|
History of Valais Occupied since prehistoric times, the canton of Valais saw the rise of an exceptional civilization during the Bronze Age. From the 4th century BC, four Celtic tribes shared its territory, which was incorporated into the Roman Empire by Augustus. The Gallo-Roman Valais, located on the important Great St Bernard Pass, was prosperous. Christianity was first established in 377, and a bishopric was opened in Martigny by 381 at the latest. With the fall of the Empire, the region became Burgundian, before being integrated into the Carolingian Frankish kingdom. On its demise, it became part of the Transjurane kingdom of Burgundy, of which the abbey of Saint-Maurice d'Agaune was the religious center. The county of Valais became the property of the bishop in 999, upon donation by Rudolph III of Burgundy. In the 11th century, it passed to the Holy Roman Empire, and feudalism fragmented it into numerous seigneuries and territories. The upper part of the territory became Germanized in successive waves between the 9th and 14th centuries, while the influence of the Counts, then Dukes, of Savoy increased in the Lower Valais. At the end of the 14th century, it became an ally of the Swiss cantons, and its border was fixed at the Morge de Conthey. During the Burgundian Wars, the Upper Valais invaded Savoy territories, annexing the Lower Valais as far as Massongex and organizing it as a subject country. In 1569, Chablais Valais was conquered, again to the detriment of Savoy. The Lower Valais remained subject to the Upper Valais, which saw the bishop's power diminish in favor of the Patriotes, who in 1634 formed a genuine federal republic, the Republic of the Seven Tithings. It wasn't until the French Revolution that the Lower Valais gained its independence. Valais fluctuated between the Helvetic Republic (1798-1802), theoretical independence (1802-1810) and incorporation into the Empire (1810-1813). Following the fall of Napoleon I, the Allies persuaded Helvetia to join the Swiss Confederation in 1815, making it the twentieth canton. Still torn between the German-speaking upper and French-speaking lower cantons, it came close to splitting into half-cantons (1840). As a member of the Sonderbund (1845-1847), it was defeated. The second half of the 19th century saw the development of transport (rail and road) and the beginnings of tourism, while the early 20th century saw the industrialization of the country (chemicals in Monthey and Visp, aluminum in Chippis) and the exploitation of water resources. From 1950 onwards, mass tourism developed and numerous resorts sprang up. Prehistory and protohistoryPalaeolithicThe Valais has been inhabited since prehistoric times. The only surviving traces of Neanderthals, dating from the Palaeolithic period, were found in the Lake Tanay region and date back some 32,000 years.[1] The Würm glaciation, when the Rhône glacier covered the whole of the Valais between 25,000 and 19,000 BC, probably irreparably disrupted most of the earlier human traces. After the glacial retreat, hunter-gatherers seem to have colonized the Valais; nevertheless, only the Scex du Châtelard cave has yielded a few remains of these late Paleolithic hunters (-13000).[2] By contrast, no traces have been found of the hunter-gatherer cultures that colonized the rest of the Alps at the end of the Palaeolithic, around 10000 BC.[3] Due to the extension of Lake Geneva, whose surface was at 405 m, which at that time filled the Rhône plain as far as the Saint-Maurice cluse, it seems that reindeer, and hence the Magdalenian culture, did not penetrate the Valais,[4] although a settlement is attested in the Chablais vaudois at Villeneuve.[5] The lowering of Lake Geneva's water level during the Epipaleolithic period enabled Azilian culture to spread into the Chablais region, but less probably upstream of the Saint-Maurice cluse.[6] Although no remains have been found, camps must have existed on the plains and at high altitudes, for hunting ibex.[7] MesolithicA rock shelter dating from the Mesolithic, around 8,000 BC, has been excavated in the Vionnaz region, associated with the Sauveterrian.[8] Traces of human occupation from the same period have been found near Zermatt, attesting to the presence of humans at altitude from this remote period. Neolithic Three elements support the hypothesis of population migration as the source of Neolithization in the Valais, in contrast to the acculturation phenomenon favored in the western Alps. Firstly, the simultaneous disappearance of Mesolithic techniques and the emergence of all Neolithic techniques in the Valais: there is no intermediate state.[9] Secondly, the absence from the local fauna of the wild ancestors' domesticated species, implying that herds had to be imported. Finally, the absence of any transition between hunting and livestock-based economies.[10] Because of the proximity of ceramics, it is generally accepted that it was shepherds from south of the Alps who,[9][11] guiding their herds through the Alpine passes (Simplon, Theodule, Collon, etc.), brought the new agricultural techniques to the region.[12] Villages were located on the plain, on river alluvial fans, on the sunny side of the valley. The site of Sion (Planta) seems to have been well occupied by the 6th millennium BC, and hunting seems to have been no more than a secondary activity.[10] At this time, the livestock seems to have consisted mainly of goats and cattle in roughly equal proportions.[13] Wheat and starch were also grown.[14] Ceramics, influenced by the southern Alps, are different from those of the Swiss Plateau, and the Valais civilization is referred to as the Early Neolithic culture of the Valais. Some authors see the importance of the region's settlement as a sign of the site's importance in the export throughout Europe of green obsidian polished axes from the southern Alps, at the time a symbol of power throughout Western and Northern Europe. A new culture appeared at the beginning of the Middle Neolithic (early 5th millennium BC), related to the Early Cortaillod of the Swiss plateau, but with distinct motifs (fluting on ceramics): this was called the Cortaillod ancien valaisan (Early Valais Cortaillod).[15] Also in the 5th millennium, an original culture, known as Saint-Léonard, developed, characterized by ceramics with original decorations. Southern influences were joined by influences from the West. The Saint-Léonard culture is particularly well represented in Sion and upstream. On the other hand, in the Lower Valais, at La Barmaz in the commune of Collombey-Muraz, two major necropolises associated with the Cortaillod civilization have been found;[16] this would indicate two cultural areas in the Valais: the Chablais under the influence of the Cortaillod civilization and the upper Valais under that of the Saint-Léonard civilization. It is from this period that Chamblandes-type tombs composed of a cist generally contain a single skeleton in a folded position. Nearly 900 of these tombs have been found in Valais (Sion, Sembrancher, Saint-Léonard, La Barmaz near Monthey, Waldmatte, etc.). While copper metallurgy first appeared on the Swiss plateau, no trace of this technique has been found in the Valais during this period. The Late Neolithic saw the development of a megalithic civilization. The Petit-Chasseur necropolis in Sion, with its dolmens and anthropomorphic stelae, is a monumental example. During the first half of the 3rd millennium BC, the stelae, known as type A, were characterized by small heads and few representations of weapons. The graves are collective, although their small number in relation to the estimated population suggests an unequal society,[17] probably a lineage society: this is the Valaisan Final Neolithic. Then, between 2500 BC and 2200 BC, the Bell Beaker culture also spread to the Valais.[18] The graves of the Petit-Chasseur became individual, and the stelae, known as Type B, were characterized by larger heads and a greater number of weapon figurations. Near the access routes to the Alpine passes, numerous scattered objects have been found, testifying to a probable intensification of trade. A number of cupstones found in the Valais (Zermatt, Anniviers, Saint-Léonard, Évolène) also date from this period.[19] By the end of the Late Neolithic, local metallurgy was very primitive.  Bronze Age As early as the xxi century BC, traces of the Bronze Age were discovered throughout the upper Rhône valley. A specific culture, the Rhône culture, developed. Nevertheless, there was no break with the Campaniform period: the Petit-Chasseur necropolis was still in use, and individual tombs with type B megalithic stelae were still being erected. The first phase, the culture du Rhône préliminaire (Early Rhone culture), is characterized by copper objects (less than 1% tin) and seems specific to the central Valais, although a grave near Thun may indicate that this culture extended to both sides of the Bernese Alps.[20] The following period saw the spread of Rhone culture. The entire Valais was now part of this culture's territory, as were the Aare and Sarine valleys, and the Lake Geneva region near Lausanne. Rhône culture also extended to the French Jura and part of the Middle Rhône valley. Valais is part of the Rhône-Aar group. Classic Rhone culture is influenced by the Únětice culture attested in the Danube region. These influences seem to have come from roads north of the Alps, but also from the south and northern Italy.[20] Between 1800 and 1600 BC, the Rhône culture, in its so-called advanced phase, extended even further territorially for the Rhône-Aar group: the shores of lakes Neuchâtel, Biel and Murten are included, as well as the western end of Lake Geneva, as far as Geneva. Metal objects are abundant, although the variety of forms is declining, heralding the decline of the culture.[21] From the 16th century B.C. onwards, the Rhône culture declined rapidly; apart from the Valais, where it seemed to survive somewhat, it was replaced in the rest of its geographical area by the tumulus culture originating in Central Europe. Valais mines no longer appeared to be exporters, and the influence of the southern Alps gradually increased.[22] As early as 1450 BC, the Valais, which was completely outside the tumulus culture dominating the Swiss plateau, saw the development of fortified settlements and came under the influence of the Alba-Scamozzina culture, which seemed to control Alpine transit.[23] By the end of the 15th century B.C., southern Valais seemed to be under the northern Italian influence of the Canegrate culture, although many indigenous elements were mixed in, particularly in the Sion region. Valais thus appears to be on the borderline between two cultural groups: Canegrate south of the Alps and Rhine-Rhone-Danube culture to the north. The regional culture is referred to as the groupe alpin de la culture de Canegrate (Alpine group of the Canegrate culture). The intensification of Alpine exchanges is evident.[24] Rock shelters have been discovered above Zermatt and in the Val d'Hérens: the seasonal transhumance of herds between the plains and the alpine pastures, already attested at the end of the Neolithic, continued.  Iron Age During the Early Iron Age, between 800 BC and 480 BC, the Valais was on the geographical fringe of the Hallstatt civilization, which had a profound influence on the Chablais and Lower Valais regions, even though a specific evolution was recorded in terms of metallurgy. Numerous heavy bracelets have been found in the central Valais, known as Valaisan bracelets.[25] These bracelets, also known from the Swiss plateau, survived in the Valais until the 1st century. For example, the Don Bosco necropolis at Sion in central Valais has yielded several tumuli dated between the 9th century BC and the 2nd century BC, typical of the Hallstatt period.[26] The Upper Valais, however, seems to be further removed from the Hallstatt civilization and is more strongly influenced by northern Italian civilizations, such as the Golasecca culture, particularly in terms of burial rites. From the 4th century BC, and into the Second Iron Age, four Celtic tribes shared the region: the Nantuates, who occupied the Monthey region, the Veragri the Martigny region (then called Octoduros), the Seduni (their oppidum is present-day Sion, perhaps already called Drousomagos unless this name was only given after the Roman conquest by Tiberius and Drusus) and the Ubères (on the territory of today's German-speaking districts). These four tribes have more in common with the Lepontii and Salassi, their neighbors to the south of the Alps, than with the Helvetii, their neighbors to the north. The Binntal, although located on the Valais side of the Albrun pass linking the Valais to the Val d'Ossola via the Val Devero, was, according to archaeological data, inhabited by Lepontians occupying the Val d'Ossola, the Ticino valleys and part of present-day Milan.[27] The Ayent inscription, discovered in 2003 above Sion, confirms the close relationship between the Valais and the Celtic populations south of the Alps. Not only is the inscription written in Boustrophedon, in the late Lugano alphabet used by the Celts of the Po basin, whereas the Celts of Gaul generally used the Greek alphabet, but the Celtic dialect indicates a phonetic evolution specific to the peoples of northern Italy.[28] The Veragri coin, attested as early as the 1st century B.C. and also used by the Seduni,[29] uses motifs from south of the Alps and does not seem to have been influenced by coins from the mid-Rhône valley.[30] Little is known about the religion of the Celts in the Valais: the oppidum of the Nantuates, Tarnaiae, today's Massongex, derives its name from Taranis, the Celtic god.[31] There also seems to have been a sanctuary at Saint-Maurice and topical deities, such as Poeninus at the Great St. Bernard Pass (Summus Poeninus)[32] and perhaps Sylvius at the Theodule Pass (Mons Sylvius), which seems to be the origin of the Matterhorn's name. Roman periodConquest During the Gallic War, Julius Caesar, with the help of the Thunderbolt Twelfth Legion (Legio XII Fulminata) under the command of Servius Galba, attempted to occupy Martigny, the key to the Grand Saint-Bernard Pass (Summus Poenus), but the Romans withdrew after their hard-fought victory at the Battle of Octodurus in autumn 57 BC.[33][34] The road to the pass was then a mule track with a reputation for difficulty.[35] Although the incorporation into the Roman Empire of the Salassi of Valle d'Aosta, subdued in 27 BC, must already have greatly reduced the autonomy of the four Valais tribes, it was probably in 15 BC,[36] after a military campaign led by the future emperor Tiberius and Drusus, that the Celtic tribes of the Alps were defeated and Emperor Augustus incorporated the region into the new province of Rhetia-Vindelicia, whose capital was Augsburg. Each of the four tribes formed a Roman city (civitas), and at first, seems to have retained a high degree of internal autonomy: documents refer to each of the cities independently, or refer to them generically as the four Valaisan cities, indicating the possible existence of a league.[37] In all cases, the cities are considered to have been conquered in 6BC, their names appearing on the Tropaeum Alpium at La Turbie. High Empire During the reign of Claudius (41-54), Valais was detached from Rhaetia-Vindelicia to become Vallis poenina, a province that often, perhaps always, had the same governor as Tarentaise (Graian Alps), another Alpine province.[38] In 47, or shortly before,[39] the emperor founded Forum Claudii Augustii in the immediate vicinity of the Celtic town of Octodure, which was renamed Forum Claudii Vallensium[40] on his death, capital of the civitas vallensium,[39] the only city grouping together the four ancient tribes. The Roman city, with an estimated population of 5,000, was made up of ten insulae (districts), one of which was entirely occupied by a forum[41] and included an amphitheater. The organization of the province seems classical, with several epitaphs referring to duoviri iuri dicundo, indicating the presence of two judges, probably elected for annual terms as elsewhere in the empire. To facilitate troop mobility in anticipation of the invasion of the British Isles in 49, the Romans may have made the strategic Mont-Joux pass road passable, but this hypothesis is debated.[42] Relays (mutationes) and stopping places (mansiones) were created and maintained on the main routes. The Pax Romana, which lasted for almost three centuries, led to a boom in the region, with Acaunus becoming a customs post collecting the Quadragesima Galliarum.[43] Roman civilization took root in the Valais: alongside Martigny, the region's only real town and the city's capital, vici developed, for example in Sion and Massongex; villae were created but remained few in number (e.g. the villa de Marendeux in Monthey), as indigenous Celtic farms retained their importance. Civitas Vallensium was subject to Roman law, and Roman citizenship was granted to local councillors and their families in a straight ascending and descending line, enabling acculturation of the local population. Throughout the High Empire, no permanent troops were stationed in the Alps, although small detachments to protect the roads were documented. Roman arts and traditions spread throughout the Valais. Several thermal baths have been found (at Massongex, Martigny and Sion) and sculptural art was highly developed. Excavations of the amphitheatre in Martigny unearthed several bronze statues, including the head of a Hérens cow.[44] Only one mosaic has been found, in the Massongex thermal baths; like the other first-century mosaics found in Switzerland, it is monochrome. Low RomanWhen the Alamanni raided the Swiss Plateau around 275–277, they seem to have been driven back to the Saint-Maurice cluse.[45] At the same time, localities downstream of the cluse, particularly Massongex, the ancient Tarnaiae (spiritual capital of the Valais Celts), faltered, as did others on the Swiss plateau. As early as the 2nd century, cults of Asian origin are attested, such as Cybele and above all Mithra, a mithraeum having been found in Martigny. By the mid-fourth century, Christianity was spreading in the Valais. The earliest dated evidence (377) is a Chrism on an inscription by a Roman aedile, found in Sion.[46] The first evidence of a bishop in Valais, at Martigny, dates back to 381, when Theodore signed the Acts of the Council of Aquileia as Bishop of Octodure.[47] A Christian chapel dating from the mid-fourth century has been found in Martigny, replaced in the following century by a double church, typical of episcopal sees of the period. It was Theodore who initiated the cult of Saint-Maurice in Agaune, where he "discovered" the remains of the martyrs of Agaunum and built the site's first Christian sanctuary. From the beginning of the 5th century, the economic and political ups and downs of the Roman Empire began to make themselves felt, and trade diminished.[48] The Forum Claudii Vallensium was abandoned in favor of the nearby market town of Octodurus; the inhabitants of Sion abandoned the right bank of the Sionne, giving up their baths and dwellings, and occupied only the Cité district, backing onto the hills of Valère and Tourbillon. From the Burgundians to the Kingdom of Burgundy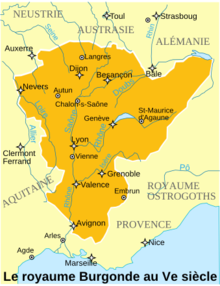 When the Burgundians arrived as federates in the lands of the Roman Empire (434), the Valais seems not to have been part of the Sapaudia granted to them. What's more, there seems to have been an immigration of notables from this area. But as soon as imperial power in Gaul came to an end (454), foreshadowing its definitive fall in 476, the Valais was rapidly incorporated into the Kingdom of Burgundy: society was governed by the Gombette law as soon as it was promulgated by Gundobad in 502, and the future king Sigismund (in 515) founded the abbey of Saint-Maurice. Freshly converted from Arianism to Catholicism, he made the site a symbol of his people's faith and an important place of pilgrimage.  The history of the Valais then became intertwined with that of Burgundy, which was soon annexed by the Frankish monarchy (534). The natural disaster of Tauredunum, perhaps Grammont, in 563 saw a section of mountain collapse, destroying a castle and a hamlet creating a giant wave on Lake Geneva, which caused extensive damage as far away as Geneva.[49] In 574, the abbey of Saint-Maurice was destroyed by the Lombards, who were finally defeated at Bex by the Franks;[50] King Guntram had the monastery rebuilt. Shortly afterwards, around 585, probably to protect it from looting and perhaps following an assassination attempt on the bishop by monks from Saint-Maurice, the episcopal see was moved from Octodure to Sion, which had meanwhile become the region's principal city.[51] Two coin workshops from this period are attested in Valais, in Sion, and Saint-Maurice.[52] Valais was part of Charlemagne's empire, whose expeditionary force crossed the Great St. Bernard in 773 on its way to fight the Lombards. The earliest mention of the pagus vallensis, attributed to Lothaire, was made at Worms in May 839, when a plan was drawn up for the division of the Carolingian empire. The Treaty of Verdun in 843 confirmed that the Valais belonged to Middle Francia. In 859, the Valais belonged to Louis II, King of Italy. In 888, the Count of Auxerre, Rodolphe I, founded the kingdom of Transjurane Burgundy, which included the Valais. He was crowned king at the Abbey of Saint-Maurice. His successor, Rudolf II, bought the kingdom of Provence in 934, founding the kingdom of Arles, which survived for almost a century.[53] In the 8th and 9th centuries, part of the Valais became Germanized, with the gradual infiltration of populations speaking dialects of the Upper Alemannic group. Of Aleman origin, they came from the Bernese Oberland over the Grimsel, Gemmi and perhaps Lötschen passes. They seem to be colonizing new lands, clearing them at altitude. The linguistic border, once between Brig and Visp, moved further downstream, along the Lonza River, around the 11th century.[54] Saracens, moving up the Rhone valley from the Mediterranean, sacked and occupied Saint-Maurice in 940; they were expelled from the kingdom of Arles in 974 by a popular uprising, marked by the battle of Tourtour (973), shortly after taking the abbot Maïeul de Cluny hostage in July 972 on the road from the Grand-Saint-Bernard to Orsières, at the Château du Châtelard.[54][55] Feudal Valais In 999, King Rudolf III entrusted county rights to the Bishop of Sion and his successors. This document, The Charter of Donation of 999, drafted at Cudrefin, on the shores of Lake Neuchâtel, is the true founding act of the Valais as a state. Along with a similar donation to the bishop of Basel in the same year, it was the first time in Swiss territory that regal rights were transferred to local lords.[56] Surprisingly, the boundaries of the commitatis vallensis were not clearly defined; it wasn't until the 11th century that the border was fixed near the Dranse at Martigny, at the place known as Croix d'Ottans, a hamlet that no longer exists today.[54] Feudalism gradually spread throughout the region, while transalpine traffic gradually picked up again in the course of the tenth century, as a result of the renewed stability of the continent. In 1032, on the death of Rudolf III, the County of Valais, like the rest of the Kingdom of Burgundy, became part of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1189, the county benefited from imperial immediacy,[57] and the Bishop of Sion became Prince of the Empire. The bishopric is now the episcopal principality of Sion.  The great feudal neighbors, the Zähringens to the north and the Savoys to the west, tried to extend their power over the Valais. In 1211, Berthold V of Zähringen was defeated at the Battle of Ulrichen.[58] On the other hand, the Lower Valais gradually fell into the hands of the Counts of Savoy; faced with the threat, Bishop Henri of Raron joined forces with Bern (1252), placing the county in the relatively loose and incoherent zone of regional alliances known to historians as the Burgundian Confederation:[59] Peter II of Savoy seized the pretext and invaded Valais in the spring of 1260.[60] La Bâtiaz Castle in Martigny, Château du Crest in Ardon and Château de la Soie in Savièse fell under his control, and the bishop was forced to sign a peace agreement establishing the border between the two states at the Morge de Conthey.[60] This border was reaffirmed in 1262. From then on, the Valais was split in two: the independent Upper Valais in the hands of the Bishop of Sion, and the Lower Valais part of the Savoyard possessions. In 1268, the Val d'Hérémence became part of the Savoyard territory, and was attached to the Conthey castellany against its will.[61] It was also at this time that the Conseil général (General Council), the future Diet, appeared in the Episcopal Valais. At first, towards the end of the 13th century, it was an exceptional meeting of the great feudal lords, representatives of the communes and a few ecclesiastics with temporal power, mainly representatives of the Sion chapter. With the disappearance of the great secular seigneuries, the limited power of ecclesiastics other than the bishop, and the grouping of communes into dizains, the council evolved in the 14th century into a body that met on request - but at least once, then twice a year - to deal with the affairs of the country. While the General Council normally brought together all seven dizains (Consilium generale patrie or Consilium generale tocius terre Vallesii), councils bringing together the five German-speaking dizains (Populares universitatis Vallesii Allemanorum) sometimes took place; these were later also known as diétines. After the disappearance of the great secular estates, the nobility no longer participated as a special body, but they retained their influence in the dizains, and their delegates were often chosen from among their descendants.  Similarly, the seigneuries and communes of the Savoy-dominated Lower Valais were regularly represented in the States of Savoy in the 14th century. In 1348–1349, Valais was ravaged by the Black Death. Between 25% and 50% of the population died, depending on the locality. The disease, which had been absent from Europe for at least five centuries, continued to cause six epidemics in the Valais until 1450.[54] Following the reunification of the territories west of the Morge under Savoyard authority, the seigneury of Ardon-Chamoson passed into Savoyard hands in 1348,[62] as did the episcopal châtellenie of Martigny in 1384.[63] Similarly, east of the Morge, it was also in 1348 that Guichard Tavelli, Bishop of Sion, paid homage for the last time to the Duke of Savoy for the seigneury of Mörel, which had been in Episcopal hands since at least 1224, after having been in Savoy possession.[64] The seigneury of Ayent, meanwhile, changed hands in 1376, becoming the property of the bishop. Parallel to these Savoyard claims, a number of noble families in the Upper Valais were able to build up sizeable estates: of particular note were the seigneurs de la Tour, who dominated the Lötschental and the Niedergesteln region, as well as a significant part of the Bernese Oberland, and the de Raron family. Savoy continued to lay claim to the Upper Valais, wishing to control north–south traffic across the Simplon Pass. Fighting was fierce, Sion was pillaged several times, and its bishop Guichard Tavelli was even defenestrated in 1375 from the top of the Soie Castle by vassals of Antoine I de la Tour, a Savoy ally at the time. The ensuing revolt culminated in the battle of Saint-Léonard the same year, where Antoine I was defeated. Having fled to Savoy, his Valais territories, Niedergesteln and the Lötschental, became subject to the five Upper Valais dizains (Conches, Brigue, Viège, Rarogne and Loèche). In 1388, at the Battle of Visp, the patriots of the Upper Valais defeated the Savoyard troops. The conflict ended in 1392, with Savoy definitively abandoning its hold on the Upper Valais, which had become less strategically important since the opening of the Gotthard and the diminished importance of the Champagne fairs. The separation of the Episcopal Valais from the Savoyard Valais is complete. The Upper Valais moved even closer to the Confederate cantons, maintaining a network of alliances with them. The Prince-Bishop continued to fight against the last great feudal lords of the Upper Valais: the Rarogne family was defeated at the Battle of Ulrichen during the Raron affair (1410-1419). Battles between patriots and the prince-bishopOnce the great feudal lords had disappeared, it was the dizains and their elite, the Patriotes who had assimilated the local nobility, who wished to hold temporal power. Between 1420, with the fall of the de Rarogne family, and 1634, with the abolition of the Constitutio Criminalis Carolina and the end of the bishop's temporal power as an elective prince, two centuries of often violent struggles began, marked by participation in the Italian wars and attempts to establish the Reformation, which was used for political ends.  In 1415, after besieging the Château de la Soie, the patriots of the Upper Valais, with the exception of those from Sion, obtained from Bishop Guillaume VI of Raron control over the appointment of the bishop and senior civil servants. This right was enshrined in an official document in 1435, the organisation judiciaire (judicial organization) giving the Diet the power to confirm priests and civil servants; Bishop André de Gualdo also granted the communities of Sept-Dizains the right to appoint their own châtelains on an annual basis. On January 28, 1446, the Articles of Naters, wrested from the bishop, gave legislative power to the Diet; they were annulled on February 7, 1451, by his newly elected successor, Henri Asperlin. The witch trials in the Valais began in 1428, foreshadowing the great witch-hunt in Europe.[65][66][67] Relations with the Aosta Valley were more strained in the 15th century: while many nobles from the Aosta Valley had settled in the Valais in previous centuries, several bishops, such as Boniface de Challant, came from Aosta, and the Cathedral Chapter was sometimes almost half made up of members from the region, disputes over alpine pastures led to threats of military invasion of the Aosta Valley by the Valais.[68] In 1475, at the height of the Burgundy Wars, the Bishop of Sion, Walter Supersaxo, allied with the Bernese, attacked Conthey, a Savoy possession and ally of Charles the Bold. The latter reacted, and on November 13, 1475, the Battle on the Planta took place in front of the walls of Sion. The town almost fell, but the arrival of 3,000 Confederate soldiers over the Sanetsch Pass saved it and led to the defeat of the Savoyard troops. The Valaisans then occupied the Lower Valais as far as the Saint-Maurice pass, and annexed it on December 31, 1476, shortly after the signing of the Treaty of Fribourg. The Lower Valais became a subject country of the Upper Valais. Savoy did not recognize this annexation until 1526. At the same time, the Bernese and their allies from Gessenay invaded the Chablais region on the right bank of the Rhône, definitively separating it from the secular Valais. Thus, for a quarter of a century, the conflict between the Patriotes and the bishop was muted, in order to reclaim "the patrimony of Saint-Théodule" over Savoy. The conflict resumed with Walter Supersaxo's successor, Jost von Silenen.  At the end of the Ossola Wars between 1484 and 1495, unsuccessful attempts (as at the Battle of Crevola in 1487) to annex the eponymous valley belonging to the Duchy of Milan, the Bishop of Sion, Jost von Silenen, allied with France, signed a peace treaty with Milan in 1495: the southern slopes of the Simplon as far as Gondo were incorporated into the Valais. In the years that followed, the Bishop of Sion, Cardinal Matthäus Schiner, became a strong supporter of the Pope (against France). His incessant intrigues dragged Valais and the confederate cantons into the Italian wars, culminating in the defeat at Marignano in 1515. Valais then joined the Swiss cantons in the Treaty of Fribourg signed with France in 1516.[69] Internally, Matthieu Schiner violently opposed Georges Supersaxo, representative of the Patriotes. He even excommunicated him in 1512. Schiner fought to assert the bishop's temporal power, and in 1514 published a law instituting regalian rights for the Church. But Supersaxo, taking advantage of one of the bishop's many absences, proclaimed in 1517 the "Peace of the Patriots", affirming the political pre-eminence of the Patriots and the replacement of the prince-bishop after an absence of six months. Schiner, who was abroad at the time, was banished and unable to return to Valais; he settled in Zurich and died five years later in Rome.  In 1536, when Bern invaded the Pays de Vaud for the second time after 1476, the Valaisans invaded the Chablais as far as Lake Geneva, also in the hands of the Duchy of Savoy. They even occupied the region between Saint-Gingolph and Thonon, and wanted to push as far as Evian, but joined forces with Bernese troops from Geneva at the Dranse. Under the 1569 Treaty of Thonon, the Duke of Savoy granted them Chablais, and the Valaisans reluctantly returned what is now French Chablais, between Saint-Gingolph and Thonon, with the right bank of the Morge de Saint-Gingolph marking the border. The parish of Saint-Gingolph, now situated between two states, nonetheless remained part of the diocese of Annecy, formerly the diocese of Geneva. Although the presence of Protestants in Valais was attested to as early as September 1524, the choice of religion was a means of exerting pressure on the bishop, as a major conversion could lead to the secularization of episcopal property. Capuchins and Jesuits were called in to preach the Counter-Reformation. Finally, Valais renewed its alliance with the Swiss Catholic cantons, and in 1604 the Diet ordered the Reformed to convert or go into exile. In practice, with the exception of a few exalted exiles, the decision was applied sparingly, with Protestants essentially barred from high state office. Republic of the Seven Tithings In 1613, the patriots finally won the power struggle by imposing a charter, the Conclusum, on the prince-bishop and the chapter. The latter could still nominate candidates, but it was the Diet, representative of the seven dizains, that conferred the insignia of power on the new bishop. The bishop then becomes a true elective prince, and power now belongs to the dizains, who form a veritable federal republic: the Republic of the Seven Tithings. Under the impetus of Michel Mageran, a Protestant notary from Leuk, who converted to Catholicism in 1624 to take up political office, power was concentrated in the hands of the Diet and Councils. In 1627, he obtained the expulsion of the Jesuits, followed by the condemnation and execution of Antoine Stockalper, a defender of episcopal authority. Mageran became Governor of Monthey, then secretary of state and finally, in 1631, Grand Bailli, i.e. head of government. In 1632, he convinced the government to set up a centralized state treasury.[70] He died in 1638, having helped force the bishop and chapter to renounce La Caroline for a second time in 1634. In the 17th century, a new economic boom began, stimulated by improved transport links. In 1640, Gaspard Jodoc Stockalper organized a mail service between Milan and Geneva via the Simplon Pass, and financed a canal between Vouvry and Collombey to lower the cost of transporting salt, for which he had a monopoly. The canal was completed on June 10, 1659. Other important works were also carried out: the Sion town hall was built between 1657 and 1665. During this period, many Valaisans served under foreign flags. For example, the King of France maintained the Courten Regiment between 1690 and 1792. Valais during the French Revolution and the Napoleonic eraLower Valais revolutionAs soon as the first echoes of the French Revolution resounded, unrest set in across the seven dizains' subject lands. In 1790, the Monthey region was rocked by the Gros-Bellet affair, and the following year by the Crochets conspiracy. While echoes favorable to revolutionary ideas circulated mainly by word of mouth and pamphlets,[71] unfavorable echoes arrived through French priests taking refuge in the region, fleeing France and describing the massacres of the Terror.[72] The government was worried, and in 1794 promulgated a Code pénal pour le Bas-Vallais (Criminal Code for Lower Vallais), containing a veritable plea against liberty.[73] Some communities took advantage of the period to buy back royalties or servitudes; for example, the Lötschental freed itself from its last feudal servitudes between 1786 and 1790[74] and Anniviers between 1792 and 1802,[75] completing the emancipation of the communities of the dizains of the Upper Valais). It was in Saint-Maurice that the first tree of liberty was planted in Valais, on January 28, 1798.[76] The revolution ignited the whole of the Lower Valais, and on February 5, 1798, an assembly of delegates from the Lower Valais took place, attended by a delegation from the dizains of the Upper Valais, presided over by the burgomaster of Sion, Pierre-Joseph de Riedmatten. The latter read out a declaration renouncing domination of the Lower Valais territories by the upper dizains.[77] On March 16, 1798, a constituent assembly at the Abbey of Saint-Maurice proclaimed the République des Dix-Dizains: the three dizains of Monthey, Saint-Maurice and Entremont joined the seven upper dizains.[78] The historiography of this period is peculiar: historians of the Lower Valais tend to reinforce the importance of the elements of 1790 and consider the revolution to be primarily an internal revolt, whereas historians of the Upper Valais prefer to emphasize the external aspect, i.e. a revolution fomented by France. Canton of the Helvetic Republic Finally, following the French invasion of Switzerland, Valais was incorporated into the new Helvetic Republic, after French general Lorge had to defeat an Upper Valais rebellion. On May 17, he defeated some 600 insurgents in Sion, leaving the town to be pillaged. The country was not quiet, however, and the French defeated the Upper Valais troops led by Ferdinand Venetz on May 27 and 28, 1799, at the Battle of Finges. The Helvetic Republic's minister of worship and education, Philipp Albert Stapfer, prepares a Swiss law on schools, and conducts a study: the Valais leaders themselves are appalled by the low level of schooling in the Valais. From May 15 to 21, 1800, as part of the second Italian campaign, Napoleon Bonaparte crossed the Great St Bernard Pass with his reserve army. This event was the subject of Jacques-Louis David's equestrian portrait of Napoleon Crossing the Alps. In November 1801, the Valais was once again occupied by the French. General Turreau's troops did not leave the country until August 1802, when independence was proclaimed. Republic of Valais (1802-1810)Napoleon Bonaparte considered annexing the Valais in 1802, while preparing the Act of Mediation, in order to better control passage to Italy. In the end, he made it a sister republic, and Valais regained its theoretical independence in 1802. Called the Republic of Valais, it was in fact a French protectorate, and Napoleon only opted for independence in view of the communes' desire to remain Swiss, whose representatives crossed the Gemmi Pass in winter to show their support for the Helvetic Republic.[79] The republic was governed by the constitution of August 30, 1802. The organization into dizains was modified; two new ones were added to the ten dizains of 1798: the dizains of Hérémence and Martigny were detached from those of Entremont and Sion.[80] The number of representatives for each dizain at the Diet is proportional to its population (1 deputy for every 2,000 inhabitants). They were appointed by the dizain council, and only citizens who had already held political office, officers and notaries, regardless of their commune of origin, were eligible. The executive power was completely separate: it consists of a three-member Council of State appointed by the Diet; its president bears the title of Grand Bailiff. In contrast to the Ancien Régime, the dizains were no longer able to reject the decisions of the Diet. In 1804, François-René de Chateaubriand briefly represented the emperor in Valais. Central power remained weak, and work on the Simplon Pass road made little progress. Moreover, as soon as France promulgated a law on May 30, 1806, prohibiting the import and transit of goods from England, the legislative transposition of Napoleon's continental blockade, the problem of contraband arose.[81] In their report of October 3, 1810, the French commissioners for Valais affairs proposed moving the customs frontier to the limits of Valais.[82] Simplon department (1810-1813) In November 1810, Valais was finally incorporated into the First French Empire under the name of Département du Simplon. A prefect headed the department, which was divided into three arrondissements (Monthey, Sion and Brigue) headed by sub-prefects, grouping together the thirteen cantons, corresponding to the twelve dizains of 1802, plus Mörel, legally detached from Rarogne, to which it was not geographically contiguous. The organization is identical to that of any French department. Subject to French laws enacted in Paris, the department is governed by an executive body consisting of a prefect, the head of local administration, appointed by Paris, and a Conseil de préfecture (Prefectural Council), as instituted by the law of 28 pluviôse an VIII (February 17, 1800), responsible for settling disputes with the administration. Appeals are lodged with the French Conseil d'État. The departmental Prefecture Council is made up of the three sub-prefects of the three arrondissements created. Transitional government (1814-1815) On December 26, 1813, after the departure of French notables, including the Prefect Claude-Philibert Barthelot de Rambuteau, fleeing the imminent arrival of the Austrians, the Valais became independent once again; this state of affairs was confirmed de iure by the Treaty of Paris of May 30, 1814.[83] The Prefecture Council assumed the power vacuum. On the 28th, Austrian colonel Joseph-Franz von Simbschen entered Valais via the Saint-Maurice pass, reaching Sion the following day. He ordered the raising of a defensive troop, and despite the council's refusal, the deputies of the Haut réunis reluctantly granted him 400 men and appointed a delegation to represent Valais to the Prince of Schwarzenberg, commander of the army of occupation. On December 31, Simbschen proclaimed the dismissal of the Prefectural Council and appointed a Direction centrale (Central Board) consisting of a president and twelve members, and named a supporter of independence, Gaspard-Eugène Stockalper, as president. This structure, whose composition varied according to local diets and Simbschen's decisions, was dissolved on January 24 after it refused to raise 466 additional men to create a battalion to serve Austria. Simbschen set up a provisional government of five men and two deputies, still headed by Stockalper. On January 21, Simbschen also abolished the departmental courts and the French-appointed judges; he abolished the Napoleonic Code and re-established the Statuta Vallesiae, written in Latin and still in manuscript, in force before 1798.[84] Napoleon I abdicated and left Fontainebleau on April 20, 1814; two days later, a French officer arrived at the Great St Bernard Pass from Ivrea with a request for an armistice, which was ignored by the provisional government. On May 11, Simbschen and his troops left the Valais. Without consulting the people of Valais, the allies had decided that Valais should become part of Switzerland.[85] The government convened an extraordinary Diet in Sion from May 30 to June 1, 1814, and requested incorporation into the Swiss Confederation. In order to do so, Valais had to adopt a constitution approved by the Federal Diet and the allies.[86] A constituent commission was appointed, with representatives from the thirteen cantons of the French administrative division, including Mörel, as well as the bishop. After two long sessions in August and September 1814, it failed. For each major article, the commission produced two versions, one advocated by the dizains of the Upper region and the bishop, the other by those of the Lower region. Two main differences divided the Valais. Firstly, the voting system at the future Diet: per dizain for the Upper Valais and the bishop, versus a system proportional to the population of each dizain for the Lower Valais. Then came the territorial division: the bishop and Upper Valais wanted ten dizains, a return to the situation of the short-lived Valais Republic of 1798, while Lower Valais wanted twelve, the situation of the Constitution of August 30, 1802. Mörel supported the division into ten dizains, but wished to retain one dizain, the thirteenth, should the solution proposed by the Lower Valais prevail. On September 12, 1814, the Allies offered mediation. The Valaisans sent four independent delegations to Zurich: one from the Upper, one from the Lower, one from the town of Sion, and one from the rural communes of the Sion region (the Val d'Hérens and the Ayent region). Mediation took place with representatives from the United Kingdom, Stratford Canning and Henry Unwin Addington, Austria, Franz-Alban von Schraut, and Russia, Ioannis Kapodistrias and Paul de Krüdner. After rejecting the motions of both the Upper and Lower delegations, and after the Lower delegation had made a new proposal of fifteen dizains, but with one vote per dizain as demanded by the Upper, they published a prononciatum dividing the Valais into thirteen dizains. The dizain of Mörel was again merged with that of Rarogne, as before the annexation; the dizain of Conthey was created; the dizain of Martigny, created in 1802, was confirmed, as was that of Hérémence, renamed Hérens and including the Ayent region, which was thus not transformed into a dizain; similarly, the dizain of Entremont was retained and not split into the districts of Sembrancher and Bagnes. On the other hand, each dizain had one vote in the Diet, as did the bishop. The territorial division was thus in line with the former subject countries, while the voting system favored the Upper. Immediately, the Lower Valais created the dizain of Conthey, while the Upper Valais convened a Constituent Assembly. The Assembly drew up a draft constitution in line with the prononciatum, but appointed the new government two days before it was ratified. The delegates from the Lower Valais refused to take part in the vote, and their elected representatives did not recognize their election. A dietin was called in the Lower Valais, proclaiming its independence. The communities of the Lower Valais were far from united by this decision: many politicians disagreed, and many communes in the Saint-Maurice region expressed their attachment to a unified Valais. With the start of the Hundred Days, a government of union, with military powers, was set up and, after some procrastination, the Lower Valais agreed to take part. Under pressure from the Allies, who sent imperative notes, one of which was a new draft constitution, a new constituent assembly was convened, and the new constitution was adopted on May 12, 1815. On August 4, 1815, Valais became the twentieth canton of the Swiss Confederation. On August 7, 1815, the two Valais delegates to the Federal Diet, Michel Dufour and Léopold de Sépibus, took the oath to the Federal Pact on behalf of the République et canton du Valais (Republic and Canton of Valais). Tensions between conservatives, liberals and radicals (1815-1848)After the adoption of the cantonal constitution of 1815, tensions between the former subject dizains, who were liberal or even radical, and the conservative dizains of the Upper Valais region, did not cease. Indeed, the new constitution did away with some of the gains of the previous ones: representation proportional to the population of the dizains of 1802 was abolished, even though the new dizain of Conthey was created to partially compensate for the over-representation in the Diet of the dizains of the Upper Valais in relation to their population. Thus, each dizain, regardless of its size and population, had four deputies, elected in each dizain by grand electors; the bishop also had four votes, and the presidents of the dizains were members, as were the vice-president of the Council of State, its treasurer, and the other 2 councillors of state.[87] Eligibility requirements for the Diet were draconian, and favored the establishment. The right of citizenship is communal, and changing commune means losing one's political rights. Finally, the separation of power is once again imperfect, with the legislative and executive branches headed by the same president. Moreover, the social situation was not good: not only had seventeen years of unrest impoverished the canton (famine, poor harvests, maintenance of foreign troops, raising of troops), but the harvests of 1816 and 1817 were poor, leading to severe famines; malaria was endemic. Finally, the transit of goods via the Simplon was declining: the Kingdom of Sardinia imposed heavy taxes on it, and traffic tended to shift to Mont Cenis. The number of poor people increased, and beggars were numerous. The government had to legislate, and published a law on begging in 1827. The increase in property crime -theft of food, clothing and tools- between 1816 and 1839 is further evidence of the worsening situation. Industrialization was beginning to take hold, but workers remained few in number and subject to the vagaries of the economy. Although mercenary service was successful, only a few dozen Valaisans embarked for the New World, and emigration remained limited.[88] In 1826, the Diet published a new electoral law, the loi organique du 20 mai 1826 (Organic Law of May 20, 1826), which created a new body in the dizains, the Communal Council, responsible, among other things, for electing the Council of the dizain, itself responsible since 1815 for appointing local representatives to the Diet. This additional level further detached the citizens of the dizains from those who made the decisions. By 1831, discontent had turned to rebellion in the Lower Valais. The movement was disorganized, and as both liberals and conservatives did not want any upheaval, it resulted in a simple reworking of the organic law, allowing the new liberal classes that had emerged - lawyers, notaries and officers - to accede to political office. In 1833, the consultation on the revision of the Federal Treaty of 1815, the new version of which provided for a strong central power, rekindled divisions between Upper and Lower Switzerland. On April 11, a brawl broke out in Martigny between supporters and opponents of the new pact. The Upper region, with a majority in the Diet, won out politically. The reform-minded forces of the Lower, united for the first time, wanted a revision of the cantonal constitution. Their 1834 petition was rejected. The Upper Valais deputies left the Diet in 1839 and set up a second government in Sierre. In the same year, the episode of the Guerre du Fromage (Cheese War) also highlighted the tensions. Two new constitutions were adopted in 1839. The first on January 30, the second on August 30. The Diet was renamed the Grand Council, with each dizain sending a number of deputies proportional to its population. The deputies are appointed by the Tenne Council, making it a two-degree election system. The title of Grand Bailli was abolished, and each State body - the Conseil d'Etat for the executive and the Grand Conseil for the legislative - was again separated, as in 1802, and each had its own president. In 1840, the canton was on the verge of dividing into two half-cantons; Guillaume de Kalbermatten, commander of the Sion garrison, prevented this. Leading the troops of the Old Switzerland, he defeated the conspirators of the "Young Switzerland" movement at the battle of Trient in 1844. Several of the conspirators, including Maurice Barman, were forced into exile. A new constitution was finally ratified by the people the same year. A new constitution was adopted on September 14, 1844. Conservative ideas triumphed.  In 1845, Valais joined the Catholic cantons of the Sonderbund, created in 1844. Shortly after the Federal Diet ordered the dissolution of the alliance, when war seemed inevitable, Guillaume de Kalbermatten was approached to command the troops of the entire Sonderbund, but he refused the distinction and settled for command of the Valais troops. Nevertheless, the canton surrendered without a fight in 1847 when federal troops under General Dufour arrived. On November 30, 2,000 Valais citizens gathered on the Place de la Planta in Sion to dismiss the government; they also introduced laws designed to reduce the influence of Catholic prelates in politics. The Jesuits were expelled, the combination of religious and civil mandates was forbidden, and public education was entrusted to the State.[89] Relations between Church and State gradually normalized with the accession of Alexis Allet to the cantonal government, then with the appointment of Bishop Adrien VI Jardinier in 1875: a definitive arrangement was finally signed in 1879.[89] Under the influence of Maurice Barman, who returned from exile in 1847, Valais adopted a new constitution in 1848. It was during this period that the last feudal rights were bought out: in 1844, Nendaz bought out those still held by the Abbey of Saint-Maurice d'Agaune, even though the former territorial seigneury had not owned the region since the 11th century.[90] Industrialization and modernization By 1850, tourism was booming: hotels were being built in the side valleys (Zermatt, Arolla, Lötschental, etc.). This was the "golden age of mountaineering", with Englishmen such as Leslie Stephen climbing many of the canton's peaks for the first time, including the Bietschhorn and Zinalrothorn. The arrival of railways in the 19th century (the Tonkin Railway and, above all, the Simplon Railway) changed the linguistic balance of the canton. German lost ground to French, and the towns of Sion and Sierre became French-speaking once again. The metre-gauge Visp-Zermatt line was inaugurated in 1891, before being extended to Brig in 1930. The country's industrialization progressed: the chemical industry made its appearance with the opening of the Ciba plant in Monthey in 1904, and the beginnings of aluminum metallurgy took place in Chippis in 1908. In 1907, a new cantonal constitution came into force.  In 1910, Géo Chavez became the first aviator to cross the Alps by air, flying from Brig to Domodossola over the Simplon Pass, but dying just a few metres from his landing point. In 1913, a Brig-Berne line was inaugurated, via the Lötschberg tunnel.  In 1916, the Brig - Gletsch railway line was inaugurated, via the 1.8 km Furka summit tunnel; in 1926, it was extended to Disentis. In 1982, the 15.4 km Furka base tunnel was inaugurated, enabling accompanied combined transport of cars.[91] On January 25, 1920, the constitution was revised by the introduction of proportional representation to ensure fairer party representation in the Grand Council, replacing the majority system that had always been in force. During World War II, the Valais became a strategic location within the reduced national territory, particularly under Italian pressure in the south and German troops at Le Bouveret. The 1946 earthquake particularly affected the Valais region. The second half of the 19th century saw the development of tourism, and by 1950 numerous resorts had become an important part of the regional economy. Valais' entry into modernity was also marked by the damming of the Rhône, the first phase of which took place between 1863 and 1876. The decision had been taken in the wake of the terrible floods of 1860 and their consequences for the nascent rail traffic. A second correction took place between 1930 and 1960, and a third is scheduled for completion between 2008 and 2030. The 20th century also saw the development of hydroelectricity. The Grande-Dixence Dam was inaugurated in 1961, replacing an older structure dating from 1930. Numerous other dams were built at the same time. On April 12, 1970, Valais became the seventh Swiss canton to grant women the right to vote and stand for election at cantonal level, almost a year before women were granted this right at federal level. After several unsuccessful attempts, including that of Gabrielle Nanchen, elected in terms of votes cast but not elected because a better-placed candidate came from the same district, Esther Waeber Kalbermatten became the first woman to be elected to the cantonal government in 2009. On March 11, 2007, the canton's constitution was amended once again, transferring the power to grant citizenship from the commune bourgeoisiale to the commune municipale. In 2016, a committee launched a campaign to collect signatures for a cantonal popular initiative aimed at completely revising the canton's constitution. Submitted on July 27,[92] the initiative was put to a popular vote on March 4, 2018. Citizens were asked to vote on the total revision of the Constitution, and whether this should be carried out by the Grand Council or a Constituent Assembly, elected specifically for this purpose. Despite opposition from the PDC,[93] both the initiative and the Constituent Assembly were approved by the people, triggering elections for the end of the year.[94] The new Constituent Assembly was sworn in on December 17, 2018. References
AppendixRelated articles
External links
Bibliography
|