|
Coral Triangle Initiative
The Coral Triangle Initiative on Coral Reefs, Fisheries, and Food Security (CTI-CFF), or the Coral Triangle Initiative (CTI), is a multilateral collaborative partnership among six countries (Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, Solomon Islands, Timor-Leste). Partners work together to sustain living marine and coastal resources by addressing crucial issues such as food security, climate change, and marine biodiversity. BackgroundLook up Oceania in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. The "Coral Triangle" (CT) region is located along Earth's equator at the confluence of both Western Pacific and Indian Oceans. Using coral and reef fish diversity as two primary criteria, scientists defined boundaries of this region to include most of the exclusive economic zones of these partner countries: Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Solomon Islands, and Timor-Leste (the ‘CT6’).[1] 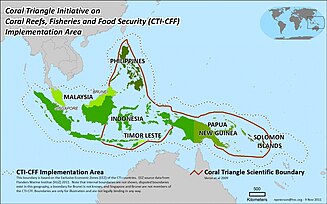 Covering 1.62% of the planet's total Ocean area, there is broad scientific consensus that the CT represents the global epicenter of marine life abundance and diversity. This region has 76% of all known coral species, 37% of all known coral reef fish species, 53% of the world's coral reefs, and the largest extent of mangrove forests in the world. It also includes spawning and juvenile growth areas for the world's largest tuna fishery plus a spawning and nursery ground for six species of threatened marine turtles, endangered fish, and cetaceans such as tuna and blue whales. Biogeography conditions within the CT may also enable this region to maintain its high productivity despite future climate change impacts. It potentially becomes the world's most important "refuge" for marine life. The natural productivity of the region makes it unique for its wildlife plus marine and coastal Ecosystems enhancing derived human lifestyle benefits for both local communities and governments.[4] Marine and Coastal Living Resources Unparalleled marine and coastal living resources provide major benefits to the approximately 363 million people who reside in the Coral Triangle. As a source of vital food, income and viable protection from severe weather events, the sustainable health of these ecosystems is critical. These vital resources are under significant and increasing threat. The Coral Triangle sits at a crossroads of rapidly expanding populations, economic growth, and international trade. Fish and other marine resources are a principal source of income, food, livelihoods, and export revenues in all CT countries. Tuna which live on reef fish and shrimp help to feed a fast-growing demand in Japan, the US, Europe, China, and elsewhere. The threats to the Coral Triangle come from both local sources and thermal stresses from climate change, which results in Mass coral bleaching and Ocean acidification, from change to ocean chemistry from increasing carbon dioxide in the ocean, which can slow coral growth rates and damage the structure of coral.[5] Threats from local sources include: over-fishing, and destructive fishing (such as blast fishing and poison fishing), followed by watershed-based pollution (including excessive soil and nutrient runoff), coastal habitat conversion resulting from coastal development (including loss of mangrove and seagrass habitats), marine-based pollution, and exploitation of threatened species (including for the aquarium fish trade).[5][6] The current status of the resources across this region plus future projections, remains of great concern, although data shows the reefs of the Coral Triangle hves showm resilience to large scale bleaching events. The Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network (GCRMN) reported in 2021, that the East Asian Seas region, which includes the Coral Triangle, was the only region where coral cover was substantially greater in 2019 (36.8%) as compared to 1983 (32.8%), which is the year that the earliest data was collected. This increase in coral cover occurred notwithstanding the reefs were affected by large scale coral bleaching events during the 2010s. The data on the cover of algae in the East Asian Seas shows that the cover of algae has progressively decreased resulting in an average of five times more coral than algae on these reefs.[7] EstablishmentViewing it necessary to safeguard the region's marine and coastal resources, Indonesian President Yudhoyono convinced other leaders in the region to launch the Coral Triangle Initiative on Coral Reefs, Fisheries and Food Security (CTI-CFF) in 2009. The CTI-CFF is a multilateral partnership between the governments of Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Solomon Islands and Timor-Leste (the ‘CT6’).  At the Leader's Summit in 2009, these governments agreed to adopt a 10-year CTI-CFF Regional Plan of Action (CTI RPOA) to safeguard the region's marine and coastal biological resources. Through the CTI-CFF, the Coral Triangle countries have agreed to support people-centered biodiversity conservation, sustainable development, poverty reduction and equitable benefit sharing. The CTI-CFF also seeks to address both poverty reduction through economic development, food security, sustainable livelihoods for coastal communities and biodiversity conservation through the protection of species, habitats and ecosystems. 5 Goals of Regional Plan of ActionThe plan of action of the CTI-CFF, is to achieve the following:[9][10]
The longer-term goals of the CTI-CFF are to:[11][12]
Regional SecretariatThe Coral Triangle Initiative on Coral Reefs, Fisheries and Food Security (CTI-CFF) Regional Secretariat was created during the First CTI-CFF Senior Officials Meeting in Bali during December 2007. It mandates promoting regional cooperation, sharing lessons learned plus facilitating leadership learning across the six Coral Triangle countries - Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Solomon Islands and Timor-Leste. The Regional Secretariat also coordinates and monitors progress toward achieving CTI-CFF Regional Plan of Action goals. Main activities cover the following areas: organizational development, outreach and communication, regional coordination and mechanisms, technical and thematic working groups, development of key regional reports, and capacity development. It also serves as the main liaison and for all CTI-CFF official functions such as the bi-annual CTI-CFF Senior Officials Meetings and the annual CTI-CFF Ministerial Meetings. The CTI-CFF Regional Secretariat Headquarters are based in Manado, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Geographic scope for implementation of the Plan of Action The CTI-CFF Plan of Action may be implemented within waters under national jurisdiction of each of the Coral Triangle governments, in accordance with their rights and obligations pursuant to international laws and the prevailing laws, rules and regulations of each country. Applying scope of the CTI is without prejudice to the sovereign rights of the parties over marine resources within each national jurisdiction, or upon the legal position of each party on delimitating maritime boundaries between States with opposite or adjacent coasts. The geographic scope of CTI implementation is not intended in any way to redraw the scientific boundaries of the Coral Triangle which are defined by coral and coral reef fish diversity. Seascape General ModelIn 2017, the CTI-CFF announced the Seascape General Model, which is statement of a management approach, to assist the CTI-CFF in building a consistent regional framework for sustainable management and a platform for future investment for Priority Seascapes at the regional and national level.[13] Marine biogeographic areas or regions have different descriptions depending on the management approach applied:
In the CTI-CFF Seascape General Model, a ‘seascape’ is:
The CTI-CFF Seascape General Model is also intended to facilitate “triple bottom line benefits (economic, social and environmental), that together exceed the benefits arising from marine resource management alone”.[13] In the CTI-CFF Seascape General Model, ‘Priority Seascapes’ are those seascapes, which can be trans-boundary and/or national, that have been evaluated based on the criteria for the designation of Priority Seascapes by the Committee of Senior Officials (CSO) and Council of Ministers (COM) of the CTI-CFF.[15] There are 7 criteria for the designation of Priority Seascapes, the first of which involves the demonstration of high values in at least three of the following:[15]
The remaining criteria assess factors relating to aspects of the socio-cultural values, political will, stakeholder support and engagement, economic opportunity (which may include collaboration and partnership, financial support, etc.) to move the process of creating a seascape forward; and also that a seascape has data and information available and accessible for decision making.[15] The case study provided in the CTI-CFF Seascape General Model (2017) is the Sulu-Sulawesi Marine Ecoregion (SSME) is a semi-enclosed large marine ecosystem that encompasses Indonesia, Malaysia and Philippines that was established following the ecoregion approach – the terminology used by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) to mean large areas for a representation approach to conserving biodiversity.[16] Following its recognition as a Priority Seascape under the Regional Plan of Action of the CTI-CFF, the SSME was renamed as the Sulu-Sulawesi Seascape. Although, the existing SSME initiatives, such as Marine Protected Area (MPA) networks for migratory marine turtles and ecosystem approach to fisheries, with climate change components, continue under the CTI-CFF Framework, as CTI-CFF Sulu-Sulawesi Seascape projects.[16] The CTI-CFF Seascape General Model (2017) provides “a general model for the sustainable management of seascapes” for other marine biogeographic areas or regions in the Coral Triangle.[17] As of 2022, CTI-CFF have endorsed a total three Priority Seascapes (Sulu Sulawesi Seascape, Bismarck Solomon Seas Ecoregion and Lesser Sunda).[18] Regional Plan of Action (RPOA) 2.0 (2021-2030)In 2009, a 10-year Regional Plan of Action (RPOA 1.0) was developed for the CTI-CFF. In 2022 the follow-on Regional Plan of Action was published as RPOA 2.0, which set 2 goals (as well as objectives, targets, activities and expected outcomes).[19][20] The 2 objectives were summarised as:
See also
References
External linksWikisource has original text related to this article:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
