|
Glycosuria
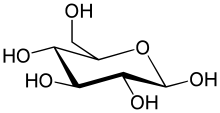
Glycosuria is the excretion of glucose into the urine. Ordinarily, urine contains no glucose because the kidneys are able to reabsorb all of the filtered glucose from the tubular fluid back into the bloodstream. Glycosuria is nearly always caused by an elevated blood sugar level, most commonly due to untreated diabetes. Rarely, glycosuria is due to an intrinsic problem with glucose reabsorption within the kidneys (such as Fanconi syndrome), producing a condition termed renal glycosuria.[1] Glycosuria leads to excessive water loss into the urine with resultant dehydration, a process called osmotic diuresis. Alimentary glycosuria is a temporary condition, when a high amount of carbohydrate is taken, it is rapidly absorbed in some cases where a part of the stomach is surgically removed, the excessive glucose appears in urine producing glycosuria. Additionally, SGLT2 inhibitor medications ("gliflozins" or "flozins") produce glycosuria as their primary mechanism of action, by inhibiting sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 in the kidneys and thereby interfering with renal glucose reabsorption. Follow-upIn a patient with glucosuria, diabetes is confirmed by measuring fasting or random plasma glucose and glycated hemoglobin(HbA1c).[2] PathophysiologyBlood is filtered by millions of nephrons, the functional units that comprise the kidneys. In each nephron, blood flows from the arteriole into the glomerulus, a tuft of leaky capillaries. The Bowman's capsule surrounds each glomerulus, and collects the filtrate that the glomerulus forms. The filtrate contains waste products (e.g. urea), electrolytes (e.g. sodium, potassium, chloride), amino acids, and glucose. The filtrate passes into the renal tubules of the kidney. In the first part of the renal tubule, the proximal tubule, glucose is reabsorbed from the filtrate, across the tubular epithelium and into the bloodstream. The proximal tubule can only reabsorb a limited amount of glucose (~375 mg/min[3]), known as the transport maximum. When the blood glucose level exceeds about 160–180 mg/dL (8.9-10 mmol/L), the proximal tubule becomes overwhelmed and begins to excrete glucose in the urine.
This point is called the renal threshold for glucose (RTG).[5] Some people, especially children and pregnant women, may have a low RTG (less than ~7 mmol/L[5] glucose in blood to have glucosuria). If the RTG is so low that even normal blood glucose levels produce the condition, it is referred to as renal glycosuria. Glucose in urine can be identified by Benedict's qualitative test. If yeast is present in the bladder, the sugar in the urine may begin to ferment, producing a rare condition known as urinary auto-brewery syndrome. References
External links |
||||||||||||||||||||||||