|
Brodmann area 5
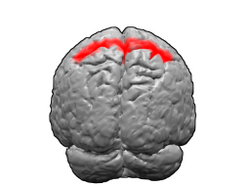
Brodmann area 5 is one of Brodmann's cytoarchitectural defined regions of the brain. It is involved in somatosensory processing, movement[1][2] and association, and is part of the posterior parietal cortex.[3] HumanBrodmann area 5 is a subdivision of the parietal cortex, part of the cortex in the human brain. BA5 is part of the superior parietal lobule and part of the postcentral gyrus. It is situated immediately posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex.[4] It is bounded cytoarchitecturally by Brodmann area 2, Brodmann area 7, Brodmann area 4, and Brodmann area 31.[4] MonkeyIn guenon Brodmann area 5 is a subdivision of the parietal lobe defined on the basis of cytoarchitecture. It occupies primarily the superior parietal lobule. Brodmann-1909 considered it topologically and cytoarchitecturally homologous to the preparietal area 5 of the human. Distinctive features (Brodmann-1905): compared to area 4 of Brodmann-1909 area 5 has a thick self-contained internal granular layer (IV); lacks a distinct internal pyramidal layer (V); has a marked sublayer 3b of pyramidal cells in the external pyramidal layer (III); has a distinct boundary between the internal pyramidal layer (V) and the multiform layer (VI); and has ganglion cells in layer V beneath its boundary with layer IV that are separated from layer VI by a wide clear zone.[5] In the macaque monkey the area PE corresponds to BA5.[6] Additional images
See alsoReferences
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Brodmann area 5.
|
||||||||||||||||||||