazone,[1] and is commonly used in horses.[2] SynthesisSuxibuzone is synthesized by the following method:[3] Patent:[4] (Precursor:[5])  Phenylbutazone [50-33-9] (1) is hydroxymethylated with formaldehyde giving ~86% 4-butyl-4-(hydroxymethyl)-1,2-diphenylpyrazolidine-3,5-dione [23111-33-3] (2). This is then esterified with succinic anhydride. [108-30-5] (3) to give (4). References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||