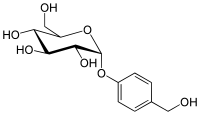
Gastrodin
Chemical structure of gastrodin
Names
IUPAC name
4-(Hydroxymethyl)phenyl β-D -glucopyranoside
Systematic IUPAC name
(2R ,3S ,4S ,5R ,6S )-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-6-[4-(hydroxymethyl)phenoxy]oxane-3,4,5-triol
Other names
GastrodineD -glucopyranosyloxy)benzyl alcohol
Identifiers
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.208.712
UNII
InChI=1S/C13H18O7/c14-5-7-1-3-8(4-2-7)19-13-12(18)11(17)10(16)9(6-15)20-13/h1-4,9-18H,5-6H2/t9-,10-,11+,12-,13-/m1/s1
N Key: PUQSUZTXKPLAPR-UJPOAAIJSA-N
N InChI=1/C13H18O7/c14-5-7-1-3-8(4-2-7)19-13-12(18)11(17)10(16)9(6-15)20-13/h1-4,9-18H,5-6H2/t9-,10-,11+,12-,13-/m1/s1
Key: PUQSUZTXKPLAPR-UJPOAAIJBX
O(c1ccc(cc1)CO)[C@@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)CO
Properties
C 13 H 18 O 7
Molar mass
−1
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
Gastrodin is a chemical compound which is the glucoside of gastrodigenin . It has been isolated from the orchid Gastrodia elata Galeola faberi [ 1] 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde by Datura tatula [ 2]
G. elata is a herb used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat headache, and it is standardized in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia by gastrodin and gastrodigenin content.[ 3] over-the-counter drug to treat neurasthenia , headache , and migraine .[ 4] dietary supplement in other countries.
A Chinese literature review considers it useful for a range of central nervous system disorders, with the evidence coming from mostly Chinese researches.[ 5]
References
^ Li, Y. M.; Zhou, Z. L.; Hong, Y. F. (1993). "Studies on the phenolic derivatives from Galeola faberi Rolfe". Yao Xue Xue Bao = Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica . 28 (10): 766– 71. PMID 8009989 . ^ Gong, J.; Ma, W.; Pu, J.; Xu, S.; Zheng, S.; Xiao, C. (2006). "Production of Gastrodin Through Biotransformation of p-hydroxybenzaldehyde Using Cell Suspension Cultures of Datura tatula L". Chinese Journal of Biotechnology . 22 (5): 800– 804. doi :10.1016/S1872-2075(06)60056-3 . PMID 17037205 . ^ 国家药典委员会 (2015). "天麻 / GASTRODIAE RHIZOMA". 中国药典 ISBN 978-7-5067-7337-9 ^ "Gastrodin Tablets (天麻素片) Monograph" . drugs.dxy.cn .^ Liu, Y; Gao, J; Peng, M; Meng, H; Ma, H; Cai, P; Xu, Y; Zhao, Q; Si, G (2018). "A Review on Central Nervous System Effects of Gastrodin" . Frontiers in Pharmacology . 9 : 24. doi :10.3389/fphar.2018.00024 PMC 5801292 PMID 29456504 .