Sufficiency of disclosure
|
Read other articles:

Pour les autres articles nationaux ou selon les autres juridictions, voir Conseil constitutionnel. Ne doit pas être confondu avec le Comité consultatif constitutionnel (1958). Conseil constitutionnelLogo du Conseil constitutionnel.Salle des délibérés du Conseil constitutionnel.HistoireFondation 4 octobre 1958Origine Constitution du 4 octobre 1958CadreSurnoms Conseil des sages, (en) The wise, (en) Wise OnesType Cour constitutionnelle, cour suprêmeForme juridique Autorité constitu…
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)[2…

American gridiron football player (1989–2015) Not to be confused with former American football player Adrien Robinson. For the Botswana swimmer, see Adrian Robinson (swimmer). For the British geographer, see Adrian Henry Wardle Robinson. American football player Adrian Robinson Jr.No. 57, 99, 97Position:LinebackerPersonal informationBorn:(1989-11-21)November 21, 1989Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, U.S.Died:May 16, 2015(2015-05-16) (aged 25)Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S.Height:6 ft 1 …

American film director This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Nikole Beckwith – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Nikole Beckwith is an American director, screenwriter, and playwright. She has also performed live with a handful of bands and sings on Tiger Saw's 2005 record Sing!&…

关于与「內閣總理大臣」標題相近或相同的条目页,請見「內閣總理大臣 (消歧義)」。 日本國內閣總理大臣內閣總理大臣紋章現任岸田文雄自2021年10月4日在任尊称總理、總理大臣、首相、阁下官邸總理大臣官邸提名者國會全體議員選出任命者天皇任期四年,無連任限制[註 1]設立法源日本國憲法先前职位太政大臣(太政官)首任伊藤博文设立1885年12月22日,…

Katedral AmalfiKatedral Santo Andreasbahasa Italia: Cattedrale di Sant'Andrea/Duomo di AmalfiKatedral AmalfiLokasiAmalfiNegaraItaliaDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaArsitekturStatusKatedralStatus fungsionalAktifAdministrasiKeuskupan AgungKeuskupan Agung Amalfi-Cava de' Tirreni Katedral Amalfi (bahasa Italia: Duomo di Amalfi; Cattedrale di Sant'Andrea) adalah sebuah gereja katedral Katolik bergaya abad pertengahan yang terletak di Piazza del Duomo, Amalfi, Italia. Katedral ini didedikasikan u…

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддійсь…

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يناير 2019) IC 434 الكوكبة الجبار[1] رمز الفهرس IC 434 (كتالوج مفهرس)LBN 953 (Lynds' Catalogue of Bright Nebulae)[2] المكتشف ويليمينا فليمنغ تاريخ الاكتشاف 1888 شاهد أيضًا: مج�…
Ice skating competition in Obihiro, Japan 2023–24 ISU Speed Skating World Cup 1VenueMeiji Hokkaido-Tokachi OvalObihiroJapanDates10 — 12 November 2023 2023–24 ISU Speed Skating World CupMen and womenWorld Cup 1 ObihiroWorld Cup 2 BeijingWorld Cup 3 StavangerWorld Cup 4 Tomaszów MazowieckiWorld Cup 5 Salt Lake CityWorld Cup 6 Quebec Cityvte The first competition weekend of the 2023–24 ISU Speed Skating World Cup is being held at the Meiji Hokkaido-Tokachi Oval in Obihiro, Japan, from Frid…
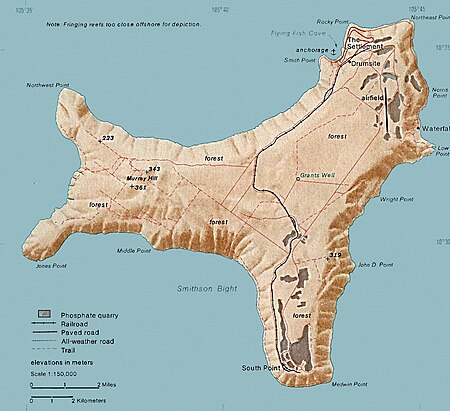
External territory of Australia This article is about the Australian territory in the Indian Ocean. For the island of Kiribati, see Kiritimati. For other uses, see Christmas Island (disambiguation). 10°29′24″S 105°37′39″E / 10.49000°S 105.62750°E / -10.49000; 105.62750 Place in AustraliaChristmas IslandAustralian Indian Ocean TerritoryExternal territory of AustraliaTerritory of Christmas Island圣诞岛领地 / 聖誕島領地 (Chinese)Wilayah Pulau Krism…

1936 filmI Love to SingaDirected byFred AveryProduced byLeon SchlesingerMusic byNorman SpencerAnimation byCharles JonesVirgil RossColor processTechnicolorProductioncompanyLeon Schlesinger ProductionsDistributed byWarner Bros. PicturesThe Vitaphone CorporationRelease dates July 18, 1936 (1936-07-18) (original release) November 18, 1944 (1944-11-18) (Blue Ribbon reissue) Running time8:14LanguageEnglish I Love to Singa is a 1936 Warner Bros. Merrie Melodies ani…

غران فيامعلومات عامةالتقسيم الإداري مدريد البلد إسبانيا شبكة المواصلات مترو مدريد المالك Consorcio Regional de Transportes de Madrid (en) الإدارة Metro de Madrid S.A. (en) الخطوط Madrid Metro Line 1 (en) Madrid Metro Line 5 (en) المحطات المجاورة تريبيونالعلى الخط: Madrid Metro Line 1 (en) باتجاه: Pinar de Chamartín (en) — Chueca (en) على الخط: Madrid Metr…

Azerbaijani natural gas and oil plant This article is about the oil and gas terminal. For the village, see Sanqaçal. Sangachal TerminalSangachal Terminal, — located on the coast of the Caspian Sea 28 mil south of Baku, AzerbaijanClick on the map for a fullscreen viewLocationCountryAzerbaijanLocationSanqaçalCoordinates40°12′05″N 49°28′53″E / 40.201262°N 49.481270°E / 40.201262; 49.481270DetailsOpened1996Operated byBPOwned byAzerbaijanType of harbourOil and …

Type of electronic audio manipulation Fuzzbox redirects here. For other uses, see Fuzzbox (disambiguation). This article is about distortion in music. For distortion in general, see Distortion. The DS-1 was the first ever distortion guitar effect pedal manufactured by Boss An auditory example of the distortion effect with the clean signal shown first. Distortion and overdrive are forms of audio signal processing used to alter the sound of amplified electric musical instruments, usually by increa…

2022 UCI Track Cycling World ChampionshipsVenueSaint-Quentin-en-Yvelines, France Date(s)12–16 OctoberVelodromeVélodrome NationalEvents22← Roubaix 2021Glasgow 2023 → 2022 UCI Track CyclingWorld ChampionshipsSprintmenwomenTime trialmenwomenIndividual pursuitmenwomenTeam pursuitmenwomenTeam sprintmenwomenKeirinmenwomenScratchmenwomenPoints racemenwomenMadisonmenwomenEliminationmenwomenOmniummenwomenvte The 2022 UCI Track Cycling World Championships started on 12 October and…

China Southern Airlines中国南方航空公司Zhōngguó Nánfāng Hángkōng Gōngsī IATA ICAO Kode panggil CZ CSN CHINA SOUTHERN Didirikan1991; 33 tahun lalu (1991)AOC #C4XF535FPenghubung Bandar Udara Internasional Ibu Kota Beijing Bandar Udara Internasional Jiangbei Chongqing Bandar Udara Internasional Baiyun Guangzhou Bandar Udara Internasional Diwopu Ürümqi Kota fokus Bandar Udara Internasional Longjia Changchun Bandar Udara Internasional Huanghua Changsha Bandar Udara Internasiona…

1960 studio album by Bob BrookmeyerJazz Is a KickStudio album by Bob BrookmeyerReleased1960RecordedMay 9 & 16, 1960New York CityGenreJazzLength36:27LabelMercuryMG 20600/60600ProducerChuck DarwinBob Brookmeyer chronology Portrait of the Artist(1960) Jazz Is a Kick(1960) The Blues Hot and Cold(1960) Jazz Is a Kick is an album by jazz trombonist and arranger Bob Brookmeyer recorded in 1960 for the Mercury label.[1][2] Reception Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRati…

High-speed railway line between Osaka and Fukuoka, Japan San'yō ShinkansenN700A Series Shinkansen between Nishi-Akashi and Himeji, February 2021OverviewNative name山陽新幹線Owner JR WestLocaleOsaka, Hyōgo, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi and Fukuoka PrefecturesTerminiShin-ŌsakaHakataStations19Color on map Blue (#24197c)ServiceTypeHigh-speed rail (Shinkansen)SystemShinkansenServicesMizuho, Sakura, Nozomi, Hikari, KodamaOperator(s)JR WestDepot(s)Osaka, Okayama, Hirosh…

NASCAR Seri Piala Sprint 2008 Sebelum: 2007 Sesudah: 2009 Jimmie Johnson mencetak hat-trick juara musim pada 2008. NASCAR Seri Piala Sprint 2008 merupakan musim ke 60 dari NASCAR Seri Piala Sprint. Musim ini berlangsung dari tanggal 17 Februari 2008 lewat Daytona 500 di Daytona International Speedway dan berakhir pada 16 November dalam Ford 400 di Homestead-Miami Speedway. Nama sponsor utama NASCAR Seri Piala berubah dari NEXTEL menjadi Sprint karena adanya merger antara kedua perusahaan yang sa…

Infection caused by Bacillus anthracis bacteria For other uses, see Anthrax (disambiguation). The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this article, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new article, as appropriate. (October 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Medical conditionAnthraxA skin lesion with black eschar characteristic of anthraxSpecialtyInfectious diseaseSymptomsSkin form: small blister wit…