|
Kokusai Ki-76
The Kokusai Ki-76, or Liaison Aircraft Type 3 (in Japanese: 三式指揮連絡機), was a Japanese, high-wing monoplane artillery spotter and liaison aircraft that served in World War II. The Allied reporting name was Stella. Design and developmentIn 1940, the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force ordered the Nippon Kokusai Koku Kogyo to produce an artillery spotting and liaison aircraft. The resulting Ki-76 was inspired by, and similar to, the German Fieseler Fi 156 "Storch", although not a direct copy.[1] Like the "Storch", it was a high-winged monoplane with a fixed tailwheel undercarriage. However, rather than the slotted flaps used by the German aircraft, the Ki-76 used Fowler flaps, while it was powered by Hitachi Ha-42 radial engine rather than the Argus As 10 inline engine of the "Storch". First flying in May 1941, the Ki-76 proved successful when evaluated against an example of the Fi-156 and was ordered into production as the Army Type 3 Command Liaison Plane in November 1942.[2] Operational history The Ki-76 remained in service as an artillery spotter and liaison aircraft until the end of the War. Ki-76s were also used as anti-submarine aircraft, operating from the Japanese Army's escort carrier, the Akitsu Maru, being fitted with an arrestor hook and carrying two 60 kg (132 lb) depth charges.[3] OperatorsSpecifications (Ki-76)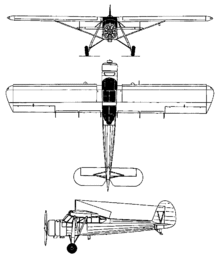 Data from Encyclopedia of Military Aircraft,[4] Japanese Aircraft of the Pacific War[5] General characteristics
Performance
Armament
See alsoAircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists References
Sources
External links=Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kokusai Ki-76. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
