|
Paleogeography of the India–Asia collision system
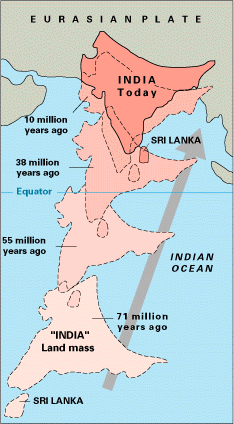
The paleogeography of the India–Asia collision system is the reconstructed geological and geomorphological evolution within the collision zone of the Himalayan orogenic belt. The continental collision between the Indian Plate and Eurasian Plate is one of the world's most renowned and most studied convergent systems. However, many mechanisms remain controversial. Some of the highly debated issues include the onset timing of continental collision, the time at which the Tibetan plateau reached its present elevation and how tectonic processes interacted with other geological mechanisms. These mechanisms are crucial for the understanding of Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution, paleoclimate and paleontology, such as the interaction between the Himalayas orogenic growth and the Asian monsoon system,[1][2] as well as the dispersal and speciation of fauna.[3] Various hypotheses have been put forward to explain how the paleogeography of the collision system could have developed. Important ideas include the synchronous collision hypothesis, the Lhasa-plano hypothesis and the southward draining of major river systems. Timing of collision onsetDefinitionThe onset of continental collision is determined by any point along the plate boundary where the oceanic lithosphere is completely subducted and two continental plates first come into contact.[4] In the case of the India–Asia collision, it would be defined by the first point of disappearance of the Neo-Tethys oceanic crust, where the India and Asia continent come into contact with each other. Such process is defined by a point since the shape of continental margins is irregular. The complete consumption of the oceanic crust could occur non-synchronously along the collision front.[5] Different methods can be used to constrain the age of collision onset. Commonly used geological evidences include stratigraphy, sedimentology and paleomagnetic data. Stratigraphy and sedimentology indicates the transfer of materials from one continent to another when two continents, meet, as well as the change in depositional environment after the oceanic basin is closed and sea water is completely expelled.[6] Paleomagnetic data indicates collision when the paleolatitudes of both continental margins overlap.[7] The onset of the India–Asia collision has been poorly constrained from Late Cretaceous to Oligo-Miocene due to different interpretations of geological evidences by different researchers.[5]  Diachronous collision hypothesisThe diachronous collision hypothesis involves mechanisms with two stages of collision, where the first stage starts during the Paleocene to Eocene.[8][9] Paleogene arc-continent collision hypothesis The Paleogene arc-continent collision suggests that the Indian continent experienced a two-stage collision.[8] The first stage involves the collision with an intraoceanic island arc in the Tethys Ocean at approximately 55 million years (Ma) ago.[8] The second stage involves the collision between the Indian continent (together with the "merged" island arc) and the Asian continent at approximately 33 Ma.[8] This hypothesis is mainly based on the observation of lithostratigraphic patterns within and around the Yarlung-Zangbo suture zone (YZSZ).[8] The YZSZ itself consists of ophiolite[10] and basaltic to andesitic volcanic rocks,[8] which is comparable to typical rock suites in an island arc subduction system. The north of the YZSZ is the Lhasa terrane of the Tibetan Plateau, while the south of the YZSZ is the Indian superterrane.[8] The fact that the YZSZ separates two continental terrane suggests that it could have been an intraoceanic island arc in the past, locating in between the Asian continental margin (Lhasa terrane) and the Indian continental margin (Indian superterrane) before collision occurred.[8] Volcanic rocks in the Zedong terrane, which belongs to the YZSZ, has high K2O content and are classified as shoshonites.[11] Shoshonites are potassium-rich basaltic andesite which are commonly found in modern intraoceanic arc settings.[12] It therefore favours the prediction of the YZSZ as a paleo-intraoceanic island. However, recent studies suggest that volcanic rocks in the Zedong terrane have been altered such that the mobile ion ratios (e.g. K and Na) are unreliable.[13] Immobile elements such as Zr/TiO2 ratios should be used instead for classification.[13] New data suggests that volcanic rocks in the Zedong terrane has a calc-alkaline composition,[13] which is common for volcanic island arc but not necessarily intraoceanic island. Moreover, volcanic rocks in the Zedong terrane share a similar geochemical pattern with Lower Jurassic-aged volcanic rocks from southern Lhasa terrane of the Tibetan Plateau.[14] This suggests that the Yarlung-Zangbo suture zone is part of the Asian continental margin instead of a separate intraoceanic island.[14] Greater India Basin hypothesis The Greater India Basin hypothesis suggests that there was a two-stage collision between India and Asia continent.[9] The first stage occurred at approximately 50 Ma, where a microcontinent from the Indian plate collided with the Asian continent.[9] It was followed by the subduction of the oceanic Great India Basin, which was located in between the microcontinent and the major Indian craton, under the Asian continent.[9] The second stage of collision occurred after the oceanic crust of the Great India Basin had been consumed, where the major Indian craton finally came into contact and collided with the Asian continental margin (including the previously "merged" microcontinent, which was interpreted to be the modern Tibetan Plateau) at 25–20 Ma.[9] This hypothesis is mainly based on the observation of crustal shortening deficit in the Himalayas. The convergence of the Indian and Eurasian plate since the Cretaceous should have led to crustal shortening of approximately 3,600 ± 35 km.[15] However, the observed shortening in the Himalayas and the Asian continent accounts for only 30–50% of the total convergence.[16] The Greater India Basin model is therefore put forward to explain such observation, where the total amount of convergent has actually been dispersed into two separate stages of crustal thickening, i.e. the uplift of the microcontinent (Tibetan Plateau) and the Himalaya orogeny. The subduction and disappearance of the Great Indian Basin oceanic crust beneath the microcontinent reduces the measurable amount of total convergence expressed by crustal shortening at the surface.[9] Paleomagnetic data suggests that the Indian continent had experienced a N-S extension with minimum extension rates of 40–67 mm/y during 118 and 68 Ma.[9] Such extensional rate is comparable to typical records of intracontinental rifting.[17] Therefore, the hypothesized oceanic Greater India Basin could have existed and separated a microcontinent from the major India craton.[9] However, rock records in the Greater Himalayan crystalline complex, which is located south to the Tibetan Plateau and should have contained remnants of the oceanic Greater Indian Basin if it had existed, do not show supporting evidences.[18] No ophiolite obduction from the oceanic Basin nor typical rock suites from arc-trench subduction system are found.[18] Synchronous collision hypothesis The synchronous collision hypothesis limits the age of collision onset at 59 Ma by dating the oldest turbidites formed on the passive margin of the India continent,[19] which indicates the incoming of materials from the active Asian continental margin. Geological evidence of rocks younger than 59 Ma and deposited on top of the turbidite sequence can be considered as indicators to reconstruct tectonic evolution after collision had begun. Various evidence documented along NE-SW and NW-SE sections of the India–Asia collision zone synchronize with each other, being in favour of a "one-off" collision.[19]
Kshiroda PlateAs per geological research conducted in 2015, there possibly existed two subduction zones between the Indian and Eurasian plates.[24] A hypothetical lost oceanic plate called the Kshiroda Plate is supposed to have existed between the two subduction zones. It is now believed that this oceanic plate is actually a broken-off fragment of the above mentioned "Neo-Tethys oceanic basin". The bed of the Tethys sea lay on the Kshiroda Plate and was carried along with it towards Eurasia. The southernmost part of the Eurasian plate was actually the Lhasa block, which itself had drifted north and joined the landmass, simultaneous to the drift of the Indian Plate. This, however, is not included in the hypothesis, as it does not gravely affect the tectonic activities. According to this hypothesis, the Kshiroda Plate after being subducted under the Eurasian Plate caused the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and also the delamination of the Indian Plate beneath the plateau.[25] Paleo-elevation of Tibetan PlateauEvolution of Tibet's geomorphology When and how did the Tibetan Plateau reach its present-day elevation has long been widely debated. Tibet has an average elevation of 5 km, which makes it the highest plateau and one of the highest topographic features on Earth. It is very rare to see the Earth's crust achieving such a large extent of thickening.[27] This is why Tibet attracts scientific interest. It was previously believed that Tibet uplifting is solely resulted from the Indian-Asian continental collision.[28] However, more and more studies revealed that Tibet might have reached its present-day elevation as early as in the Cretaceous period (145—66 Ma). Diversified scientific evidences have been put forward to support such hypothesis, such as paleomagnetic reconstruction,[29] sedimentology and igneous petrology,[30][31] structural geology[32] and geochemistry.[33] For example, Ingalls et al. (2018) uses δ18O (oxygen-isotope) in meteoric water and Δ47 (clumped-isotope) in non-marine carbonates to reconstruct paleotemperature and paleoprecipitation of the Tibetan Plateau. It is suggested that the southern part of Tibet is around 3–4 km high and have an average temperature of 10 °C as early as in Late Cretaceous (92 Ma). This shows that southern Tibet has to be already at its present-day sub-equatorial latitude, such that 10 °C, an extremely warm temperature for highly elevated regions, can be maintained.[33] It is now generally accepted that Tibet grew differentially, with its southern part reaching present day elevation first, followed by its northern part.[34][35][36] For example, Fei et al. (2017) uses 40Ar/39Ar and (U-Th)/He thermochronology[37] to track the growth of the Plateau through time and the results are positive. The figure below shows a generalized evolution model of when did different areas of the Tibetan Plateau reaches its present-day elevation.[26] Although the age is not well-constrained, a clear north-younging trend can be observed.[26] Tectonic models for crustal thickening Miocene uplift modelThe Miocene model suggested that the Indian-Asian collision is the major cause for Tibet's uplift,[28] which is likely to be wrong due to reasons discussed above. In this model, the Lhasa tectonic block, equivalent to the southern Tibet, experienced initial uplift due to compressional force created when the Indian and Asian continent collided and the Tethys oceanic slab broke off (45—30 Ma).[28] This is supported by the presence of Adakite in the Lhasa block.[38] Adakite is an intermediate to felsic rock which is commonly related to oceanic subduction. Geochemical analysis of the Lhasa Adakite suggests that it is originated from magmatic activities triggered by slab breakoff.[38] This further reinforces the hypothesis that Lhasa block is uplifted during the initial continental collision phase. Later, magmatic activity ceased as the continent collision occurred. Denser materials in the Indian and Asian continental crust sank to the bottom part of the crust, making the lower crust extremely dense and heavy. It thus broke off and sank into the mantle. The removal of the dense lower crust reduced gravitational pull on the Lhasa block and allowed it to rise (30—26 Ma).[28] Together with the intense compressional force and thrusting it experienced amidst collision, intense crustal thickening occurred, resulting in the major phase of uplift in South Tibet. As the collision proceed (26—13 Ma), the Northern Tibet continental block experienced compression, thrusting and shortening as well.[28] This interpretation is supported by the thermochronological data of apatite fission tracks from the North Tibetan Plateau, which indicate phases of rapid exhumation and compression from 20 Ma onwards.[35][36] Mesozoic uplift model The Mesozoic model suggested that southern Tibet experienced intense crustal shortening and thickening as early as in Jurassic to Cretaceous time. It is widely accepted that the Indian plate began to approach the Eurasian plate during the Mesozoic times as a result of the break up of Gondwana supercontinent.[31] In the Mesozoic time, there was an oceanic basin in between the Lhasa block and the North Tibet continental block. Subduction of the oceanic slab underneath the North Tibet block started in the Triassic. In Jurassic to Cretaceous, the Mesozoic ocean is closed. The Lhasa continental block and the North Tibet continental block collided with each other, resulting in intense crustal shortening and thickening of the Lhasa block, i.e. South Tibet.[31] The closing of Mesozoic ocean, the continental collision between Lhasa block and North Tibet block and the early crustal thickening of Lhasa block is indicated by the presence of ultra-high pressure metamorphic rocks in the Qiangtang metamorphic belt in Central Tibet.[40] By the time when the Indian continent and the Asian continent collided, South Tibet has already reached 3–4 km elevation.[29][30][31][33] The compressional force resulted from the Indian-Asian collision further topped up Lhasa block's elevation and triggered crustal thickening in the North Tibet as the Indian continent proceed northwards. Although the timing of Lhasa block thickening in this model is conformable with geological evidences available, details remained debated.[31] Common consensusAlthough the actual timing of occurrence of various geological events involving the Tibetan Plateau remains widely debated, there is a common consensus on the evolution of continental block configuration through time among what different studies have put forward. Royden et al. (2008)[41] suggested a tectonic reconstruction model to illustrate how continental blocks of North and South Tibet has evolved throughout the Indian-Asian collision. This model also emphasizes the point that the Lhasa block is first deformed, followed by the North Tibet block. Moreover, the collision between the Lhasa block and the North Tibet block occurred later in the East than in the South. This suggests that detail collision mechanisms could be complicated and require further investigation. A single tectonic model is not likely to be able to explain the whole process. For example, although the above-mentioned Mesozoic uplift model is consistent with the onset timing of South Tibet crustal shortening, other details need to be refined.[41]  Paleo-drainage configurationDrainage pattern responding to tectonic processes Rivers are features formed by water eroding into the land surface. Drainage patterns provide clues not only to hydrological conditions, but also to geology and tectonic evolution. Burbank (1992)[42] proposed a model to explain how uplift driven by different factor can result in different drainage patterns, where uplifting is the upward movement of landmass with reference to the Earth's center.[42] In the case of tectonic driven uplift, an active thrust front is present, constantly driving crustal materials upwards. This adds weight to the Earth's surface, causing land subsidence. Since the nearer a spot is to the active thrust front, the greater the effect of weight the uplifted crust has on the land surface, asymmetric subsidence is resulted. Groundmass nearer to the uplifted crust subside more, while those which are further subside less. This is reflected by the asymmetrical fan shape of sedimentary strata deposited during subsiding, where columns closer to the point of maximum subsidence are thicker while columns further are thinner.[42] Tectonic driven uplift results in longitudinal rivers dominating the area instead of transverse rivers. Transverse rivers are rivers cutting at right angle to mountain ridges, while longitudinal rivers flow parallel to them. During active uplift and subsidence, accommodation space is created quickly and continually, while erosion rate remains relatively slow. Therefore, transverse rivers developed on the uplifted mountain range are not able to extend beyond the area nearest to the thrust front, where subsidence is the most intense. Instead, longitudinal rivers dominated most of the area.[42] On the contrary, in the case of erosional driven uplift, active thrust front is absent. Uplifting of the crust is driven by isostatic rebound. The fact that materials are constantly eroded and removed reduces weight adding on the Earth's crust, causing it to "bounce" higher. Since erosion dominates the whole area, uplifting is not limited to sections near to the mountain range. The uplifting rate of the whole drainage basin is rather equal, as reflected by symmetrical shape and equal thickness of sedimentary stratum deposited during uplifting.[42] Erosion driven uplift results in transverse rivers dominating the area instead of longitudinal rivers. During active erosion and isostatic rebound, accommodation space is reduced quickly and continually, while sedimentation rate is also high. Therefore, transverse rivers developed on the uplifted mountain range are able to extend way beyond the foot of the mountain range. Longitudinal rivers only dominate distal parts of the drainage basin.[42] Evolution of major river systems and their implicationsBrookfield (1998)[43] reconstructed the evolution of major river systems of the Indian-Asian collision zone based on tectonic history of the area. It is suggested that the most significant changes in drainage patterns occurred during Pliocene to Quaternary (5.3 Ma onwards). Detail changes in fluvial processes will not be discussed here. Major focuses are how river systems of the area responded to changing geological processes through time, as well as how regional drainage patterns are capable of reflecting tectonic evolution.[43] Before the continental collision occurred (which is defined as 50 Ma or before in Brookfield's model), longitudinal river system had dominated the Asian continent, where major river systems run parallel to the approaching regional thrust. Amidst the collision (which is referred as 20 Ma in Brookfield's model), the shape of river channels were affected by the approaching Indian continent. Although major river systems still flowed parallel to the thrust, they bent around both sides of the Indian continent since the collision exerted compressional force to the drainage basin. Such effect is most obviously reflected by the Indus river and the Ganges river. The westward flowing Indus river wraps around the western boundary of the thrust while the eastward flowing Ganges wraps around the eastern boundary of the thrust.[43] In present days, the regional drainage configuration is very different from how it originally was. River systems were eastward flowing, with the Indus as an exception, before the continental collision started. At present, most rivers are flowing south to southeast. The Salween, Yom, Mekong and Red river are drastically bent around the northeastern "tip" of the Indian continent. By further examining and studying the deformation patterns in these river basins, a two-phase deformation model in the East Himalayas is verified.[44] This shows that rivers are reliable indicators of crustal strain and useful in reconstructing regional tectonic history.[44] Moreover, the Indus and the Ganges river originally flowed parallel to the regional thrust on the Asian continent, but are now flowing perpendicular to it. They crossed the thrust and extended onto the Indian continent. This is conformable to the above-mentioned model proposed by Burbank (1992).[42] Since tectonic uplift has significantly slowed down nowadays compared to when the collision has just started, the present day Indian-Asian collision region is dominated by erosional processes. Rivers like the Indus and Ganges, which originated from the Lhasa block, are therefore able to flow as transverse rivers and reach beyond the proximal part of the Himalayas mountain range.[44]  Paleogeography and paleoclimateSouth Asian monsoon system and the debate The South Asian monsoon system primarily affects the continents of South Asia and their surrounding water bodies. In this particular system, summer monsoon blows as onshore northeasterly while winter monsoon blows as offshore westerly. The driving force of monsoon systems is the pressure difference between landmasses and waterbodies. This is most commonly a result of differential heating of land and sea due to specific heat capacity difference. However, in the case of the South Asia monsoon system, the huge pressure gradient force is induced by the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau. The Himalaya orogenic belt the highest elevated mountain range on Earth. In summer, air mass across the South Asia is heated up in general. On the contrary, airmass above the Himalayas and Tibet experiences adiabatic cooling and sinks rapidly, forming an intense high pressure cell. This cell is therefore capable of facilitating landward airflow towards itself, thus sustaining the onshore summer monsoon.[45] The onset of South Asian monsoon is poorly constrained since limited paleoclimatic data is available. It is generally accepted to have occurred during the Eocene-Oligocene climate transition (33.9 Ma onwards).[46] The onset mechanism has long been debated and remained poorly understood. On one hand, it is believed that the uplift of the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau is the major trigger of South Asian monsoon onset, since only such elevated landmass can change regional airflow configurations.[45][1][47] On the other, numerical modelling and thermalchronological data suggest that Eocene uplift of the Himalayas and Tibet is driven by monsoon-intensified denudation, i.e. erosional driven uplift.[48][49] This gives rise to a "chicken or egg" paradox.  The channel flow model As mentioned above, a lot has been done on examining how the uplift of the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau has triggered the onset of the South Asian monsoon. The approach of most studies is to first establish or make use of pre-existing tectonic models to constrain the timing of uplift and topographic evolution, then evaluate the significance of topography in controlling regional climate by numerical modeling. Various significant tectonic models have been discussed in previous sections. However, the only quantitative model which has assigned a significant role for climate suggests the opposite, i.e. the exhumation of the southern flank of the Tibetan plateau is a result of monsoon-intensified denudation.[50] The channel flow model explains the South Tibetan uplift in two stages. The first stage took place during Eocene to Oligocene. It is hypothesized that the middle part of the Tibet continental crust was partially melted at that time and was bounded by a "channel" formed from the rigid upper and lower crust. The molten middle crust is thought to be represented by high-temperature rock suites in the Greater Himalayan Crystalline Complex. Since the upper crust was rather strong, the melt cannot propagate towards the surface. The second stage took place during early to mid Miocene. The South Asian monsoon developed and the regional climatic condition was changed. Rainfall and wind intensified denudation and weakened the upper crust mechanically (but not thermally). The molten middle crust was therefore able to break through the upper crust and flow outward to the surface.[50] The dilemma is that the South Asian monsoon was believed to have originated from topographic rise of the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau. The channel flow model predicts that the rise of Tibetan Plateau requires the presence of South Asian monsoon, which leaves the Himalayas as the only possible candidate responsible for initiating the monsoon system. However, a study done by Boos & Kuang (2010) eliminated such possibility.[50] The study uses computer model to simulate the growth and evolution of the South Asian monsoon under three conditions: (1) both the Himalayas and Tibet are present, (2) Only Tibet is present, (3) both the Himalayas and Tibet are absent. Results shows that both condition (1) and (2) are able to produce similar monsoonal climate patterns, meaning that the Himalayas is climatically insignificant.[50] Directions for future studiesSlab dynamics  Webb et al. (2017) proposed a model to explain Himalayan topographic evolution by taking slab dynamics into account. The model suggests temporal differences in topographic evolution in the East-central and Western Himalayas. Such differences allowed a series of positive climatic feedbacks to occur sequentially and remain sustainable. Feedback mechanisms include topographically-induced monsoon, monsoon-intensified erosion, and erosional-driven uplift (isostatic rebound).[51] Although the discussion of this model is limited to 20 Ma onwards, such concept can be implemented to future studies focusing on the Tertiary period so as to better understand how Tibet and the South Asian monsoon co-evolved.[51]
Climatic proxiesQuaternary climatic reconstructions of the Tibetan Plateau area are mostly based on pollen analysis,[52][53][54] while Mesozoic climatic reconstructions are done by analyzing benthic foraminifera from paleo-oceanic basins.[55][56] Little study has focused on the Tertiary period, at which the South Asian monsoon is thought to have initiated. Further studies on Tertiary carbon isotope composition of paleosols could be carried out to examine the shift in C3/ C4 vegetation ratio. C3 and C4 plants practice different carbon fixation mechanism. C4 fixation is more water-efficient and therefore favours plant adaptation to extreme climatic conditions. Therefore, C4 plants are generally more abundant in cold and arid-temperate regions.[57] Carbon isotopes in paleosols are remains of dead plants and therefore accurately reflects climatic regime shifts. Phylogenetic reconstructions of animal taxa is also useful as climate change may promote speciation or trigger extinction.[58]
See alsoReferences
|
||||||||||||||||||||