|
Geosiphon
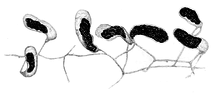
Geosiphon is a genus of fungus in the family Geosiphonaceae. The genus is monotypic, containing the single species Geosiphon pyriformis, first described by Kützing in 1849 as Botrydium pyriforme.[1] In 1915, Von Wettstein characterized Geosiphon pyriforme as a multinucleate alga containing endosymbiotic cyanobacteria, although he also noted the presence of chitin, a component of fungal cell walls.[2] In 1933, Knapp was the first to suggest the fungal origin of the species and described it as a lichen with endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.[3] It is the only member of the Glomeromycota known to not form a symbiosis with terrestrial plants in the form of arbuscular mycorrhiza. Life cycleGeosiphon pyriformis is known for being the symbiont of Nostoc. The Geosiphon-Nostoc symbiosis, as by modern definitions, is not a lichen, since it is an intracellular association. Also, by functional and evolutionary implications it is more comparable to the arbuscular mycorrhiza symbioses than to lichens. The Geosiphon-Nostoc symbiosis is the only known fungal endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria and is characterised by a "siphonal bladder" that is made of a swollen fungal hypha, 0.5–2 mm in size and growing on the soil surface. The upper 2/3 of the "bladder" contains the Nostoc filaments and Nostoc heterocysts, the lower 1/3 is filled with lipid droplets.[4] ReproductionThe fungal spores are 250 micrometres in diameter, formed at the end of one hypha, or intercalarly (within a hyphae) and resemble those of other members of the Glomeromycota, with a particular resemblance to spores of others in the polyphyletic genus Glomus. [5] Somatic structure Geosiphon has a specialised bladder used to harbour cyanobacteria, usually Nostoc punctiforme, although other Nostoc species are known to be incorporated by the fungus.[6] Geosiphon bladders are photosynthetically active,[7] and are also capable of fixing nitrogen from the atmosphere.[8] The walls of the bladder have a small pore radius (approximately 0.5 nm), which make it act as an osmotic barrier. This limits the free exchange of nutrients (like sugars) with the environment and increases the need to derive these carbon sources from internal sources.[9] It has been suggested that the organization of the symbiotic interface between the fungus and Nostoc in G. pyriforme is homologous to the symbiotic interface between plant and fungus in arbuscular mycorrhiza in terms of thickness, chitin content, and ultrastructure of layers.[10] G. pyriformis however, is not known to form arbuscular mycorrhiza. The bladder structure may be considered to be equivalent to a symbiosome, a specialized membraned structure in some plants and animals that forms a structural and functional interface between the host and its symbiont counterpart.[11] The symbiosome may be divided into three functional areas:[10]
The space between the symbiosome membrane and the Nostoc cell wall contains a 30–40 nm thick layer of carbohydrate material such as mannose, fucose, GalNAc, sialic acid, and galactose.[10] References
External links |
||||||||||||||||||||||||