|
History of surface weather analysisThe history of surface weather analysis concerns the timetable of developments related to surface weather analysis. Initially a tool of study for the behavior of storms, surface weather analyses became a work in progress to explain current weather and as an aid for short term weather forecasting. Initial efforts to create surface weather analyses began in the mid-19th century by using surface weather observations to analyze isobars, isotherms, and display temperature and cloud cover. By the mid-20th century, much more information was being placed upon the station models plotted on weather maps and surface fronts, per the Norwegian cyclone model, were being analyzed worldwide. Eventually, observation plotting went from a manual exercise to an automated task for computers and plotters. Surface analysis remains a manual and partially subjective exercise, whether it be via hand and paper, or via a workstation. Mid-nineteenth centuryThe use of weather charts in a modern sense began in the middle portion of the 19th century. Weather map pioneers include William Charles Redfield, William Reid, Elias Loomis,[1] and Sir Francis Galton, who created the first weather maps in order to devise a theory on storm systems.[2] The invention of the telegraph in 1837 made it possible to gather weather information from multiple distant locations quickly enough to preserve its value for real-time applications.[3] The Smithsonian Institution developed its network of observers over much of the central and eastern United States between the 1840s and 1860s once Joseph Henry took the helm.[4] Beginning in 1849, the Smithsonian started producing surface analyses on a daily basis using the 150 stations in their network.[5] The U.S. Army Signal Corps inherited this network between 1870 and 1874 by an act of Congress, and expanded it to the west coast soon afterwards. Three times daily, all stations would telegraph in their observations to the central office which would then plot the information on a map upon which isobars, or lines of equal pressure, would be drawn which would identify centers of high and low pressure, as well as squall lines.[6] At first, all the data on the map was not taken at exactly the same time in the early days of these analyses because of a lack of time standardization. The first attempts at time standardization took hold in the Great Britain by 1855. However, in the United States, standard time did not come to pass until 1883, when time zones started to come into use across America for railroad use. The entire United States did not finally come under the influence of time zones until 1905, when Detroit finally established standard time.[7]  Late nineteenth centuryThe earliest surface analyses from the United States featured a map of the continental U.S. with indications of cloud cover and wind direction arranged on an early form of what has become a station model. A general indication of the weather for various cities around the country was also included on the bottom of the map. Within a short time, the Signal Corps added a tables showing eight-hour pressure change, 24-hour temperature change, relative humidity, and 24-hour precipitation. The Signal Office also added a general discussion of synoptic weather features and forecast, before adding isobars and isotherms onto the maps. By the end of 1872, the maps had established the format it would use until the introduction of frontal analysis.[8] By the 20th century, most of the weather-related functions under the U. S. Signal Corps branched off into a new civilian agency known as the U. S. Weather Bureau, the forerunner of today's National Weather Service. Internationally, other countries followed the lead of the United States, in regards to taking simultaneous weather observations, starting in 1873.[9] Other countries then began preparing surface analyses. In Australia, the first weather map showed up in print media in 1877.[10] Japan's Tokyo Meteorological Observatory, the forerunner of the Japan Meteorological Agency, began constructing surface weather maps in 1883.[11] The London Times published the first weather map on April 1, 1875.[12] In the United States, the 1876 Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania demonstrated that daily weather map transmission via telegraph could be accomplished. The New York Daily Graphic published weather maps from mid-1879 through the summer of 1882. By 1894, there were four daily newspapers publishing weather maps in Boston, New Orleans, Cincinnati, and San Francisco.[13] Twentieth century The use of frontal zones on weather maps did not appear until the introduction of the Norwegian cyclone model in the late 1910s, despite Loomis' earlier attempt at a similar notion in 1841.[14] Since the leading edge of air mass changes bore resemblance to the military fronts of World War I, the term "front" came into use to represent these lines.[15] An increasing amount of newspapers published weather maps early in the century across the United States, before the fad passed in 1912. While the number of newspapers carrying weather maps decreased beyond 1912, many continued publishing them until interest in flight increased interest in the maps once more in the 1930s.[16] Beginning in 1930, radiofax broadcasts of weather information and forecasts were broadcast for use by ships at sea, emanating from the United States military and the United States Weather Bureau on a cooperative basis.[17] Starting in 1935, Weather Bureau/National Weather Service weather maps were published in newspapers via the Associated Press in a slightly processed format as Wirephoto weather maps.[18]  Despite the introduction of the Norwegian cyclone model just after World War I, the United States did not formally analyze fronts on surface analyses until August 1, 1941, just before the WBAN Analysis Center opened in downtown Washington, D.C.[19][20][21] The effort to automate map plotting began in the United States in 1969,[22] with the process complete in the 1970s. Hong Kong completed their process of automated surface plotting by 1987.[23] By 1999, computer systems and software had finally become sophisticated enough to allow for the ability to underlay on the same workstation satellite imagery, radar imagery, and model-derived fields such as atmospheric thickness and frontogenesis in combination with surface observations to make for the best possible surface analysis. In the United States, this development was achieved when Intergraph workstations were replaced by n-AWIPS workstations.[24] Twenty-first century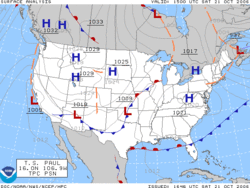 By 2001, the various surface analyses done within the National Weather Service were combined into the Unified Surface Analysis, which is issued every six hours and combines the analyses of four different centers.[25] Recent advances in both the fields of meteorology and geographic information systems have made it possible to devise finely tailored products that take us from the traditional weather map into an entirely new realm. Weather information can quickly be matched to relevant geographical detail. For instance, icing conditions can be mapped onto the road network. This will likely continue to lead to changes in the way surface analyses are created and displayed over the next several years.[26] See alsoReferences
|