|
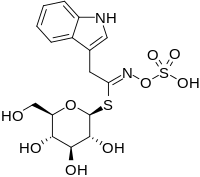
Glucobrassicin
Glucobrassicin is a type of glucosinolate that can be found in almost all cruciferous plants, such as cabbages, broccoli, mustards, and woad. As for other glucosinolates, degradation by the enzyme myrosinase is expected to produce an isothiocyanate, indol-3-ylmethylisothiocyanate. However, this specific isothiocyanate is expected to be highly unstable, and has indeed never been detected. The observed hydrolysis products when isolated glucobrassicin is degraded by myrosinase are indole-3-carbinol and thiocyanate ion (plus glucose, sulfate, and hydrogen ion), which are envisioned to result from a rapid reaction of the unstable isothiocyanate with water. However, a large number of other reaction products are known, and indole-3-carbinol is not the dominant degradation product when glucosinolate degradation takes place in crushed plant tissue[1] or in intact plants.[2][3] Glucobrassicin is also known to be a highly active egg-laying stimulant of cabbage white butterflies such as the small white (Pieris rapae) and the large white (Pieris brassicae). Several derivatives of glucobrassicin are known. The compound itself was first isolated from Brassica plants, hence the ending of the name. When a second, similar natural product was discovered, it was named neoglucobrassicin. When further derivatives were discovered, a more systematic nomenclature was used. Currently, the following six derivatives are known from plants:
The three first mentioned derivatives are as frequent in crucifers as glucobrassicin itself. The additional three derivatives appear to be rare in nature. 4-methoxyglucobrassicin was recently reported to be a signal molecule involved in plant defence against bacteria and fungi.[2][3] Biosynthesis from tryptophanThe biosynthesis of glucobrassicin begins with tryptophan produced through several steps from the shikimic acid pathway compound, chorismic acid.[4] Tryptophan is converted to indole-3-acetaldoxime (IAOx) by cytochrome p450 enzymes (the redundant CYP92B3 and CYP79B3 in Arabidopsis thaliana) using NADPH and molecular Oxygen.[5] A separate p450 enzyme (CYP83B1 in Arabidopsis) catalyzes a second subsequent monooxygenase reaction to create a proposed the intermediate 1-aci-nitro-2-indolyl-ethane.[5] A cysteine is utilized by glutathione S-transferase (GST) in a conjugation process to produce an S-alkylthiohydroximate derivative, which is then cleaved off by a carbon–sulfur lyase (like the SUR1 enzyme found in Arabidopsis) to create a free thiol.[6] A single glucosylation occurs attaching a glucose molecule to the indole hydroximate through a thioether linkage. Finally, the hydroximate itself is sulfated creating glucobrassicin.[5]  See alsoReferences
Further reading
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||