Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
HIST1H3B Available structures PDB Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB List of PDB id codes 3WKJ , 3B95 , 2C1J , 3AYW , 3WA9 , 3U4S , 5AVB , 2CV5 , 5AV5 , 3U31 , 2UXN , 3AZK , 2C1N , 5C11 , 3QO2 , 3X1V , 5C13 , 4A0J , 4U68 , 5AV8 , 4LLB , 3U5O , 1O9S , 4FT2 , 4HON , 3W99 , 3ZVY , 4Z0R , 5AVC , 1CT6 , 1Q3L , 3O37 , 3W97 , 3SOW , 3KMT , 4YM6 , 4A7J , 3UEE , 2KWK , 4F4U , 3UEF , 3UIG , 4BD3 , 3AZL , 4QBR , 4F56 , 3AFA , 4LKA , 5CPK , 5FFV , 3V43 , 5CH1 , 3U5P , 3AZI , 3U5N , 3AZH , 3UIK , 4QBQ , 1U35 , 4UY4 , 2OT7 , 5AV9 , 2B2W , 3U3D , 3AZF , 3W98 , 4I51 , 4X3K , 4FWF , 2B2T , 2B2V , 4A0N , 2KWJ , 3WAA , 3QJ6 , 5DAH , 3AZG , 3AZE , 3X1T , 3RIY , 2L75 , 3A1B , 2VPG , 4QBS , 3O35 , 5CPJ , 3ZG6 , 4YM5 , 3AZJ , 2RI7 , 3AZN , 3AVR , 5CPI , 2LBM , 3W96 , 3O34 , 2M0O , 4L7X , 5CH2 , 5AV6 , 3AZM , 4UP0 , 3X1S , 2OX0 , 3UII , 3SOU , 4N4H , 4TN7 , 1CS9 , 3X1U , 4LXL , 2B2U , 2OQ6 , 3RIG , 5C3I , 4YHP , 5B24 , 5D6Y , 4YHZ , 4Z2M , 5HJD , 5HJC , 5HJB , 5B2I , 5HYN , 5FB0 , 5FB1 , 5IQL , 5B2J , 5JIN
Identifiers Aliases H3C2 External IDs OMIM : 602819 ; MGI : 2448351 ; HomoloGene : 136775 ; GeneCards : H3C2 ; OMA :H3C2 - orthologs Wikidata
Histone H3.1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the H3C2 gene .[ 5] [ 6] [ 7]
Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. This structure consists of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a nucleosome, an octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H3 family. Transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails; instead, they contain a palindromic termination element. This gene is found in the large histone gene cluster on chromosome 6p22-p21.3.[ 8]
References
^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000274267 – Ensembl , May 2017^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000074403 – Ensembl , May 2017^ "Human PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ Zhong R, Roeder RG, Heintz N (Jan 1984). "The primary structure and expression of four cloned human histone genes" . Nucleic Acids Res . 11 (21): 7409– 25. doi :10.1093/nar/11.21.7409 . PMC 326492 PMID 6647026 . ^ Albig W, Kioschis P, Poustka A, Meergans K, Doenecke D (Apr 1997). "Human histone gene organization: nonregular arrangement within a large cluster". Genomics . 40 (2): 314– 22. doi :10.1006/geno.1996.4592 . PMID 9119399 . ^ Marzluff WF, Gongidi P, Woods KR, Jin J, Maltais LJ (Oct 2002). "The human and mouse replication-dependent histone genes". Genomics . 80 (5): 487– 98. doi :10.1016/S0888-7543(02)96850-3 . PMID 12408966 . ^ "Entrez Gene: HIST1H3B histone cluster 1, H3b" .
Further reading
Albig W, Kardalinou E, Drabent B, Zimmer A, Doenecke D (1991). "Isolation and characterization of two human H1 histone genes within clusters of core histone genes". Genomics . 10 (4): 940– 8. doi :10.1016/0888-7543(91)90183-F . PMID 1916825 . Marashi F, Helms S, Shiels A, Silverstein S, Greenspan DS, Stein G, Stein J (1986). "Enhancer-facilitated expression of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes using human histone gene 5' regulatory sequences". Biochem. Cell Biol . 64 (4): 277– 89. doi :10.1139/o86-039 . PMID 3013246 . Ohe Y, Iwai K (1982). "Human spleen histone H3. Isolation and amino acid sequence". J. Biochem . 90 (4): 1205– 11. doi :10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133573 . PMID 7309716 . Kardalinou E, Eick S, Albig W, Doenecke D (1993). "Association of a human H1 histone gene with an H2A pseudogene and genes encoding H2B.1 and H3.1 histones". J. Cell. Biochem . 52 (4): 375– 83. doi :10.1002/jcb.240520402 . PMID 8227173 . S2CID 42454232 . Albig W, Meergans T, Doenecke D (1997). "Characterization of the H1.5 gene completes the set of human H1 subtype genes". Gene . 184 (2): 141– 8. doi :10.1016/S0378-1119(96)00582-3 . PMID 9031620 . Albig W, Doenecke D (1998). "The human histone gene cluster at the D6S105 locus". Hum. Genet . 101 (3): 284– 94. doi :10.1007/s004390050630 . PMID 9439656 . S2CID 38539096 . El Kharroubi A, Piras G, Zensen R, Martin MA (1998). "Transcriptional Activation of the Integrated Chromatin-Associated Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Promoter" . Mol. Cell. Biol . 18 (5): 2535– 44. doi :10.1128/mcb.18.5.2535 . PMC 110633 PMID 9566873 . Goto H, Tomono Y, Ajiro K, Kosako H, Fujita M, Sakurai M, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Okigaki T (1999). "Identification of a novel phosphorylation site on histone H3 coupled with mitotic chromosome condensation" . J. Biol. Chem . 274 (36): 25543– 25549. doi :10.1074/jbc.274.36.25543 PMID 10464286 . Hsu JY, Sun ZW, Li X, Reuben M, Tatchell K, Bishop DK, Grushcow JM, Brame CJ, Caldwell JA (2000). "Mitotic phosphorylation of histone H3 is governed by Ipl1/aurora kinase and Glc7/PP1 phosphatase in budding yeast and nematodes" . Cell . 102 (3): 279– 91. doi :10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00034-9 PMID 10975519 . S2CID 16057773 . Deng L, de la Fuente C, Fu P, Wang L, Donnelly R, Wade JD, Lambert P, Li H, Lee CG (2001). "Acetylation of HIV-1 Tat by CBP/P300 increases transcription of integrated HIV-1 genome and enhances binding to core histones" . Virology . 277 (2): 278– 295. doi :10.1006/viro.2000.0593 PMID 11080476 . S2CID 20145752 . Lachner M, O'Carroll D, Rea S, Mechtler K, Jenuwein T (2001). "Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins". Nature . 410 (6824): 116– 20. Bibcode :2001Natur.410..116L . doi :10.1038/35065132 . PMID 11242053 . S2CID 4331863 . Deng L, Wang D, de la Fuente C, Wang L, Li H, Lee CG, Donnelly R, Wade JD, Lambert P (2001). "Enhancement of the p300 HAT activity by HIV-1 Tat on chromatin DNA" . Virology . 289 (2): 312– 26. doi :10.1006/viro.2001.1129 PMID 11689053 . Yang L, Xia L, Wu DY, Wang H, Chansky HA, Schubach WH, Hickstein DD, Zhang Y (2002). "Molecular cloning of ESET, a novel histone H3-specific methyltransferase that interacts with ERG transcription factor". Oncogene . 21 (1): 148– 52. doi :10.1038/sj.onc.1204998 . PMID 11791185 . S2CID 10912876 . Goto H, Yasui Y, Nigg EA, Inagaki M (2002). "Aurora-B phosphorylates Histone H3 at serine28 with regard to the mitotic chromosome condensation". Genes Cells . 7 (1): 11– 7. doi :10.1046/j.1356-9597.2001.00498.x . PMID 11856369 . S2CID 23717416 . Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, Derge JG, Klausner RD, Collins FS, Wagner L, Shenmen CM, Schuler GD (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences" . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A . 99 (26): 16899– 903. Bibcode :2002PNAS...9916899M . doi :10.1073/pnas.242603899 PMC 139241 PMID 12477932 . Preuss U, Landsberg G, Scheidtmann KH (2003). "Novel mitosis-specific phosphorylation of histone H3 at Thr11 mediated by Dlk/ZIP kinase" . Nucleic Acids Res . 31 (3): 878– 85. doi :10.1093/nar/gkg176 . PMC 149197 PMID 12560483 . Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, Edwards CA, Ashurst JL, Wilming L, Jones MC, Horton R, Hunt SE (2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6" . Nature . 425 (6960): 805– 811. Bibcode :2003Natur.425..805M . doi :10.1038/nature02055 PMID 14574404 .
External links
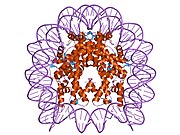
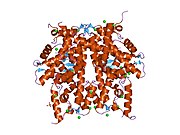
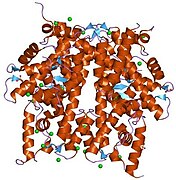
PDB gallery
1aoi : COMPLEX BETWEEN NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE (H3,H4,H2A,H2B) AND 146 BP LONG DNA FRAGMENT
1eqz : X-RAY STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE AT 2.5 A RESOLUTION
1f66 : 2.6 A CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE CONTAINING THE VARIANT HISTONE H2A.Z
1hq3 : CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HISTONE-CORE-OCTAMER IN KCL/PHOSPHATE
1kx3 : X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP146, at 2.0 A Resolution
1kx4 : X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP146b, at 2.6 A Resolution
1kx5 : X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP147, at 1.9 A Resolution
1m18 : LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA
1m19 : LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA
1m1a : LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA
1p34 : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3a : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3b : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3f : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3g : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3i : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3k : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3l : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3m : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3o : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1p3p : Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants
1s32 : Molecular Recognition of the Nucleosomal 'Supergroove'
1tzy : Crystal Structure of the Core-Histone Octamer to 1.90 Angstrom Resolution
1u35 : Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle containing the histone domain of macroH2A
1zbb : Structure of the 4_601_167 Tetranucleosome
1zla : X-ray Structure of a Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus LANA peptide bound to the nucleosomal core
2aro : Crystal Structure Of The Native Histone Octamer To 2.1 Angstrom Resolution, Crystalised In The Presence Of S-Nitrosoglutathione
2cv5 : Crystal structure of human nucleosome core particle
2f8n : 2.9 Angstrom X-ray structure of hybrid macroH2A nucleosomes
2fj7 : Crystal structure of Nucleosome Core Particle Containing a Poly (dA.dT) Sequence Element
2hio : HISTONE OCTAMER (CHICKEN), CHROMOSOMAL PROTEIN
2hue : Structure of the H3-H4 chaperone Asf1 bound to histones H3 and H4
2io5 : Crystal structure of the CIA- histone H3-H4 complex
2nzd : Nucleosome core particle containing 145 bp of DNA