|
Motu Nui Motu Nui (large island in the Rapa Nui language) is the largest of three islets just south of Easter Island and is the westernmost place in Chile. All three islets have seabirds, but Motu Nui was also an essential location for the Tangata manu ("Bird Man") cult which was the island religion between the moai era and the Christian era (the people of the island were converted to Roman Catholicism in the 1860s). Motu Nui is the summit of a large volcanic mountain which rises over 2,000 meters from the sea bed. It measures 3.9 hectares in land area and is the largest of the five satellite islets of Easter island. It is one of three islands that is closest to Point Nemo, the place in the ocean that is farthest from land, the other two being Ducie Island, one of the Pitcairn Islands, and Maher Island in Antarctica.[1][2] 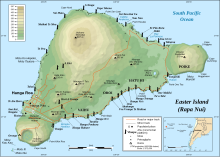 (largest of three tiny islets located off lower left corner of Rapa Nui in bottom left corner of map) The ritual of the "Bird Man" cult was a competition to collect the first egg of the manutara. This took place starting from Motu Nui where the Hopu (representatives from each clan) waited for the sooty terns to lay their first eggs of the season. The Hopu who seized the first egg raced to swim back to Easter Island, climbed the cliffs to Orongo and presented the egg to their sponsor in front of the judges at Orongo. This gave their sponsor the title of Tangata manu and great power on the island for a year. Many Hopu were killed by sharks or by falling. The winning clan gained certain rights, including the collecting of eggs and young birds from the islets. Motu means "island" in Rapa Nui language, and there are two smaller motus located nearby: Motu Kao Kao (a sea stack, rising around 20 meters (65 feet) above sea level) and Motu Iti (near Motu Nui). Motu Nui was scientifically surveyed by the Routledge expedition of 1914, which reported that six other varieties of seabirds nested there in addition to the sooty tern. They explored two caves on Motu Nui, in one of which the Hopu used to stay while waiting for the first egg of the season, and the other used to contain Moai Maea "The Boundary of the Land," a small moai that had already been taken to the Pitt Rivers Museum in Oxford, England. Although the Tangata Manu cult's rituals have long since been discontinued (the last competition known to have taken place in 1888), current visitors to Rapa Nui often enjoy the beauty of the Motus via small boat excursions from Hanga Roa, the island's only town. The diving in the sea between Motu Nui and Kau Kau is exceptional, and it is a highly sought-after scuba diving location for dive enthusiasts from around the world. Once heavily populated with sharks, the coastal waters of Rapa Nui are now much safer, due in large part to overfishing.  References
External links |