|
Rhombic icosahedron
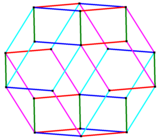
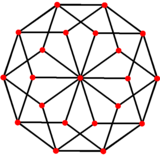
 The rhombic icosahedron is a polyhedron shaped like an oblate sphere. Its 20 faces are congruent golden rhombi;[1] 3, 4, or 5 faces meet at each vertex. It has 5 faces (green on top figure) meeting at each of its 2 poles; these 2 vertices lie on its axis of 5-fold symmetry, which is perpendicular to 5 axes of 2-fold symmetry through the midpoints of opposite equatorial edges (example on top figure: most left-hand and most right-hand mid-edges). Its other 10 faces follow its equator, 5 above and 5 below it; each of these 10 rhombi has 2 of its 4 sides lying on this zig-zag skew decagon equator. The rhombic icosahedron has 22 vertices. It has D5d, [2+,10], (2*5) symmetry group, of order 20; thus it has a center of symmetry (since 5 is odd). Even though all its faces are congruent, the rhombic icosahedron is not face-transitive, since one can distinguish whether a particular face is near the equator or near a pole by examining the types of vertices surrounding this face. ZonohedronThe rhombic icosahedron is a zonohedron. The rhombic icosahedron has 5 sets of 8 parallel edges, described as 85 belts.
The rhombic icosahedron forms the convex hull of the vertex-first[clarification needed] projection of a 5-cube to 3 dimensions[citation needed]. The 32 vertices of a 5-cube map into the 22 exterior vertices of the rhombic icosahedron, with the remaining 10 interior vertices forming a pentagonal antiprism. In the same way, one can obtain a Rhombic dodecahedron from a 4-cube, and a rhombic triacontahedron from a 6-cube. Related polyhedraThe rhombic icosahedron can be derived from the rhombic triacontahedron by removing a belt of 10 middle faces with parallel edges.
(*) (For example, on the left-hand figure): The orthogonal projection of the (vertical) belt of 10 middle faces of the rhombic triacontahedron is just the (horizontal) exterior regular decagon of the common orthogonal projection. Removal of a further belt of 8 faces with parallel edges from the icosahedron results in the Bilinski dodecahedron, which is topologically equivalent but not congruent to the regular rhombic dodecahedron. References
External links |
||||||||||||||||||||