|
Marginal profit
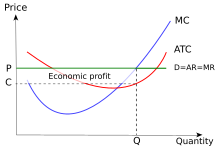 In microeconomics, marginal profit is the increment to profit resulting from a unit or infinitesimal increment to the quantity of a product produced. Under the marginal approach to profit maximization, to maximize profits, a firm should continue to produce a good or service up to the point where marginal profit is zero. At any lesser quantity of output, marginal profit is positive and so profit can be increased by producing a greater amount; likewise, at any quantity of output greater than the one at which marginal profit equals zero, marginal profit is negative and so profit could be made higher by producing less. Since profit is revenue minus cost, marginal profit equals marginal revenue minus marginal cost.[1] References
|