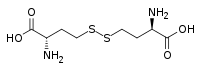
Homocystine
Names
IUPAC name
(2S ,2′ S )-4,4'-Disulfanediylbis(2-aminobutanoic acid)
Other names
L -Homocystine; L -4,4′ -Dithiobis(2-aminobutanoic acid)
Identifiers
ChEBI
ECHA InfoCard 100.009.966
UNII
InChI=1S/C8H16N2O4S2/c9-5(7(11)12)1-3-15-16-4-2-6(10)8(13)14/h5-6H,1-4,9-10H2,(H,11,12)(H,13,14)/t5-,6-/m0/s1
Key: ZTVZLYBCZNMWCF-WDSKDSINSA-N
C(CSSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N)[C@@H](C(=O)O)N
Properties
C 8 H 16 N 2 O 4 S 2
Molar mass
−1
Appearance
colorless solid
Melting point
281–284 °C (538–543 °F; 554–557 K)[ 1]
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
Homocystine is the organosulfur compound with the formula (HO2 CCH(NH2 )CH2 CH2 S)2 . It is disulfide derived from oxidation of homocysteine .[ 2] cystine and cysteine .
References
^ "L-Homocystine" . Sigma-Aldrich .^ Jackson, Peter; Stanley, Keith; Luzio, J. Paul (1986). "Specific fluorescent detection of disulphide-bridged peptides on thin-layer chromatograms". Biochemical Society Transactions . 14 (4): 750– 751. doi :10.1042/bst0140750 .