|
Hypophosphoric acid
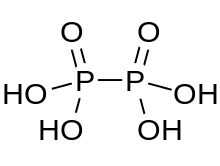
Hypophosphoric acid is a mineral acid with the formula H4P2O6, with phosphorus in a formal oxidation state of +4. In the solid state it is present as the dihydrate, H4P2O6·2H2O. In hypophosphoric acid the phosphorus atoms are identical and joined directly with a P−P bond. Isohypophosphoric acid is a structural isomer of hypophosphoric acid in which one phosphorus has a hydrogen directedly bonded to it and that phosphorus atom is linked to the other one by an oxygen bridge to give a phosphorous acid/phosphoric acid mixed anhydride. The two phosphorus atoms are in the +3 and +5 oxidation states, respectively. Preparation and reactionsHypophosphoric acid can be prepared by the reaction of red phosphorus with sodium chlorite at room temperature.[2]
A mixture of hypophosphoric acid, phosphorous acid (H3PO3) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is produced when white phosphorus oxidises in air when partially immersed in water.[2] The tetrasodium salt Na4P2O6·10H2O crystallises at pH 10 and the disodium salt, Na2H2PO6·6H2O at pH 5.2.[1] The disodium salt can be passed through an ion exchange column to form the acid dihydrate, H4P2O6·2H2O.[2] The anhydrous acid can be formed by vacuum dehydration over P4O10 or by the reaction of H2S on lead hypophosphate, Pb2P2O6.[1] Hypophosphoric acid is tetraprotic with dissociation constants pKa1 = 2.2, pKa2 = 2.8, pKa3 = 7.3 and pKa4 = 10.0.[1] On standing the anhydrous acid undergoes rearrangement and disproportionation to form a mixture of isohypophosphoric acid, HPO(OH)-O-PO2(OH); pyrophosphoric acid H2P2O7 and pyrophosphorous acid.[1] Hypophosphoric acid is unstable in hot hydrochloric acid, in 4 M HCl it hydrolyses to give H3PO3 + H3PO4.[1] StructureHypophosphorus acid contains oxonium ions and is best formulated [H3O+]2 [H2P2O6]2−. The acid is isostructural with the diammonium salt which contains the [HOPO2PO2OH]2− anion with a P−P bond length of 219 pm.[2] The HOPO2PO2OH2− anion in Na2H2P2O6·6H2O has a symmetric, staggered ethane-like structure with a P−P bond of length 219 pm. Each phosphorus atom has two P−O bonds with length 151 pm, and a P−OH bond length of 159 pm.[3] Hypophosphate saltsMany hypophosphate salts are known, for example, K4P2O6·8H2O, Ca2P2O6·2H2O, K3HP2O6·3H2O, K2H2P2O6·2H2O, KH3P2O6. On standing in air, hypophosphates tend to oxidise to pyrophosphates containing the P PolyhypophosphatesPolyhypophosphates are known containing linear anions, for example Na5P3O8 containing O(PO2)3O5− with a P−P−P chain and Na6P4O10·2H2O containing O(PO2)4O6−, with a P−P−P−P chain. The cyclic anion (PO See also
References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||