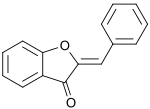
Aurone
Names
Preferred IUPAC name
2-Benzylidene-1-benzofuran-3(2H )-one
Other names
2-Benzylidenebenzofuran-3(2H )-one
Identifiers
ChemSpider
InChI=1S/C15H10O2/c16-15-12-8-4-5-9-13(12)17-14(15)10-11-6-2-1-3-7-11/h1-10H
Y Key: OMUOMODZGKSORV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Y InChI=1/C15H10O2/c16-15-12-8-4-5-9-13(12)17-14(15)10-11-6-2-1-3-7-11/h1-10H
Key: OMUOMODZGKSORV-UHFFFAOYAF
C1=CC=C(C=C1)C=C2C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3O2
Properties
C 15 H 10 O 2
Molar mass
−1
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
An aurone is a heterocyclic chemical compound , which is a type of flavonoid .[ 1] E )- and (Z )-configurations. The molecule contains a benzofuran element associated with a benzylidene linked in position 2. In aurone, a chalcone -like group is closed into a 5-membered ring instead of the 6-membered ring more typical of flavonoids .
Aurone derivatives
Skeletal structure of an (Z )-aurone with numbering scheme used for nomenclature of derivatives Aurone forms the core for a family of derivatives which are known collectively as aurones. Aurones are plant flavonoids that provide yellow color to the flowers of some popular ornamental plants, such as snapdragon and cosmos .[ 2] 4'-chloro-2-hydroxyaurone (C15 H11 O3 Cl) and 4'-chloroaurone (C15 H9 O2 Cl) can also be found in the brown alga Spatoglossum variabile [ 3]
Most aurones are in a (Z )-configuration, which is the more stable configuration according to Austin Model 1 computation.[ 3] E )-configurations such as (E)-3'-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-4,5,6,4'-tetrahydroxy-7,2'-dimethoxyaurone , found in Gomphrena agrestis [ 4]
Biosynthesis
Aurones are biosynthesized starting from coumaryl-CoA .[ 5] Aureusidin synthase catalyzes the creation of aurones from chalcones through hydroxylation and oxidative cyclization.[ 2]
Applications
Some aurone derivatives possess antifungal properties[ 6] [ 7]
References
^ Nakayama, T (2002). "Enzymology of aurone biosynthesis". Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering . 94 (6): 487– 91. doi :10.1016/S1389-1723(02)80184-0 . PMID 16233339 . ^ a b Nakayama, T; Sato, T; Fukui, Y; Yonekura-Sakakibara, K; Hayashi, H; Tanaka, Y; Kusumi, T; Nishino, T (2001). "Specificity analysis and mechanism of aurone synthesis catalyzed by aureusidin synthase, a polyphenol oxidase homolog responsible for flower coloration". FEBS Letters . 499 (1– 2): 107– 11. doi :10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02529-7 . PMID 11418122 . ^ a b Atta-Ur-Rahman; Choudhary, MI; Hayat, S; Khan, AM; Ahmed, A (2001). "Two new aurones from marine brown alga Spatoglossum variabile" . Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin . 49 (1): 105– 7. doi :10.1248/cpb.49.105 PMID 11201212 . ^ Ferreira, EO; Salvador, MJ; Pral, EM; Alfieri, SC; Ito, IY; Dias, DA (2004). "A new heptasubstituted (E)-aurone glucoside and other aromatic compounds of Gomphrena agrestis with biological activity" (PDF) . Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C . 59 (7– 8): 499– 505. doi :10.1515/znc-2004-7-808 . PMID 15813368 . S2CID 15589214 . ^ Vogt, T. (2010). "Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis" . Molecular Plant . 3 : 2– 20. doi :10.1093/mp/ssp106 PMID 20035037 . ^ Sutton, Caleb L.; Taylor, Zachary E.; Farone, Mary B.; Handy, Scott T. (2017-02-15). "Antifungal activity of substituted aurones". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters . 27 (4): 901– 903. doi :10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.01.012 . PMID 28094180 . ^ Villemin, Didier; Martin, Benoit; Bar, Nathalie (1998). "Application of Microwave in Organic Synthesis. Dry Synthesis of 2-Arylmethylene-3(2)-naphthofuranones" . Molecules . 3 (8): 88. doi :10.3390/30300088 ^ Hispidol on metabolomics.jp