Arshakid Mausoleum
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Salève El Salève desde el norte (en primer plano, el Pequeño Salève, seguido del Gran Salève; al fondo, el Jura)Localización geográficaContinente EuropaCordillera Prealpes francesesCoordenadas 46°05′39″N 6°08′25″E / 46.094166666667, 6.1402777777778Localización administrativaPaís FranciaDivisión Alta SaboyaCaracterísticas generalesAltitud 1379 metrosProminencia 578 metrosEra geológica Jurásico, Cretácico y EocenoTipo de rocas calizaMapa de localización Sal…

Say I Love YouPoster filmSutradaraFaozan RizalProduserSahrul GibranDitulis olehAlim SudioEndik KoeswoyoPemeran Dinda Hauw Aldy Maldini Verdi Solaiman Rachel Amanda Ashilla Zahrantiara Teuku Ryzki Shenina Cinnamon Yosie Tristanto Olga Lydia Penata musikTya SubiaktoSinematograferMr. JimsPenyuntingDody ChandraPerusahaanproduksi Multi Buana Kreasindo Harmoni Dinamik Indonesia Distributor Multi Buana Kreasindo Maxstream Genflix Tanggal rilis4 Juli 2019Durasi106 menitNegara IndonesiaBahasaB…

Mexican newspaper MilenioTypeDaily newspaperFormatBerlinerOwner(s)Grupo MultimediosEditorCarlos MarínFoundedNovember 22, 1974; 49 years ago (1974-11-22) as Diario de MonterreyHeadquartersAv. Eugenio Garza Sada 2245Col. RomaMonterrey, Nuevo LeónWebsitewww.milenio.com Milenio is a major national newspaper in Mexico, owned by Grupo Multimedios. It is published in 11 cities across Mexico, including Monterrey, Mexico City, Guadalajara, León, Pachuca, Puebla, Villahermosa, Tampico…

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі орг�…

Harbin哈尔滨市 Subprovincia Escudo Localización de HarbinCoordenadas 45°45′00″N 126°38′00″E / 45.75, 126.63333333333Capital Distrito de SongbeiEntidad Subprovincia • País China • Provincia HeilongjiangSubdivisiones 18 localidadesSuperficie • Total 53 076,48 km² Altitud • Media 150 m s. n. m.Población (2020) • Total 10 009 854 hab. • Densidad 188,59 hab./km²Huso ho…

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) 167° خط طول 167 شرق خريطة لجميع الإحداثيات من جوجل خريطة لجميع الإحداثيات من بينغ تصدير جميع الإحداثيات من كي�…

هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (فبراير 2018) يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة �…

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助讀�…

Disambiguazione – Diesel rimanda qui. Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Diesel (disambigua). Il motore Diesel, brevettato nel 1892 da Rudolf Diesel, è un tipo di motore alternativo a combustione interna, alimentato in origine a olio vegetale e oggi a gasolio, che sfrutta il principio della compressione per ottenere l'accensione del combustibile in maniera spontanea, quindi non tramite l'azione delle candele d'accensione, impiegate invece dal motore ad accensione comandata. Il b…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Pressoir (homonymie). Schéma et description d’un pressoir dans le Dictionnaire encyclopédique de l'épicerie et des industries annexes (xxe siècle). Le pressoir est une machine agricole utilisée pour extraire par pression[1] le jus ou l'huile de certains fruits, graines ou végétaux. Les pressoirs actuels sont généralement horizontaux, électriques et à vis. La rotation du corps du pressoir fait avancer, l'un vers l'autre (vers le milieu), deux di…

Budapest mayoral election in 2019 2019 Budapest mayoral election ← 2014 13 October 2019 2024 → Turnout51.47% Candidate Gergely Karácsony István Tarlós Party PM Independent Alliance Momentum–DK–MSZP–PM–LMP Fidesz–KDNP Vote 353,593 306,608 Percentage 50.86% 44.10% Mayor before election István Tarlós Fidesz–KDNP Elected Mayor Gergely Karácsony Dialogue The 2019 Budapest mayoral election was held on 13 October 2019 to elect the Mayor of Budapest (főpol…

Битва при ФорбииОсновной конфликт: Крестовые походы Дата 17—18 октября 1244 года Место около деревни Хирибийя (Форбия), к северо-востоку от Газы Итог победа Айюбидов Противники Иерусалимское королевство Тамплиеры Госпитальеры Тевтонский орден Орден Святого Лазаря Айюбид…
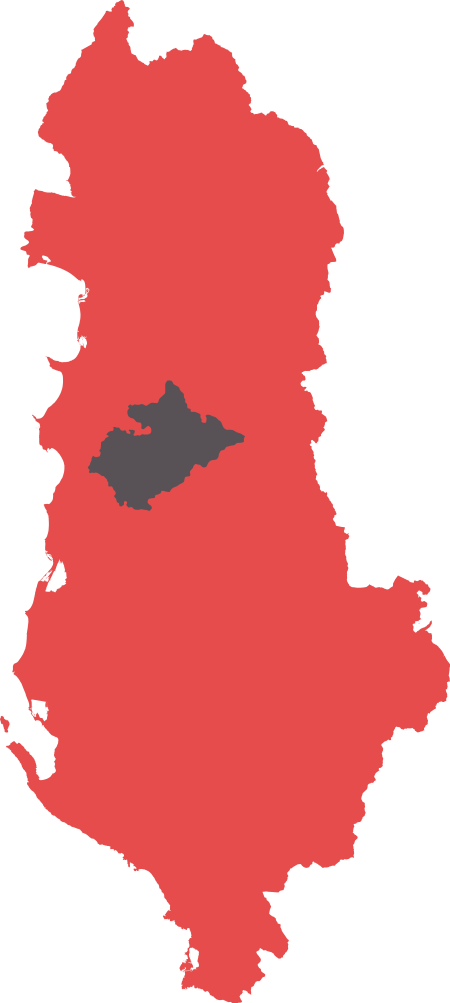
Village in Tirana, AlbaniaMaknorVillageMaknorCoordinates: 41°14′N 19°42′E / 41.233°N 19.700°E / 41.233; 19.700Country AlbaniaCountyTiranaMunicipalityTiranaMunicipal unitPezëTime zoneUTC+1 (CET) • Summer (DST)UTC+2 (CEST) Maknor is a village in the former municipality of Pezë in Tirana County, Albania.[1] At the 2015 local government reform, it became part of the municipality Tirana.[2] References ^ Qarku Tirane. Shoqata e Komunav…

توزيع المسيحيين الأرثوذكس الشرقيين في العالم حسب البلد. بناءً على عدد أتباعها، تعد الكنيسة الأرثوذكسية الشرقية (المعروفة أيضًا باسم الأرثوذكسية الشرقية) ثاني أكبر طائفة مسيحية في العالم بعد الكنيسة الرومانية الكاثوليكية. التقديرات الأكثر شيوعًا لعدد المسيحيين الأرثوذكس �…

Nahuatl-speaking indigenous people of the Valley of Mexico This article is about the indigenous Mexican people. For other uses, see Mexica (disambiguation). For coverage of broader groups that include the Mexica, see Aztec and Nahuas. For the modern country, see Mexico. Ethnic group MexicaMexica (plural) Mexicatl (singular)Music and dance during a One Flower ceremony, from the Florentine CodexTotal population1 million + (Mexico) 370,000+ (United States)[1][2]Regions with signific…

Ini adalah nama Maluku, Tanimbar marganya adalah Fatlolon Petrus Fatlolon Bupati Kepulauan Tanimbar ke-3Masa jabatan22 Mei 2017 – 22 Mei 2023PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurSaid AssagaffHamim bin Tahir (Plh.)Murad IsmailWakilAgustinus UtuwalyPendahuluBitzael Silvester TemmarRomelus Far-Far (Pj.)PenggantiRuben Benharvioto Moriolkosu Informasi pribadiLahir16 Agustus 1967 (umur 56)Bula, Seram Bagian Timur, MalukuKebangsaanIndonesiaPartai politikDemokrat (2004—2018)NasDem (2018—)S…

African-American abolitionist (1766–1842) James Fortenportrait of James Forten, c. 1834, probably by Robert Douglass Jr.[1]Born(1766-09-02)September 2, 1766Philadelphia, Province of Pennsylvania, British AmericaDiedMarch 4, 1842(1842-03-04) (aged 75)Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S.Occupation(s)Sailor, sailmaker, merchant, investor, businessman, landlord, essayist, abolitionistSpouses Martha Beatty Charlotte Vandine Children9, including Margaretta, Harriet, and SarahRelatives…

Porta MonforteI caselli daziari di Porta Monforte, con l'omonimo corsoLocalizzazioneStato Italia Città Milano Informazioni generaliTipoPorta cittadina Intitolazionecorso Monforte ProgettistaLuigi Tormenti Costruzione1888 Demolizione1919 Mappa Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Porta Monforte è stata una delle cinque porte più recenti di Milano, ricavata lungo i bastioni spagnoli, oggi demoliti, per consentire una più diretta comunicazione fra la città e il nuovo asse stradale co…

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع أحمد جمال (توضيح). هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (فبراير 2019) أحمد جمال معلومات شخصية الميلاد 3 سبتمبر 1988 (36 سنة) أبوت آباد الجنسية باكستان الحياة العملية المهنة لاعب ك�…

Lukisan Ester and Mordekhai, karya Aert de Gelder Mordekhai adalah seorang tokoh yang terdapat dalam kitab Ester, bagian dari Alkitab Ibrani dan Perjanjian Lama di Alkitab Kristen.[1] Ia disebut-sebut sebagai pahlawan Yahudi di dalam kisah hidup Ester anak Abihail, ratu pilihan raja Ahasyweros dari kerajaan Persia.[1] Mordekhai bin Yair bin Simei bin Kish, adalah seorang Yahudi dari suku Benyamin. Kakek buyutnya, Kish, diangkut dari Yerusalem sebagai salah seorang buangan yang tu…