|
Subdivisions of Belgrade
Serbia's capital city of Belgrade is divided into 17 municipalities.[1] Most of the municipalities are situated on the southern side of the Danube and Sava rivers, in the Šumadija region. Three municipalities (Zemun, Novi Beograd, and Surčin) are on the northern bank of the Sava, in the Syrmia region, and the municipality of Palilula, spanning the Danube, is in both the Šumadija and Banat regions. Municipalities
Governmental structure A municipality is a part of the territory of the City of Belgrade, in which certain operations of local self-government laid down by the City Charter are run. Pursuant to the Constitution, legislation, present Charter and bylaws of the municipality, the citizens participate in conducting operations of the municipality through the councilors elected to the municipal assembly, civil initiative, local citizens’ meeting and referendum. The bodies of the municipality are:
The number of councilors in the Municipal Assembly ranges from 19 to 75 councilors. The District Council Chairman presides over the Municipal Assembly and is a chairperson of the Municipal Council. The Municipal Assembly elects the District Council Chairman among the municipal councilors. The Municipal Council is composed of the District Council Chairman, Deputy District Council Chairman and at the most 7 members. The Municipal Council members are elected by the Municipal Assembly among both councilors and citizens further to the proposal by the District Council Chairman. History18th century During the Austrian occupation of northern Serbia 1718-1739, Belgrade was divided by the governing Austrian authorities into 6 districts: Fortress, Serbian town (modern Kosančićev Venac), German town (modern Dorćol), Lower Serbian town (Savamala), Karlstadt (Palilula) and the Great military hospital (Terazije-Tašmajdan).[3] 19th centuryDuring the First Serbian Uprising, the Serbian Administrative Council divided the liberated territory in 12 nahiyah in 1807, confirming more or less the already existing division. One of them, Belgrade Nahiyah, covered mostly the present part of the Šumadija section of the territory of City of Belgrade. The existence of the Belgrade Nahiyah was retained after the Second Serbian Uprising in 1815. In order to replace the division inherited from the Ottoman period, the new, military-based division was introduced in 1834. Belgrade Nahiya was replaced with the Belgrade Okrug, which itself was part of the super-unit of Podunavlje Serdarstvo. Belgrade Okrug occupied territory much wider than the city itself, and was divided into the srez of Kolubara (seated in Šopić), Kosmaj (Sopot), Podunavlje (Grocka), Posavina (Ostružnica) and Turija (Darosava). Almost all villages became seats of the municipalities. In 1837, Kosmaj was annexed to Podunavlje. In 1838 the military administration was replaced with the civilian one.[4] After 1806, the rebellion leaders divided Belgrade into quarters, for practical purposes. The city had no officially named streets at the time, so the houses were numbered by the quarter to which they belonged.[5] The administration of Belgrade City was established in 1839, according to the Law on the organization of municipalities. In 1841 the administration was made independent from the Ministry of the Interior, though the government still supervised the courts, police and administration.[6] On 15 March 1847, the city administration asked from the Ministry of the Interior to do the numbering of the houses. The ministry suggested the division of the entire city into quarters and on 9 February 1848 proposed division into six quarters: Metropolitan, Zerek (Dorćol), Savamala, Terazije, Palilula and Vračar.[3][5] On 2 July 1856 the srez of Turija was abolished and divided between Kosmaj and Kolubara, and the new srez of Vračar was formed from the parts of Podunavlje (which was renamed to Grocka) and Posavina. The Vračar Srez covered the area directly surrounding the city itself, including the villages of Banjica, Beli Potok, Jajinci, Kaluđerica, Kumodraž, Leštane, Mali Mokri Lug, Mirijevo, Pinosava, Rakovica, Resnik, Rušanj, Slanci Veliki Mokri Lug, Vinča and Višnjica from Podunavlje and Kneževac, Žarkovo and Železnik from Posavina. Additions to Vračar included Ostružnica on 14 March 1861, Ripanj on 14 February 1886 and Zuce in 1890, while Topčider was transferred from Podunavlje directly under the Belgrade administration, becoming part of the city on 1 July 1863.[4] In December 1859, mayor of Belgrade, at that time called "city administrator", Nikola Hristić, again suggested the division of Belgrade into quarters, which would move the city further from the oriental way of administration and mark the beginning of the modern, European way of local governing. Ministry of interior forwarded his request to the State Council and to Prince of Serbia Miloš Obrenović. They accepted the proposition and on 5 September [O.S. 24 July] 1860, Prince Miloš signed ukaz by which Belgrade, with some 3,000 houses at the time, was divided into six quarters. The quarters were sub-areal organs of the municipal administration and had certain jurisdiction over political and public security, construction, administrative works, education, health care, social care, etc.[7] By the 1883 census, the city had a population of 36,177, or by the quarters: Palilula 7,118, Terazije 6,333, Vračar 5,965, Dorćol 5,728, Savamala 5,547 and Varoš 4,519. Remaining 767 inhabitants lived in Topčider, which wasn't organized as a quarter.[8][9] Additional quarter called Grad (Town), which occupied the fortress area while it was inhabited, existed between the censuses of 1890 and 1910,[10] before being abolished on 24 August 1913.[4]   After the administrative reforms on 25 November 1889 (concerning municipalities) and 15 March 1890 (administrative division), Belgrade Okrug merged with Smedervo Okrug into Podunavlje Okrug while Vračar Srez consisted of 16 municipalities and 22 settlements in total, all of which were villages: Beli Potok (including Selo Rakovica), Kumodraž, Leštane (including Zuce), Mali Mokri Lug, Mirijevo, Pinosava, Resnik, Ripanj, Rušanj, Slanci, Veliki Mokri Lug, Veliko Selo, Vinča, Višnjica, Žarkovo and Železnik.[4] Quarters of Belgrade by the census:[9][10][11][12]
The surrounding Belgrade Okrug and its constituent srez:
20th centuryBefore World War IIBelgrade Okrug was restored in its previous borders on 24 January 1900, with the division of Podunavlje. Čukarica was transferred from Vračar Srez to the Belgrade City administration on 8 July 1907. In 1913 Belgrade Okrug consisted of two srez: Vračar, in its previous borders, and Grocka. Grocka Srez included Begaljica, Boleč, Brestovik, Vrčin, Grocka, Dražanj, Zaklopača, Kamendol, Mala Ivanča, Mali Požarevac, Pudarci, Ritopek, Senaja, Umčari and Šepšin. The law on 24 August 1913 confirmed the division of Belgrade into 7 quarters.[4] 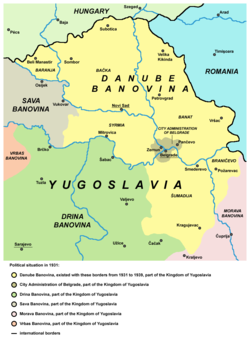 After the May Coup, a new law was adopted on 18 June [O.S. 5 June] 1903 which created a modern local self-governance. The city was administered by the cabinet of the president of the municipality, with offices for different aspects of city life, like modern secretariats. Two specific directories were the one for the trams and another for the social and health care.[6] Still, the division on six quarters remained until the Austro-German occupation of the city in 1915, during World War I. After the liberation in 1918, city was administratively expanded to include its outer suburbs like Dušanovac and Voždovac.[7] In the 1918-1921 period, after the creation of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, the division was kept and the Belgrade Okrug was restored to its pre-1913 borders. In 1922 the new state was divided into oblasts. Belgrade Oblast included just the immediate southwest surroundings of Belgrade but on the north it spread all over to the Hungarian and Romanian border. The oblasts were abolished in 1929 and replaced with banovinas.[4] In 1922 a new statute envisioned a regular elections for the city assembly every 3 years. Winning party would de allocated two thirds of the seats, while the rest would be divided among the opposition parties, using the proportional system. After the 6 January Dictatorship was introduced by the king Alexander I of Yugoslavia in 1929, part of the 1922 statute was abolished and the opposition's third in the city assembly was allocated by the prerogative of the Minister of the Interior. Administratively, area of Belgrade was expanded.[6] Towns of Zemun, across the Sava, and Pančevo, across the Danube, were annexed to the city territory on 4 October 1929,[13] forming the Administration of Belgrade City, but remained separate settlements. Zemun lost its separate status and became part of the Belgrade settlement in 1934.[14] The area of the city was divided into 14 quarters (including the original 6),[7] for the purposes of the more effective administration, police and courts.[6] In 1935 3 additional quarters were formed, lifting the total number to 17.[6] New law on municipalities in March 1933 stipulated for the creation of relatively large municipalities, with over 3,000 inhabitants. This caused a major regrouping of the municipalities in the state. Also, the self-administration of the municipalities was limited as they were heavily administered by the state administration which now became the supervising organs. In the 1921–1931, only one new municipality was formed in the Vračar Srez.[4] World War IIAfter occupation of Yugoslavia in April 1941, German occupational administration divided Occupied Serbia into 14 okrugs, one of them being Belgrade Okrug. They kept the division into srez and further into municipalities.[4] The okrug in this period included 9 srez: Belgrade [Municipality], Grocka, Umka, Sopot, Lazarevac, Mladenovac, Smederevo, [Smederevska] Palanka and Veliko Orašje.[15] Yugoslav Partisans in time formed their own administrative bodies, called people's liberation boards (NOO). At first temporary organs, after the German defeat in 1944-1945 they became the units of the new administrative division. Some of such local bodies on the present Belgrade territory included NOO Zemun (in 1943), NOO Mladenovac Srez, NOO Grocka Srez and NOO Kosmajski Srez (all in 1944).[4] After World War II After the World War II liberation, new Communist authorities abolished the quarters on formed 14 raions in November 1944. Each had its own NOO. On 11 December 1944 the raions were organized as the full local administrations, with corresponding departments. They were subordinated to the Executive Board of the Belgrade City NOO. They were merged on 8 September 1945, leaving a total of 7 raions. In June 1945, NOO's for the neighborhoods, as parts of the raions (mimicking the former quarters), were formed, but were abolished in December 1946. In May 1947 the raions were reorganized and re-numerated, lifting their number to 8 and labeling from I to VIII. Raion IX was formed in April 1949 and raion X in April 1950 (New Belgrade and Bežanija).[4][6] Belgrade Okrug was restored by the new authorities on 1 September 1945, but was abolished on 18 April 1947, with all the other okrugs in Serbia. Belgrade Okrug was divided in two: Belgrade Srez and Kosmaj Srez. Srez' were not part of the local self-administration, that is, not administered by the city government but directly by the state government. On 16 May 1950, additional administrative super-units of oblasts were created. Belgrade Oblast included 24 srez' and the Belgrade City. Oblasts were abolished on 1 December 1951.[4]
Constituent municipalities of the surrounding okrugs were:[4][16]
   On 29 May 1952 city was reorganized into 23 municipalities: 14 urban (Voždovac, Vračar, Zvezdara, Lekino Brdo, Neimar, New Belgrade, Palilula, Savski Venac, Skadarlija, Stari Grad, Stari Đeram, Terazije, Topčidersko Brdo, Čukarica); 8 suburban (Bežanija, Borča, Žarkovo, Železnik, Krnjača, Ovča, Padinska Skela, Rakovica and Zemun.[4][6] On 1 September 1955 Vračar was divided into East Vračar and West Vračar and the municipality of Karaburma was created, lifting the number of municipalities to 25.[17][18][19] By the 1952 reform, Belgrade Srez (also colloquially called Vračar Srez) consisted of 37 municipalities. In 1955, parts of the Zemun and Podunavlje srez' were annexed to the Belgrade Srez, which encircled the urban area of the city and consisted of 35 municipalities. In December 1956 the Belgrade Srez was abolished as such and the administration was taken over by the City of Belgrade, as the srez-level administrative unit. Some parts of the former srez didn't become part of the city, but were added to the surrounding, newly formed Lazarevac and Mladenovac srez'. With numerous mergers, the city was reorganized into 20 municipalities, 10 urban and 10 suburban.[4] At this point, the area was enlarged to 2,090 km2.[17][18][19] The core consisting of 10 urban municipalities remained unchanged since then: Čukarica, New Belgrade, Palilula, Rakovica, Savski Venac, Stari Grad, Voždovac, Vračar, Zemun and Zvezdara. In 1957, by the new law, city was divided into 17 municipalities.[4] Since then, municipalities were being merged, abolished an annexed. In July 1955 many municipalities, especially from the former Belgrade Srez, have been annexed to the municipalities. For example:[4][17]
Enlargement of the municipalities continued by the reorganization on 3 January 1957, which is also when separate municipalities became subordinated to the Belgrade City administration:[4][17]
After the 1955-1958 reorganization of municipalities and districts, Barajevo, Obrenovac, Sopot and Grocka became parts of Belgrade. Further changes by 1960 included:[4][17][18][19]
In 1959 Belgrade was organized in 15 municipalities: Barajevo, Čukarica, Grocka, Krnјаča, New Belgrade, Obrenovac, Palilula, Savski Venac, Sopot, Stari Grad, Surčin, Voždovac, Vračar, Zemun and Zvezdara. Rakovica was abolished and annexed to Čukarica.[4] By the constitutional reforms in 1963, People's Boards, which administered the municipalities were transformed into the Municipal Assemblies.[7] In 1965 municipalities of Surčin (annexed to Zemun) and Krnjača (annexed to Palilula) were abolished, reducing the number of municipalities to 13. Additionally, with the abolishment of Kolari municipality and its division between Smederevo and Grocka, former municipalities of Umčari, Pudarci and Kamendol were annexed to Grocka and, thus, to Belgrade. Srez' in the entire state were abolished on 13 March 1967 and Belgrade City began to fully operate as one administrative unit over its municipalities. Administrative division on urban and suburban municipalities was also abolished.[4] Municipalities of Lazarevac (14) and Mladenovac (15) were administratively annexed to Belgrade in November 1970, finishing the formation of the present city territory.[4] Rakovica (16) was reestablished on 15 October 1974 after splitting from Čukarica, while Surčin (17) split from Zemun on 24 September 2003. Development of the Belgrade administrative division by the census years:[18][19][20]
TodaySince 2006, all municipalities which constitute the cities are officially named “city municipalities”, so all 17 municipalities of the City of Belgrade were legally renamed (City municipality of Zemun, City municipality of Sopot, etc.).[7] The name is administrative and same for all municipalities, regardless of the statistical (urban/rural) or practical and colloquial division (urban/suburban). As of 2018, there are:[20]
In 2019 it was announced that the new law will restore the old distinction between the 10 urban and 7 suburban municipalities. In May 2019 the changed Law on the Capital City was adopted in the National Assembly of Serbia but it made no distinction between two zones, urban and suburban, and the official name of the suburban municipalities remained "City Municipality of...", though some of the regulations point to somewhat different jurisdiction between the two.[21] See also
References
NotesNotes: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||