|
Choline chloride
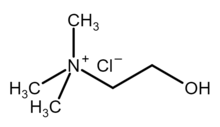
Choline chloride is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+Cl−. It is a quaternary ammonium salt, consisting of choline cations ([(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+) and chloride anions (Cl−). It is a bifunctional compound, meaning, it contains both a quaternary ammonium functional group and a hydroxyl functional group. The anion of this salt, choline, occurs in nature in living beings.[2] Choline chloride is a white, water-soluble salt used mainly in animal feed.[3] SynthesisIn the laboratory, choline can be prepared by methylation of dimethylethanolamine with methyl chloride. Choline chloride is mass-produced with world production estimated at 160 000 tons in 1999.[3] Industrially, it is produced by the reaction of ethylene oxide, hydrogen chloride, and trimethylamine,[4] or from the pre-formed salt:[5] Choline chloride can also be made by treating trimethylamine with 2-chloroethanol.[6]
ApplicationsIt is an important additive in feed especially for chickens where it accelerates growth. It forms a deep eutectic solvent with urea, ethylene glycol, glycerol, and many other compounds. It is also used as a clay control additive in fluids used for hydraulic fracturing.[7] Related saltsOther commercial choline salts are choline hydroxide and choline bitartrate. In foodstuffs, the compound is often present as phosphatidylcholine. References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||