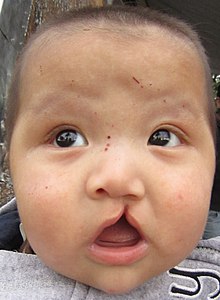
Medical condition
Pai syndrome Other names Median cleft of the upper lip-corpus callosum lipoma-midline facial cutaneous polyps syndrome Specialty Medical genetics Causes Genetic mutation Prevention none Prognosis Good Frequency very rare, between 10-80 cases have been described in medical literature
Pai syndrome , also known as Median cleft of the upper lip-corpus callosum lipoma-midline facial cutaneous polyps syndrome , is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by nervous system, cutaneous, ocular, nasal and bucal anomalies with facial dysmorphisms.[ 1]
Signs and symptoms
List of common symptoms:[ 2]
List of not-so-common symptoms:[2]
List of uncommon symptoms:[2]
Causes
A specific, shared genetic cause hasn't been found. The closest thing to it was a case reported by Masuno et al. of a Japanese girl with symptoms of the disorder plus short stature and intellectual disabilities with a spontaneous reciprocal translocation . This translocation involved chromosome Xq28 and chromosome 16q11.2 (more specifically, 46,X,t(X;16)(q28;q11.2).[ 3]
Epidemiology
According to OMIM, 18 cases have been described in medical literature,[ 4] [ 5]
References
^ "Síndrome de Pai" . Orphanet (in Spanish). Retrieved 2022-06-13 .^ "Median cleft of upper lip with polyps of facial skin and nasal mucosa" . Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program . U.S. National Institutes of Health. 2021-11-19. Archived from the original on 19 November 2021. Retrieved 2022-06-13 .^ Masuno M, Imaizumi K, Fukushima Y, Tanaka Y, Ishii T, Nakamura M, Kuroki Y (November 1997). "Median cleft of upper lip and pedunculated skin masses associated with de novo reciprocal translocation 46,X,t(X;16)(q28;q11.2)" . Journal of Medical Genetics . 34 (11): 952– 954. doi :10.1136/jmg.34.11.952 . PMC 1051130 PMID 9391896 . ^ "Cleft, Median, of Upper Lip With Polyps of Facial Skin and Nasal Mucosa" . Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) . 155145. Retrieved 2022-06-13 .^ "Pai syndrome" . Orphanet . Retrieved 2022-06-13 .