|
Nannostomus anduzei
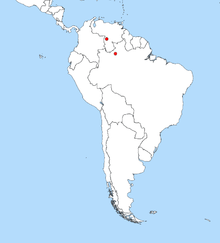
Nannostomus anduzei (common name: Anduzi's pencilfish) is a freshwater species of fish belonging to the genus Nannostomus in the characin family Lebiasinidae.[1] It is native to Venezuela and northern Brazil, particularly the upper Orinoco and Rio Ererê, a tributary of the Rio Negro. The adults grow to a maximum length of only 16 mm, making them one of the smallest pencilfish. Other common names include miniature pencilfish, miniature nannostomus, and Anduzi's nannostomus. DistributionNannostomus anduzei is restricted to the Amazonian region of the South American continent and has only been formally reported from two localities in the north of that area. The first, and site of discovery, was 20 km north of the small Venezuelan town of Puerto Ayacucho in a small lagoon, in the upper regions of the Rio Orinoco, at 5° 50' N, 67° 30' W. The second site was some 700 km to the southeast, in the Lago Caatinga, off the Rio Ererê, a tributary of the Rio Negro at 0° 14' S; 63° 53' W. These limited data are reflected in the range map above, where it is not possible to say where else the species might be found. However, because these fish occasionally do appear in the aquarium trade (see also below), their true range likely is somewhat wider than indicated. While the two known sites are geographically widely separated in two river systems, the Orinoco and the Negro are linked by the Casiquiare canal, so migration between the two sites is possible. N. anduzei does not appear in a systematic list of fishes of Columbia,[2] though the northern Orinoco locality is only a few kilometres from the Colombian border. This could represent undersampling in what is a remote part of the forest. DescriptionThis is a very small fish: even fully grown adults are only a maximum of about 16 mm and it can become sexually mature at only 11 mm. As such, it is the smallest member of its genus currently known, the next smallest being N. minimus, which is not sexually mature until about 14 mm in length. Though small in size, the species is strikingly colored. The fish is mainly golden brown with a metallic gold stripe running the length of the body along the lateral line. The most notable feature is a pair of brilliant, rich red patches on the anal and caudal fins. Some anatomical features discriminate N. anduzei from related fish, notably reduced fin ray counts on the pelvic and caudal fins and the possession of only four premaxillary teeth. These three features are perhaps related to the reduced size. N. anduzei is sexually dimorphic in that consistent differences are seen between males and females. Males show brighter coloration around the red patches on the tail and anal fins, especially when in breeding condition. Males are also slimmer-bodied and have a longer anal fin (3 mm in males; 2 mm in females), with some of the surrounding muscle modified to enable mating, a common feature shared with other members of the genus. Females can have a brighter longitudinal body stripe; the red patches are almost always somewhat paler. Discovery and identificationNannostomus anduzei was the 15th member to be discovered, according to the currently accepted taxonomical classification of the genus. It was first described by Fernandez and Weitzman in 1987[3] in a collection of about 30 specimens collected from the Orinoco site detailed above. The specimens were originally collected on December 1, 1984. The specific name was proposed by the describers in honor of Dr Pablo J. Anduze (1902-1989), a Venezuelan explorer, ethnologist, medical entomologist, and the former governor of the Amazonas State, Venezuela. Dr. Anduze provided welcome help to the senior author in her work on the fishes of Venezuela’s Amazon region. He was a supporter of their research studies on the fish in Amazonia.[4] TaxonomyNannostomus anduzei is one of 18 species currently recognized in the genus Nannostomus, which itself is one of seven genera in the Lebiasinidae, a family of freshwater fish in the Characiformes.[5] Phylogenetic relationshipsNannostomus anduzei possesses certain anatomical characteristics which indicate it is definitely a member of the Nannostomus genus—these are discussed by Fernandez and Weitzman. However, what is less well understood is its relationship to other species within the genus: i.e. it is not certain to which other species it is most closely related. DietTypically of the Lebiasinidae, N. anduzei is an omnivore, and with its small overall size and mouth takes small food items. In the wild, these likely include small invertebrates from the water column, as in an aquarium setting, where crushed flake food and dried or frozen natural food are taken. It is also reported[citation needed] to indulge in surface browsing of algae or biofilm and this may represent a significant portion of the diet. Physiological differences from other Nannostomus membersA well known characteristic of most members of the genus Nannostomus is the body color pattern change which occurs in these fish between night and day. Newly lit specimens can look dramatically different from those that have been under lighting for a few minutes. Typically, the longitudinal stripes are replaced by patches that run dorsoventrally. The physiological basis of these changes is understood in that they are known to be controlled by the melatonin system acting upon different types of melatonin receptors in melanphores located in the fish's skin.[6] See also Nannostomus trifasciatus for additional information. However, N. anduzei does not show this characteristic; instead, at night, it is reported[citation needed] simply to become much paler in color, with very little evidence of horizontal stripes, and the red on the fins fading almost to nothing. In the aquariumNannostomus anduzei is only rarely deliberately exported from the wild for the aquarium trade. Occasional specimens turn up as bycatch with other species, but dedicated shipments of substantial numbers of this species are relatively unusual.[7] As a consequence of this N. anduzei is not commonly reported on and its aquarium needs and suitability are not well characterized. It has been bred in captivity.[citation needed] Given its diminutive size, a group of individuals would probably thrive in a modest-sized aquarium. In addition, its native water conditions are acidic, warm (26-28 °C) and low in water hardness, indicating it would prefer these conditions in the aquarium. Its small size would be expected to make it especially suitable for the increasingly popular "nano aquaria". References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||