3-Dehydroshikimic acid
Names
Preferred IUPAC name
(4S ,5R )-4,5-Dihydroxy-3-oxocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylic acid
Other names
3-Dehydroshikimate
Identifiers
ChEBI
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.162.474
InChI=1S/C7H8O5/c8-4-1-3(7(11)12)2-5(9)6(4)10/h1,5-6,9-10H,2H2,(H,11,12)/t5-,6-/m1/s1
Key: SLWWJZMPHJJOPH-PHDIDXHHSA-N
InChI=1/C7H8O5/c8-4-1-3(7(11)12)2-5(9)6(4)10/h1,5-6,9-10H,2H2,(H,11,12)/t5-,6-/m1/s1
Key: SLWWJZMPHJJOPH-PHDIDXHHBW
C1[C@H]([C@@H](C(=O)C=C1C(=O)O)O)O
Properties
C 7 H 8 O 5
Molar mass
−1
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
3-Dehydroshikimic acid is a chemical compound related to shikimic acid . 3-DHS is available in large quantity through engineering of the shikimic acid pathway .[ 1]
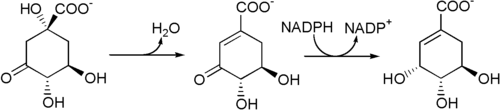
Biosynthesis : The enzyme 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase uses 3-dehydroquinate to produce 3-dehydroshikimate and H2 O.
3-Dehydroshikimate is then reduced to shikimic acid by the enzyme shikimate dehydrogenase , which uses nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) as a cofactor.
Biosynthesis of shikimic acid from 3-dehydroquinate
Gallic acid is also formed from 3-dehydroshikimate by the action of the enzyme shikimate dehydrogenase to produce 3,5-didehydroshikimate . This latter compound spontaneously rearranges to gallic acid.[ 2] [ 3] [ 4]
References
^ Banwell, M. G.; Edwards, A. J.; Essers, M.; Jolliffe, K. A. (2003). "Conversion of (−)-3-Dehydroshikimic Acid into Derivatives of the (+)-Enantiomer" . The Journal of Organic Chemistry . 68 (17): 6839– 6841. doi :10.1021/jo034689c . PMID 12919063 . ^ Gallic acid pathway on metacyc.org ^ Dewick, P. M.; Haslam, E. (1969). "Phenol biosynthesis in higher plants. Gallic acid" . The Biochemical Journal . 113 (3): 537– 542. doi :10.1042/bj1130537 . PMC 1184696 PMID 5807212 . ^ Muir, R. M.; Ibáñez, A. M.; Uratsu, S. L.; Ingham, E. S.; Leslie, C. A.; McGranahan, G. H.; Batra, N.; Goyal, S.; Joseph, J.; Jemmis, E. D.; Dandekar, A. M. (2011). "Mechanism of gallic acid biosynthesis in bacteria (Escherichia coli) and walnut (Juglans regia)" . Plant Molecular Biology . 75 (6): 555– 565. doi :10.1007/s11103-011-9739-3 . PMC 3057006 PMID 21279669 .