|
Electrolytic capacitor 
An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel electrolyte covers the surface of this oxide layer, serving as the cathode or negative plate of the capacitor. Because of their very thin dielectric oxide layer and enlarged anode surface, electrolytic capacitors have a much higher capacitance-voltage (CV) product per unit volume than ceramic capacitors or film capacitors, and so can have large capacitance values. There are three families of electrolytic capacitor: aluminium electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors. The large capacitance of electrolytic capacitors makes them particularly suitable for passing or bypassing low-frequency signals, and for storing large amounts of energy. They are widely used for decoupling or noise filtering in power supplies and DC link circuits for variable-frequency drives, for coupling signals between amplifier stages, and storing energy as in a flashlamp. Electrolytic capacitors are polarized components because of their asymmetrical construction and must be operated with a higher potential (i.e., more positive) on the anode than on the cathode at all times. For this reason the polarity is marked on the device housing. Applying a reverse polarity voltage, or a voltage exceeding the maximum rated working voltage of as little as 1 or 1.5 volts, can damage the dielectric causing catastrophic failure of the capacitor itself. Failure of electrolytic capacitors can result in an explosion or fire, potentially causing damage to other components as well as injuries. Bipolar electrolytic capacitors which may be operated with either polarity are also made, using special constructions with two anodes connected in series. A bipolar electrolytic capacitor can be made by connecting two normal electrolytic capacitors in series, anode to anode or cathode to cathode, along with diodes. General informationElectrolytic capacitors family treeAs to the basic construction principles of electrolytic capacitors, there are three different types: aluminium, tantalum, and niobium capacitors. Each of these three capacitor families uses non-solid and solid manganese dioxide or solid polymer electrolytes, so a great spread of different combinations of anode material and solid or non-solid electrolytes is available.  Charge principleLike other conventional capacitors, electrolytic capacitors store the electric energy statically by charge separation in an electric field in the dielectric oxide layer between two electrodes. The non-solid or solid electrolyte in principle is the cathode, which thus forms the second electrode of the capacitor. This and the storage principle distinguish them from electrochemical capacitors or supercapacitors, in which the electrolyte generally is the ionic conductive connection between two electrodes and the storage occurs with statically double-layer capacitance and electrochemical pseudocapacitance. Basic materials and construction Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, previously called "valve metals", which on contact with a particular electrolyte form a very thin insulating oxide layer on their surface by anodic oxidation which can function as a dielectric. There are three different anode metals in use for electrolytic capacitors:
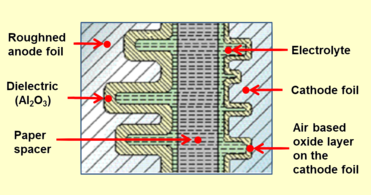
To increase their capacitance per unit volume, all anode materials are either etched or sintered and have a rough surface structure with a much higher surface area compared to a smooth surface of the same area or the same volume. By applying a positive voltage to the above-mentioned anode material in an electrolytic bath an oxide barrier layer with a thickness corresponding to the applied voltage will be formed (formation). This oxide layer acts as the dielectric in an electrolytic capacitor. The properties of these oxide layers are given in the following table:
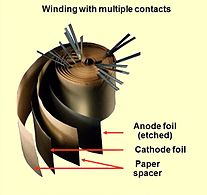
After forming a dielectric oxide on the rough anode structure, a counter electrode has to match the rough insulating oxide surface. This is accomplished by the electrolyte, which acts as the cathode electrode of an electrolytic capacitor. There are many different electrolytes in use. Generally they are distinguished into two species, “non-solid” and “solid” electrolytes. As a liquid medium which has ion conductivity caused by moving ions, non-solid electrolytes can easily fit the rough structures. Solid electrolytes which have electron conductivity can fit the rough structures with the help of special chemical processes like pyrolysis for manganese dioxide or polymerization for conducting polymers. Comparing the permittivities of the different oxide materials it is seen that tantalum pentoxide has a permittivity approximately three times higher than aluminium oxide. Tantalum electrolytic capacitors of a given CV value theoretically are therefore smaller than aluminium electrolytic capacitors. In practice different safety margins to reach reliable components makes a comparison difficult. The anodically generated insulating oxide layer is destroyed if the polarity of the applied voltage changes. Capacitance and volumetric efficiency Electrolytic capacitors are based on the principle of a "plate capacitor" whose capacitance increases with larger electrode area A, higher dielectric permittivity ε, and thinness of dielectric (d). The dielectric thickness of electrolytic capacitors is very small, in the range of nanometers per volt. On the other hand, the voltage strengths of these oxide layers are quite high. With this very thin dielectric oxide layer combined with a sufficiently high dielectric strength the electrolytic capacitors can achieve a high volumetric capacitance. This is one reason for the high capacitance values of electrolytic capacitors compared to conventional capacitors. All etched or sintered anodes have a much higher surface area compared to a smooth surface of the same area or the same volume. That increases the capacitance value, depending on the rated voltage, by a factor of up to 200 for non-solid aluminium electrolytic capacitors as well as for solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors.[5][6][7] The large surface compared to a smooth one is the second reason for the relatively high capacitance values of electrolytic capacitors compared with other capacitor families. Because the forming voltage defines the oxide layer thickness, the desired voltage rating can be produced very simply. Electrolytic capacitors have high volumetric efficiency, the so-called "CV product", defined as the product of capacitance and voltage divided by volume. Basic construction of non-solid aluminium electrolytic capacitors
Basic construction of solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors
Types and features of electrolytic capacitorsComparison of electrolytic capacitor typesCombinations of anode materials for electrolytic capacitors and the electrolytes used have given rise to wide varieties of capacitor types with different properties. An outline of the main characteristics of the different types is shown in the table below.
The non-solid or so-called "wet" aluminium electrolytic capacitors were and are the cheapest among all other conventional capacitors. They not only provide the cheapest solutions for high capacitance or voltage values for decoupling and buffering purposes but are also insensitive to low ohmic charging and discharging as well as to low-energy transients. Non-solid electrolytic capacitors can be found in nearly all areas of electronic devices, with the exception of military applications. Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid electrolyte as surface-mountable chip capacitors are mainly used in electronic devices in which little space is available or a low profile is required. They operate reliably over a wide temperature range without large parameter deviations. In military and space applications only tantalum electrolytic capacitors have the necessary approvals. Niobium electrolytic capacitors are in direct competition with industrial tantalum electrolytic capacitors because niobium is more readily available. Their properties are comparable. The electrical properties of aluminium, tantalum and niobium electrolytic capacitors have been greatly improved by the polymer electrolyte. Comparison of electrical parametersIn order to compare the different characteristics of the different electrolytic capacitor types, capacitors with the same dimensions and of similar capacitance and voltage are compared in the following table. In such a comparison the values for ESR and ripple current load are the most important parameters for the use of electrolytic capacitors in modern electronic equipment. The lower the ESR, the higher the ripple current per volume and better functionality of the capacitor in the circuit. However, better electrical parameters come with higher prices.
1) Manufacturer, series name, capacitance/voltage 2) calculated for a capacitor 100 μF/10 V, 3) from a 1976 data sheet Styles of aluminium and tantalum electrolytic capacitorsAluminium electrolytic capacitors form the bulk of the electrolytic capacitors used in electronics because of the large diversity of sizes and the inexpensive production. Tantalum electrolytic capacitors, usually used in the SMD (surface-mount device) version, have a higher specific capacitance than the aluminium electrolytic capacitors and are used in devices with limited space or flat design such as laptops. They are also used in military technology, mostly in axial style, hermetically sealed. Niobium electrolytic chip capacitors are a new development in the market and are intended as a replacement for tantalum electrolytic chip capacitors.
History 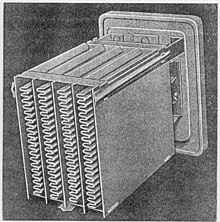 OriginThe phenomenon that in an electrochemical process, aluminium and such metals as tantalum, niobium, manganese, titanium, zinc, cadmium, etc., can form an oxide layer which blocks an electric current from flowing in one direction but which allows current to flow in the opposite direction, was first observed in 1857 by the German physicist and chemist Johann Heinrich Buff (1805–1878).[8] It was first put to use in 1875 by the French researcher and founder Eugène Ducretet,[9] who coined the term "valve metal" for such metals. Charles Pollak (born Karol Pollak), a producer of accumulators, found out that the oxide layer on an aluminium anode remained stable in a neutral or alkaline electrolyte, even when the power was switched off. In 1896, he filed a patent for an "Electric liquid capacitor with aluminium electrodes" (de: Elektrischer Flüssigkeitskondensator mit Aluminiumelektroden) based on his idea of using the oxide layer in a polarized capacitor in combination with a neutral or slightly alkaline electrolyte.[10][11] "Wet" aluminium capacitor The first industrially realized electrolytic capacitors consisted of a metallic box used as the cathode. It was filled with a borax electrolyte dissolved in water, in which a folded aluminium anode plate was inserted. Applying a DC voltage from outside, an oxide layer was formed on the surface of the anode. The advantage of these capacitors was that they were significantly smaller and cheaper than all other capacitors at this time relative to the realized capacitance value. This construction with different styles of anode construction but with a case as cathode and container for the electrolyte was used up to the 1930s and was called a "wet" electrolytic capacitor, in the sense of its having a high water content. The first more common application of wet aluminium electrolytic capacitors was in large telephone exchanges, to reduce relay hash (noise) on the 48 volt DC power supply. The development of AC-operated domestic radio receivers in the late 1920s created a demand for large-capacitance (for the time) and high-voltage capacitors for the valve amplifier technique, typically at least 4 microfarads and rated at around 500 volts DC. Waxed paper and oiled silk film capacitors were available, but devices with that order of capacitance and voltage rating were bulky and prohibitively expensive. "Dry" aluminium capacitor The ancestor of the modern electrolytic capacitor was patented by Samuel Ruben in 1925,[12][13] who teamed with Philip Mallory, the founder of the battery company that is now known as Duracell International. Ruben's idea adopted the stacked construction of a silver mica capacitor. He introduced a separated second foil to contact the electrolyte adjacent to the anode foil instead of using the electrolyte-filled container as the capacitor's cathode. The stacked second foil got its own terminal additional to the anode terminal and the container no longer had an electrical function. This type of electrolytic capacitor combined with a liquid or gel-like electrolyte of a non-aqueous nature, which is therefore dry in the sense of having a very low water content, became known as the "dry" type of electrolytic capacitor.[14] With Ruben's invention, together with the invention of wound foils separated with a paper spacer 1927 by A. Eckel of Hydra-Werke (Germany),[15] the actual development of electrolytic capacitors began.[14] William Dubilier, whose first patent for electrolytic capacitors was filed in 1928,[16] industrialized the new ideas for electrolytic capacitors and started the first large commercial production in 1931 in the Cornell-Dubilier (CD) factory in Plainfield, New Jersey.[14] At the same time in Berlin, Germany, the "Hydra-Werke", an AEG company, started the production of electrolytic capacitors in large quantities. Another manufacturer, Ralph D. Mershon, had success in servicing the radio-market demand for electrolytic capacitors.[17]  In his 1896 patent Pollak already recognized that the capacitance of the capacitor increases when roughening the surface of the anode foil. Today (2014), electrochemically etched low voltage foils can achieve an up to 200-fold increase in surface area compared to a smooth surface.[5][6] Advances in the etching process are the reason for the dimension reductions in aluminium electrolytic capacitors over recent decades. For aluminium electrolytic capacitors the decades from 1970 to 1990 were marked by the development of various new professional series specifically suited to certain industrial applications, for example with very low leakage currents or with long life characteristics, or for higher temperatures up to 125 °C.[18][19] Tantalum capacitorsOne of the first tantalum electrolytic capacitors were developed in 1930 by Tansitor Electronic Inc. USA, for military purposes.[20] The basic construction of a wound cell was adopted and a tantalum anode foil was used together with a tantalum cathode foil, separated with a paper spacer impregnated with a liquid electrolyte, mostly sulfuric acid, and encapsulated in a silver case. The relevant development of solid electrolyte tantalum capacitors began some years after William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Houser Brattain invented the transistor in 1947. It was invented by Bell Laboratories in the early 1950s as a miniaturized, more reliable low-voltage support capacitor to complement their newly invented transistor. The solution found by R. L. Taylor and H. E. Haring at Bell Labs in early 1950 was based on experience with ceramics. They ground tantalum to a powder, which they pressed into a cylindrical form and then sintered at a high temperature between 1500 and 2000 °C under vacuum conditions, to produce a pellet ("slug").[21][22] These first sintered tantalum capacitors used a non-solid electrolyte, which does not fit the concept of solid electronics. In 1952 a targeted search at Bell Labs by D. A. McLean and F. S. Power for a solid electrolyte led to the invention of manganese dioxide as a solid electrolyte for a sintered tantalum capacitor.[23] Although fundamental inventions came from Bell Labs, the inventions for manufacturing commercially viable tantalum electrolytic capacitors came from researchers at the Sprague Electric Company. Preston Robinson, Sprague's Director of Research, is considered to be the actual inventor of tantalum capacitors in 1954.[24][25] His invention was supported by R. J. Millard, who introduced the "reform" step in 1955,[26][27] a significant improvement in which the dielectric of the capacitor was repaired after each dip-and-convert cycle of MnO2 deposition, which dramatically reduced the leakage current of the finished capacitors. Although solid tantalum capacitors offered capacitors with lower ESR and leakage current values than the aluminium electrolytic capacitors, a 1980 price shock for tantalum dramatically reduced the applications of tantalum electrolytic capacitors, especially in the entertainment industry.[28][29] The industry switched back to using aluminium electrolytic capacitors. Solid electrolytes The first solid electrolyte of manganese dioxide developed 1952 for tantalum capacitors had a conductivity 10 times better than all other types of non-solid electrolytes. It also influenced the development of aluminium electrolytic capacitors. In 1964 the first aluminium electrolytic capacitors with solid electrolyte SAL electrolytic capacitor came on the market, developed by Philips.[30] With the beginning of digitalization, Intel launched its first microcomputer, the MCS 4, in 1971. In 1972 Hewlett Packard launched one of the first pocket calculators, the HP 35.[31][32] The requirements for capacitors increased in terms of lowering the equivalent series resistance (ESR) for bypass and decoupling capacitors.[33] It was not until 1983 when a new step toward ESR reduction was taken by Sanyo with its "OS-CON" aluminium electrolytic capacitors. These capacitors used a solid organic conductor, the charge transfer salt TTF-TCNQ (tetracyanoquinodimethane), which provided an improvement in conductivity by a factor of 10 compared with the manganese dioxide electrolyte.[34] [35][36] The next step in ESR reduction was the development of conducting polymers by Alan J. Heeger, Alan MacDiarmid and Hideki Shirakawa in 1975.[37] The conductivity of conductive polymers such as polypyrrole (PPy) [38] or PEDOT[39] is better than that of TCNQ by a factor of 100 to 500, and close to the conductivity of metals. In 1991 Panasonic released its "SP-Cap",[40] series of polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitors. These aluminium electrolytic capacitors with polymer electrolytes reached very low ESR values directly comparable to ceramic multilayer capacitors (MLCCs). They were still less expensive than tantalum capacitors and with their flat design for laptops and cell phones competed with tantalum chip capacitors as well. Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with PPy polymer electrolyte cathode followed three years later. In 1993 NEC introduced its SMD polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitors, called "NeoCap". In 1997 Sanyo followed with the "POSCAP" polymer tantalum chips. A new conductive polymer for tantalum polymer capacitors was presented by Kemet at the "1999 Carts" conference.[41] This capacitor used the newly developed organic conductive polymer PEDT Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), also known as PEDOT (trade name Baytron®) [42] Niobium capacitorsAnother price explosion for tantalum in 2000/2001 forced the development of niobium electrolytic capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte, which have been available since 2002.[43][44] Niobium is a sister metal to tantalum and serves as valve metal generating an oxide layer during anodic oxidation. Niobium as raw material is much more abundant in nature than tantalum and is less expensive. It was a question of the availability of the base metal in the late 1960s which led to development and implementation of niobium electrolytic capacitors in the former Soviet Union instead of tantalum capacitors as in the West. The materials and processes used to produce niobium-dielectric capacitors are essentially the same as for existing tantalum-dielectric capacitors. The characteristics of niobium electrolytic capacitors and tantalum electrolytic capacitors are roughly comparable.[45] Water-based electrolytesWith the goal of reducing ESR for inexpensive non-solid electrolytic capacitors from the mid-1980s in Japan, new water-based electrolytes for aluminium electrolytic capacitors were developed. Water is inexpensive, an effective solvent for electrolytes, and significantly improves the conductivity of the electrolyte. The Japanese manufacturer Rubycon was a leader in the development of new water-based electrolyte systems with enhanced conductivity in the late 1990s.[46] The new series of non-solid electrolytic capacitors with water-based electrolyte was described in the data sheets as having "low ESR", "low impedance", "ultra-low impedance" or "high ripple current". From 1999 through at least 2010, a stolen recipe for such a water-based electrolyte, in which important stabilizers[47][48] were absent,[49] led to the widespread problem of "bad caps" (failing electrolytic capacitors), leaking or occasionally bursting in computers, power supplies, and other electronic equipment, which became known as the "capacitor plague". In these electrolytic capacitors the water reacts quite aggressively with aluminium, accompanied by strong heat and gas development in the capacitor, resulting in premature equipment failure, and development of a cottage repair industry. Electrical characteristicsSeries-equivalent circuit The electrical characteristics of capacitors are harmonized by the international generic specification IEC 60384-1. In this standard, the electrical characteristics of capacitors are described by an idealized series-equivalent circuit with electrical components which model all ohmic losses, capacitive and inductive parameters of an electrolytic capacitor:
Capacitance, standard values and tolerances  The electrical characteristics of electrolytic capacitors depend on the structure of the anode and the electrolyte used. This influences the capacitance value of electrolytic capacitors, which depends on measuring frequency and temperature. Electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolytes show a broader aberration over frequency and temperature ranges than do capacitors with solid electrolytes. The basic unit of an electrolytic capacitor's capacitance is the microfarad (μF). The capacitance value specified in the data sheets of the manufacturers is called the rated capacitance CR or nominal capacitance CN and is the value for which the capacitor has been designed. The standardized measuring condition for electrolytic capacitors is an AC measuring method with 0.5 V at a frequency of 100/120 Hz at a temperature of 20 °C. For tantalum capacitors a DC bias voltage of 1.1 to 1.5 V for types with a rated voltage ≤2.5 V, or 2.1 to 2.5 V for types with a rated voltage of >2.5 V, may be applied during the measurement to avoid reverse voltage. The capacitance value measured at the frequency of 1 kHz is about 10% less than the 100/120 Hz value. Therefore, the capacitance values of electrolytic capacitors are not directly comparable and differ from those of film capacitors or ceramic capacitors, whose capacitance is measured at 1 kHz or higher. Measured with an AC measuring method at 100/120 Hz the capacitance value is the closest value to the electrical charge stored in the e-caps. The stored charge is measured with a special discharge method and is called the DC capacitance. The DC capacitance is about 10% higher than the 100/120 Hz AC capacitance. The DC capacitance is of interest for discharge applications like photoflash. The percentage of allowed deviation of the measured capacitance from the rated value is called the capacitance tolerance. Electrolytic capacitors are available in different tolerance series, whose values are specified in the E series specified in IEC 60063. For abbreviated marking in tight spaces, a letter code for each tolerance is specified in IEC 60062.
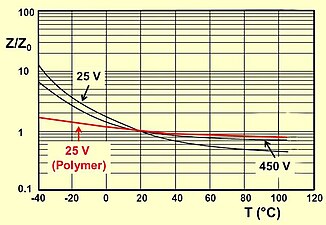
The required capacitance tolerance is determined by the particular application. Electrolytic capacitors, which are often used for filtering and bypassing, do not have the need for narrow tolerances because they are mostly not used for accurate frequency applications like in oscillators. Rated and category voltage Referring to the IEC/EN 60384-1 standard, the allowed operating voltage for electrolytic capacitors is called the "rated voltage UR" or "nominal voltage UN". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR. The voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specifies a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture at right. Applying a higher voltage than specified may destroy electrolytic capacitors. Applying a lower voltage may have a positive influence on electrolytic capacitors. For aluminium electrolytic capacitors a lower applied voltage can in some cases extend the lifetime.[5] For tantalum electrolytic capacitors lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.[50] I Surge voltageThe surge voltage indicates the maximum peak voltage value that may be applied to electrolytic capacitors during their application for a limited number of cycles.[5] The surge voltage is standardized in IEC/EN 60384-1. For aluminium electrolytic capacitors with a rated voltage of up to 315 V, the surge voltage is 1.15 times the rated voltage, and for capacitors with a rated voltage exceeding 315 V, the surge voltage is 1.10 times the rated voltage. For tantalum electrolytic capacitors the surge voltage can be 1.3 times the rated voltage, rounded off to the nearest volt. The surge voltage applied to tantalum capacitors may influence the capacitor's failure rate.[51][52] Transient voltagealuminium electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolyte are relatively insensitive to high and short-term transient voltages higher than surge voltage, if the frequency and the energy content of the transients are low. This ability depends on rated voltage and component size. Low energy transient voltages lead to a voltage limitation similar to a zener diode.[53] An unambiguous and general specification of tolerable transients or peak voltages is not possible. In every case transients arise, the application has to be approved very carefully. Electrolytic capacitors with solid manganese oxide or polymer electrolyte, and aluminium as well as tantalum electrolytic capacitors cannot withstand transients or peak voltages higher than the surge voltage. Transients may destroy this type of electrolytic capacitor.[51][52] Reverse voltage  Standard electrolytic capacitors, and aluminium as well as tantalum and niobium electrolytic capacitors are polarized and generally require the anode electrode voltage to be positive relative to the cathode voltage. Nevertheless, electrolytic capacitors can withstand for short instants a reverse voltage for a limited number of cycles. Specifically, aluminium electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolyte can withstand a reverse voltage of about 1 V to 1.5 V. This reverse voltage should never be used to determine the maximum reverse voltage under which a capacitor can be used permanently.[54][55][56] Solid tantalum capacitors can also withstand reverse voltages for short periods. The most common guidelines for tantalum reverse voltage are:
These guidelines apply for short excursion and should never be used to determine the maximum reverse voltage under which a capacitor can be used permanently.[57][58] But in no case, for aluminium as well as for tantalum and niobium electrolytic capacitors, may a reverse voltage be used for a permanent AC application. To minimize the likelihood of a polarized electrolytic being incorrectly inserted into a circuit, polarity has to be very clearly indicated on the case, see the section on polarity marking below. Special bipolar aluminium electrolytic capacitors designed for bipolar operation are available, and usually referred to as "non-polarized" or "bipolar" types. In these, the capacitors have two anode foils with full-thickness oxide layers connected in reverse polarity. On the alternate halves of the AC cycles, one of the oxides on the foil acts as a blocking dielectric, preventing reverse current from damaging the electrolyte of the other one. But these bipolar electrolytic capacitors are not suitable for main AC applications instead of power capacitors with metallized polymer film or paper dielectric. Impedance In general, a capacitor is seen as a storage component for electric energy. But this is only one capacitor application. A capacitor can also act as an AC resistor. aluminium electrolytic capacitors in particular are often used as decoupling capacitors to filter or bypass undesired AC frequencies to ground or for capacitive coupling of audio AC signals. Then the dielectric is used only for blocking DC. For such applications, the impedance (AC resistance) is as important as the capacitance value.  The impedance Z is the vector sum of reactance and resistance; it describes the phase difference and the ratio of amplitudes between sinusoidally varying voltage and sinusoidally varying current at a given frequency. In this sense impedance is a measure of the ability of the capacitor to pass alternating currents and can be used like Ohm's law. In other words, impedance is a frequency-dependent AC resistance and possesses both magnitude and phase at a particular frequency. In data sheets of electrolytic capacitors only the impedance magnitude |Z| is specified, and simply written as "Z". Regarding the IEC/EN 60384-1 standard, the impedance values of electrolytic capacitors are measured and specified at 10 kHz or 100 kHz depending on the capacitance and voltage of the capacitor. Besides measuring, the impedance can be calculated using the idealized components of a capacitor's series-equivalent circuit, including an ideal capacitor C, a resistor ESR, and an inductance ESL. In this case the impedance at the angular frequency ω is given by the geometric (complex) addition of ESR, by a capacitive reactance XC and by an inductive reactance XL (Inductance) . Then Z is given by
In the special case of resonance, in which the both reactive resistances XC and XL have the same value (XC=XL), then the impedance will only be determined by ESR. With frequencies above the resonance frequency, the impedance increases again because of the ESL of the capacitor. The capacitor becomes an inductor. ESR and dissipation factor tan δ
The equivalent series resistance (ESR) summarizes all resistive losses of the capacitor. These are the terminal resistances, the contact resistance of the electrode contact, the line resistance of the electrodes, the electrolyte resistance, and the dielectric losses in the dielectric oxide layer.[59] For electrolytic capacitors, ESR generally decreases with increasing frequency and temperature.[60] ESR influences the superimposed AC ripple after smoothing and may influence the circuit functionality. Within the capacitor, ESR accounts for internal heat generation if a ripple current flows across the capacitor. This internal heat reduces the lifetime of non-solid aluminium electrolytic capacitors and affects the reliability of solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors. For electrolytic capacitors, for historical reasons the dissipation factor tan δ will sometimes be specified in the data sheet instead of the ESR. The dissipation factor is determined by the tangent of the phase angle between the capacitive reactance XC minus the inductive reactance XL and the ESR. If the inductance ESL is small, the dissipation factor can be approximated as: The dissipation factor is used for capacitors with very low losses in frequency-determining circuits where the reciprocal value of the dissipation factor is called the quality factor (Q), which represents a resonator's bandwidth. Ripple current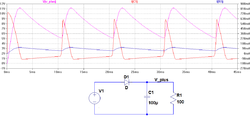 "Ripple current" is the RMS value of a superimposed AC current of any frequency and any waveform of the current curve for continuous operation within the specified temperature range. It arises mainly in power supplies (including switched-mode power supplies) after rectifying an AC voltage and flows as charge and discharge current through any decoupling and smoothing capacitors. Ripple currents generate heat inside the capacitor body. This dissipation power loss PL is caused by ESR and is the squared value of the effective (RMS) ripple current IR. This internally generated heat, additional to the ambient temperature and possibly other external heat sources, leads to a capacitor body temperature having a temperature difference of Δ T relative to ambient. This heat has to be distributed as thermal losses Pth over the capacitor's surface A and the thermal resistance β to ambient. The internally generated heat has to be distributed to ambient by thermal radiation, convection, and thermal conduction. The temperature of the capacitor, which is the net difference between heat produced and heat dissipated, must not exceed the capacitor's maximum specified temperature. The ripple current is specified as an effective (RMS) value at 100 or 120 Hz or at 10 kHz at upper category temperature. Non-sinusoidal ripple currents have to be analyzed and separated into their single sinusoidal frequencies by means of Fourier analysis and summarized by squared addition the single currents.[61] In non-solid electrolytic capacitors the heat generated by the ripple current causes the evaporation of electrolytes, shortening the lifetime of the capacitors.[62][63][64][65][66] Exceeding the limit tends to result in explosive failure. In solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte the heat generated by the ripple current affects the reliability of the capacitors.[67][68][69][70] Exceeding the limit tends to result in catastrophic failure, failing short-circuit, with visible burning. The heat generated by the ripple current also affects the lifetime of aluminium and tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid polymer electrolytes.[71] Exceeding the limit tends to result in catastrophic failure, failing short-circuit. Current surge, peak or pulse currentaluminium electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolytes normally can be charged up to the rated voltage without any current surge, peak or pulse limitation. This property is a result of the limited ion movability in the liquid electrolyte, which slows down the voltage ramp across the dielectric, and of the capacitor's ESR. Only the frequency of peaks integrated over time must not exceed the maximal specified ripple current. Solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte or polymer electrolyte are damaged by peak or pulse currents.[51][52] Solid Tantalum capacitors which are exposed to surge, peak or pulse currents, for example, in highly inductive circuits, should be used with a voltage derating. If possible, the voltage profile should be a ramp turn-on, as this reduces the peak current experienced by the capacitor. Leakage current non solid, high water content non solid, organic solid, polymer For electrolytic capacitors, DC leakage current (DCL) is a special characteristic that other conventional capacitors do not have. This current is represented by the resistor Rleak in parallel with the capacitor in the series-equivalent circuit of electrolytic capacitors. The reasons for leakage current are different between electrolytic capacitors with non-solid and with solid electrolyte or more common for "wet" aluminium and for "solid" tantalum electrolytic capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte as well as for electrolytic capacitors with polymer electrolytes. For non-solid aluminium electrolytic capacitors the leakage current includes all weakened imperfections of the dielectric caused by unwanted chemical processes taking place during the time without applied voltage (storage time) between operating cycles. These unwanted chemical processes depend on the kind of electrolyte. Water-based electrolytes are more aggressive to the aluminium oxide layer than are electrolytes based on organic liquids. This is why different electrolytic capacitor series specify different storage time without reforming.[72] Applying a positive voltage to a "wet" capacitor causes a reforming (self-healing) process which repairs all weakened dielectric layers, and the leakage current remain at a low level.[73] Although the leakage current of non-solid electrolytic capacitors is higher than current flow across the dielectric in ceramic or film capacitors, self-discharge of modern non-solid electrolytic capacitors with organic electrolytes takes several weeks. The main causes of DCL for solid tantalum capacitors include electrical breakdown of the dielectric; conductive paths due to impurities or poor anodization; and bypassing of dielectric due to excess manganese dioxide, to moisture paths, or to cathode conductors (carbon, silver).[74] This "normal" leakage current in solid electrolyte capacitors cannot be reduced by "healing", because under normal conditions solid electrolytes cannot provide oxygen for forming processes. This statement should not be confused with the self-healing process during field crystallization, see below, Reliability (Failure rate). The specification of the leakage current in data sheets is often given as multiplication of the rated capacitance value CR with the value of the rated voltage UR together with an addendum figure, measured after a measuring time of two or five minutes, for example: The leakage current value depends on the voltage applied, on the temperature of the capacitor, and on measuring time. Leakage current in solid MnO2 tantalum electrolytic capacitors generally drops very much faster than for non-solid electrolytic capacitors but remain at the level reached. Dielectric absorption (soakage)Dielectric absorption occurs when a capacitor that has remained charged for a long time discharges only incompletely when briefly discharged. Although an ideal capacitor would reach zero volts after discharge, real capacitors develop a small voltage from time-delayed dipole discharging, a phenomenon that is also called dielectric relaxation, "soakage" or "battery action".
Dielectric absorption may be a problem in circuits where very small currents are used in the function of an electronic circuit, such as long-time-constant integrators or sample-and-hold circuits.[78] In most electrolytic capacitor applications supporting power supply lines, dielectric absorption is not a problem. But especially for electrolytic capacitors with high rated voltage, the voltage at the terminals generated by the dielectric absorption can pose a safety risk to personnel or circuits. In order to prevent shocks, most very large capacitors are shipped with shorting wires that need to be removed before the capacitors are used.[79] Operational characteristicsReliability (failure rate) The reliability of a component is a property that indicates how reliably this component performs its function in a time interval. It is subject to a stochastic process and can be described qualitatively and quantitatively; it is not directly measurable. The reliability of electrolytic capacitors is empirically determined by identifying the failure rate in production accompanying endurance tests, see Reliability engineering. Reliability normally is shown as a bathtub curve and is divided into three areas: early failures or infant mortality failures, constant random failures and wear out failures. Failures totalized in a failure rate are short circuit, open circuit, and degradation failures (exceeding electrical parameters). The reliability prediction is generally expressed in a failure rate λ, abbreviated FIT (Failures In Time). This is the number of failures that can be expected in one billion (109) component-hours of operation (e.g., 1000 components for 1 million hours, or 1 million components for 1000 hours which is 1 ppm/1000 hours) at fixed working conditions during the period of constant random failures. This failure rate model implicitly assumes the idea of "random failure". Individual components fail at random times but at a predictable rate. Billions of tested capacitor unit-hours would be needed to establish failure rates in the very low level range which are required today to ensure the production of large quantities of components without failures. This requires about a million units over a long time period, which means a large staff and considerable financing.[80] The tested failure rates are often complemented with figures resulting from feedback from the field from major customers (field failure rate), which mostly results in a lower failure rate than tested. The reciprocal value of FIT is Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). The standard operating conditions for FIT testing are 40 °C and 0.5 UR. For other conditions of applied voltage, current load, temperature, capacitance value, circuit resistance (for tantalum capacitors), mechanical influences and humidity, the FIT figure can be converted with acceleration factors standardized for industrial[81] or military[82] applications. The higher the temperature and applied voltage, the higher the failure rate, for example. The most often cited source for failure rate conversion is MIL-HDBK-217F, the “bible” of failure rate calculations for electronic components. SQC Online, the online statistical calculator for acceptance sampling and quality control, provides an online tool for short examination to calculate given failure rate values for given application conditions.[83] Some manufacturers may have their own FIT calculation tables for tantalum capacitors.[84][85] or for aluminium capacitors[86] For tantalum capacitors the failure rate is often specified at 85 °C and rated voltage UR as reference conditions and expressed as percent failed components per thousand hours (n %/1000 h). That is, “n” number of failed components per 105 hours, or in FIT the ten-thousand-fold value per 109 hours. Tantalum capacitors are now very reliable components. Continuous improvement in tantalum powder and capacitor technologies have resulted in a significant reduction in the amount of impurities which formerly caused most field crystallization failures. Commercially available industrially produced tantalum capacitors now have reached as standard products the high MIL standard "C" level, which is 0.01%/1000 h at 85 °C and UR or 1 failure per 107 hours at 85 °C and UR.[87] Converted to FIT with the acceleration factors coming from MIL HDKB 217F at 40 °C and 0.5 , UR is the failure rate. For a 100 μF/25 V tantalum chip capacitor used with a series resistance of 0.1 Ω the failure rate is 0.02 FIT. aluminium electrolytic capacitors do not use a specification in "% per 1000 h at 85 °C and UR". They use the FIT specification with 40 °C and 0.5 UR as reference conditions. aluminium electrolytic capacitors are very reliable components. Published figures show for low voltage types (6.3…160 V) FIT rates in the range of 1 to 20 FIT[88] and for high voltage types (>160 …550 V) FIT rates in the range of 20 to 200 FIT.[86] Field failure rates for aluminium e-caps are in the range of 0.5 to 20 FIT.[86][88][89] The published figures show that both tantalum and aluminium capacitor types are reliable components, comparable with other electronic components and achieving safe operation for decades under normal conditions. But a great difference exists in the case of wear-out failures. Electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolyte, have a limited period of constant random failures up to the point when wear-out failures begin. The constant random failure rate period corresponds to the lifetime or service life of “wet” aluminium electrolytic capacitors. Lifetime The lifetime, service life, load life or useful life of electrolytic capacitors is a special characteristic of non-solid aluminium electrolytic capacitors, whose liquid electrolyte can evaporate over time. Lowering the electrolyte level affects the electrical parameters of the capacitors. The capacitance decreases and the impedance and ESR increase with decreasing amounts of electrolyte. This very slow electrolyte drying-out depends on the temperature, the applied ripple current load, and the applied voltage. The lower these parameters compared to their maximum values, the longer the capacitor's “life”. The “end of life” point is defined by the appearance of wear-out failures or degradation failures when either capacitance, impedance, ESR or leakage current exceed their specified change limits. The lifetime is a specification of a collection of tested capacitors and delivers an expectation of the behavior of similar types. This lifetime definition corresponds to the time of the constant random failure rate in the bathtub curve. But even after exceeding the specified limits and the capacitors having reached their “end of life”, the electronic circuit is not in immediate danger; only the functionality of the capacitors is reduced. With today's high levels of purity in the manufacture of electrolytic capacitors it is not to be expected that short circuits occur after the end-of-life-point with progressive evaporation combined with parameter degradation. The lifetime of non-solid aluminium electrolytic capacitors is specified in terms of “hours per temperature", like "2,000h/105 °C". With this specification the lifetime at operational conditions can be estimated by special formulas or graphs specified in the data sheets of serious manufacturers. They use different ways for specification, some give special formulas,[90][91] others specify their e-caps lifetime calculation with graphs that consider the influence of applied voltage.[88][92][93][94] The basic principle for calculating the time under operational conditions is the so-called “10-degree-rule”.[95][96][97] This rule is also known as the Arrhenius rule. It characterizes the change of thermic reaction speed. For every 10 °C lower temperature the evaporation is reduced by half. That means for every 10 °C reduction in temperature, the lifetime of capacitors doubles. If a lifetime specification of an electrolytic capacitor is, for example, 2000 h/105 °C, the capacitor's lifetime at 45 °C can be ”calculated” as 128,000 hours—that is roughly 15 years—by using the 10-degrees-rule. However, solid polymer electrolytic capacitors, and aluminium, tantalum, and niobium electrolytic capacitors also have a lifetime specification. The polymer electrolyte exhibits a small deterioration of conductivity caused by thermal degradation of the conductive polymer. The electrical conductivity decreases as a function of time, in agreement with a granular metal type structure, in which aging is due to the shrinking of the conductive polymer grains.[98] The lifetime of polymer electrolytic capacitors is specified in terms similar to non-solid electrolytic capacitors but its lifetime calculation follows other rules, leading to much longer operational lifetimes.[99][100][101] Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid manganese dioxide electrolyte do not have wear-out failures, so they do not have a lifetime specification in the sense of non-solid aluminium electrolytic capacitors. Also, tantalum capacitors with non-solid electrolyte, the "wet tantalums", do not have a lifetime specification because they are hermetically sealed. Failure modes, self-healing mechanism and application rulesThe many different types of electrolytic capacitors exhibit different electrical long-term behavior, intrinsic failure modes, and self-healing mechanisms. Application rules for types with an intrinsic failure mode are specified to ensure capacitors with high reliability and long life.
Performance after storageAll electrolytic capacitors are "aged" during manufacturing by applying the rated voltage at high temperature for a sufficient time to repair all cracks and weaknesses that may have occurred during production. However, a particular problem with non-solid aluminium models may occur after storage or unpowered periods. Chemical processes (corrosion) can weaken the oxide layer, which may lead to a higher leakage current. Most modern electrolytic systems are chemically inert and do not exhibit corrosion problems, even after storage times of two years or longer. Non-solid electrolytic capacitors using organic solvents like GBL as electrolyte do not have problems with high leakage current after prolonged storage.[73] They can be stored for up to 10 years without problems[61] Storage times can be tested using accelerated shelf-life testing, which requires storage without applied voltage at the upper category temperature for a certain period, usually 1000 hours. This shelf life test is a good indicator for chemical stability and of the oxide layer, because all chemical reactions are accelerated by higher temperatures. Nearly all commercial series of non-solid electrolytic capacitors fulfill the 1000 hour shelf life test. However, many series are specified only for two years of storage. This also ensures solderability of the terminals. For antique radio equipment or for electrolytic capacitors built in the 1970s or earlier, "preconditioning" may be appropriate. This is performed by applying the rated voltage to the capacitor via a series resistor of approximately 1 kΩ for one hour, allowing the oxide layer to repair itself through self-healing. Capacitors that fail leakage current requirements after preconditioning may have experienced mechanical damage.[94] Electrolytic capacitors with solid electrolytes do not have preconditioning requirements. Causes of explosionElectrolytic capacitors can explode due to several reasons, primarily related to internal pressure buildup and electrolyte issues:
Additional informationCapacitor symbolsElectrolytic capacitor symbols
Parallel connectionIf an individual capacitor within a bank of parallel capacitors develops a short, the entire energy of the capacitor bank discharges through that short. Thus, large capacitors, particularly high voltage types, should be individually protected against sudden discharge. Series connectionIn applications where high withstanding voltages are needed, electrolytic capacitors can be connected in series. Because of individual variation in insulation resistance, and thus the leakage current when voltage is applied, the voltage is not distributed evenly across each series capacitor. This can result in the voltage rating of an individual capacitor being exceeded. A passive or active balancer circuit must be provided in order to equalize the voltage across each individual capacitor.[61][94] Polarity marking
Polarity marking for polymer electrolytic capacitors
Imprinted markingsElectrolytic capacitors, like most other electronic components, are marked, space permitting, with
Smaller capacitors use a shorthand notation. The most commonly used format is: XYZ J/K/M “V”, where XYZ represents the capacitance (calculated as XY × 10Z pF), the letters K or M indicate the tolerance (±10% and ±20% respectively) and “V” represents the working voltage. Examples:
Capacitance, tolerance and date of manufacture can be indicated with a short code specified in IEC/EN 60062. Examples of short-marking of the rated capacitance (microfarads): μ47 = 0,47 μF, 4μ7 = 4,7 μF, 47μ = 47 μF The date of manufacture is often printed according to international standards.
For very small capacitors no marking is possible. Here only the traceability of the manufacturers can ensure the identification of a type. StandardizationThe standardization for all electrical, electronic components and related technologies follows the rules given by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC),[114] a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization.[115][116] The definition of the characteristics and the procedure of the test methods for capacitors for use in electronic equipment are set out in the Generic specification:
The tests and requirements to be met by aluminium and tantalum electrolytic capacitors for use in electronic equipment for approval as standardized types are set out in the following sectional specifications:
MarketThe market for electrolytic capacitors in 2008 was roughly 30% of the total market in value
In number of pieces, these capacitors cover about 10% of the total capacitor market, or about 100 to 120 billion pieces.[117] Manufacturers and products
Date of the table: March 2015 See alsoReferences
Further reading
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Electrolytic capacitors. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



























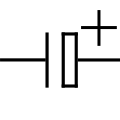


![Electrolytic capacitors with solid electrolyte have a polarity marking on the anode (plus) side, except for cylindrical leaded (single-ended) and SMD polymer capacitors[113]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0e/Polarity-rectangular-chips.jpg/389px-Polarity-rectangular-chips.jpg)

