Glutamate-sensitive fluorescent reporter A genetically engineered fluorescent protein that changes its fluorescence when bound to the neurotransmitter glutamate .[ 1] glue sniffer ') are used to monitor the activity of presynaptic terminals by fluorescence microscopy . GluSnFRs are a class of optogenetic sensors used in neuroscience research.[ 2] two-photon microscopy is typically used to monitor GluSnFR fluorescence.
Design
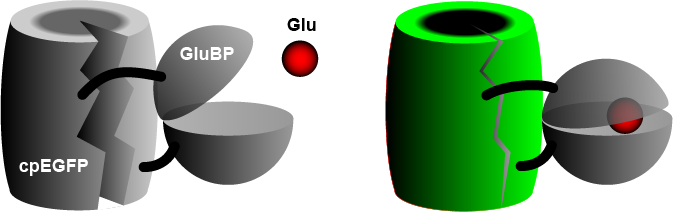
The widely used iGluSnFR consists of a circularly permuted enhanced green fluorescent protein (cpEGFP) fused to a glutamate binding protein (GluBP) from a bacterium .[ 3] glutamate molecule, it changes its shape, pulling the EGFP barrel together, increasing fluorescence. A specific peptide segment (PDGFR ) is included to bring the sensor to the outside of the cell membrane .[ 4] et al. (2022),[ 1]
History
The first genetically encoded fluorescent glutamate sensors (FLIPE, GluSnFR and SuperGluSnFR) were constructed by attaching cyan-fluorescent protein (CFP) and yellow-fluorescent protein (YFP) to a bacterial glutamate binding protein (GluBP).[ 5] [ 6] Glutamate binding changed the distance between CFP and YFP, changing the efficiency of energy transfer (FRET ) between the two fluorophores .[ 7] [ 8] EGFP producing a ~5‑fold increase in fluorescence.[ 3] [ 9] [ 10]
References
^ a b Aggarwal, Abhi; Liu, Rui; Chen, Yang; Ralowicz, Amelia J.; Bergerson, Samuel J.; Tomaska, Filip; Hanson, Timothy L.; Hasseman, Jeremy P.; Reep, Daniel; Tsegaye, Getahun; Yao, Pantong; Ji, Xiang; Kloos, Marinus; Walpita, Deepika; Patel, Ronak (2022-02-15). "Glutamate indicators with improved activation kinetics and localization for imaging synaptic transmission" : 2022.02.13.480251. doi :10.1101/2022.02.13.480251 . hdl :20.500.11850/613938 ^ Hefendehl, J. K.; LeDue, J.; Ko, R. W. Y.; Mahler, J.; Murphy, T. H.; MacVicar, B. A. (2016-11-11). "Mapping synaptic glutamate transporter dysfunction in vivo to regions surrounding Aβ plaques by iGluSnFR two-photon imaging" . Nature Communications . 7 : 13441. Bibcode :2016NatCo...713441H . doi :10.1038/ncomms13441 . PMC 5114608 PMID 27834383 . ^ a b Marvin, Jonathan S; Borghuis, Bart G; Tian, Lin; Cichon, Joseph; Harnett, Mark T; Akerboom, Jasper; Gordus, Andrew; Renninger, Sabine L; Chen, Tsai-Wen (2013). "An optimized fluorescent probe for visualizing glutamate neurotransmission" . Nature Methods . 10 (2): 162– 170. doi :10.1038/nmeth.2333 . ISSN 1548-7105 . PMC 4469972 PMID 23314171 . ^ Marvin, Jonathan S.; Schreiter, Eric R.; Echevarría, Ileabett M.; Looger, Loren L. (2011-11-01). "A genetically encoded, high-signal-to-noise maltose sensor" . Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics . 79 (11): 3025– 3036. doi :10.1002/prot.23118 . ISSN 1097-0134 . PMC 3265398 PMID 21989929 . ^ Hu, Yonglin; Fan, Cheng-Peng; Fu, Guangsen; Zhu, Deyu; Jin, Qi; Wang, Da-Cheng (2008). "Crystal Structure of a Glutamate/Aspartate Binding Protein Complexed with a Glutamate Molecule: Structural Basis of Ligand Specificity at Atomic Resolution". Journal of Molecular Biology . 382 (1): 99– 111. doi :10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.091 . PMID 18640128 . ^ De Lorimier, Robert M.; Smith, J. Jeff; Dwyer, Mary A.; Looger, Loren L.; Sali, Kevin M.; Paavola, Chad D.; Rizk, Shahir S.; Sadigov, Shamil; Conrad, David W. (2002-11-01). "Construction of a fluorescent biosensor family" . Protein Science . 11 (11): 2655– 2675. doi :10.1110/ps.021860 . ISSN 1469-896X . PMC 2373719 PMID 12381848 . ^ Okumoto, Sakiko; Looger, Loren L.; Micheva, Kristina D.; Reimer, Richard J.; Smith, Stephen J.; Frommer, Wolf B. (2005-06-14). "Detection of glutamate release from neurons by genetically encoded surface-displayed FRET nanosensors" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 102 (24): 8740– 8745. Bibcode :2005PNAS..102.8740O . doi :10.1073/pnas.0503274102 ISSN 0027-8424 . PMC 1143584 PMID 15939876 . ^ Hires, Samuel Andrew; Zhu, Yongling; Tsien, Roger Y. (2008-03-18). "Optical measurement of synaptic glutamate spillover and reuptake by linker optimized glutamate-sensitive fluorescent reporters" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . 105 (11): 4411– 4416. Bibcode :2008PNAS..105.4411H . doi :10.1073/pnas.0712008105 ISSN 0027-8424 . PMC 2393813 PMID 18332427 . ^ Helassa, Nordine; Dürst, Céline D.; Coates, Catherine; Kerruth, Silke; Arif, Urwa; Schulze, Christian; Wiegert, J. Simon; Geeves, Michael; Oertner, Thomas G.; Török, Katalin (2018-05-22). "Ultrafast glutamate sensors resolve high-frequency release at Schaffer collateral synapses" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . 115 (21): 5594– 5599. doi :10.1073/pnas.1720648115 PMC 6003469 PMID 29735711 . ^ Marvin, Jonathan S.; Scholl, Benjamin; Wilson, Daniel E.; Podgorski, Kaspar; Kazemipour, Abbas; Müller, Johannes Alexander; Schoch, Susanne; Quiroz, Francisco José Urra; Rebola, Nelson; Bao, Huan; Little, Justin P. (November 2018). "Stability, affinity, and chromatic variants of the glutamate sensor iGluSnFR" . Nature Methods . 15 (11): 936– 939. doi :10.1038/s41592-018-0171-3 . ISSN 1548-7105 . PMC 6394230 PMID 30377363 .
Optogenetic actuators Optogenetic sensors Related techniques