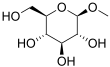
Methylglucoside
α-D -Methylglucoside
β-D -Methylglucoside
Names
IUPAC name
Methyl D -glucopyranoside
Other names
1-O -Methyl-D -glucopyranose
Identifiers
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.019.620
UNII
InChI=1S/C7H14O6/c1-12-7-6(11)5(10)4(9)3(2-8)13-7/h3-11H,2H2,1H3/t3-,4-,5+,6-,7?/m1/s1
Key: HOVAGTYPODGVJG-WLDMJGECSA-N
InChI=1/C7H14O6/c1-12-7-6(11)5(10)4(9)3(2-8)13-7/h3-11H,2H2,1H3/t3-,4-,5+,6-,7?/m1/s1
Key: HOVAGTYPODGVJG-WLDMJGECBG
O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](OC1OC)CO
Properties
C 7 H 14 O 6
Molar mass
−1
Appearance
White crystalline solid
Density
1.46 g/cm3 (α)[ 1]
Melting point
168 °C (334 °F; 441 K) (α)[ 1]
108 g/100 mL[ 1]
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
Methylglucoside is a monosaccharide derived from glucose . It can be prepared in the laboratory by the acid-catalyzed reaction of glucose with methanol .[ 2]
It is used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a variety of products including emollients, emulsifiers, humectants, moisturizers, thickening agents, plasticizers, surfactants, varnishes, and resins. The formation of methyl glycoside indicates that the structure of glucose is not open chain.[ 1] [ 3]
References