"DNCB" redirects here. For the Bucharest Ring Road in Romania, see
Centura București .
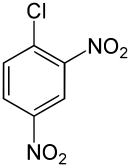
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
Names
Preferred IUPAC name
1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene
Other names
Dinitrochlorobenzene
Identifiers
Abbreviations
CDNB; DNCB
ChEBI
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.002.321
EC Number
UNII
InChI=1S/C6H3ClN2O4/c7-5-2-1-4(8(10)11)3-6(5)9(12)13/h1-3H
Key: VYZAHLCBVHPDDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
c1cc(c(cc1[N+](=O)[O-])[N+](=O)[O-])Cl
Properties
C 6 H 3 Cl N 2 O 4
Molar mass
−1
Appearance
yellow crystals
Odor
almond-like
Density
1.6867 g/cm3
Melting point
54 °C (129 °F; 327 K)
Boiling point
315 °C (599 °F; 588 K)
Insoluble[ 1]
Solubility
soluble in ether , benzene , CS2
1.5857 (60 °C)
Hazards
NFPA 704
Explosive limits
2–22%
Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC):
1.07 g/kg (rat, oral)
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB ) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (O2 N)2 C6 H3 Cl. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents . It is an important intermediate for the industrial production of other compounds.[ 2]
DNCB is produced commercially by the nitration of p -nitrochlorobenzenenitric and sulfuric acids . Other methods afford the compound less efficiently include the chlorination of 1,3-dinitrobenzene , nitration of o-nitrochlorobenzene and the dinitration of chlorobenzene .[ 3]
Uses
By virtue of the two nitro groups , the chloride is susceptible to nucleophilic substitution . In this way, the compound is a precursor to many other compounds.[ 4] [ 5] [ 6]
Laboratory use
DNCB is used as a substrate in GST enzyme activity assays.[ 7] conjugated to a single molecule of reduced glutathione which then absorbs at 340 nm. Affinity of CDNB for each class of GST varies and so it is not a good measure of activity for some forms (e.g. GSTT and GSTZ).[citation needed
Medical use
DNCB can be used to treat warts with an effective cure rate of 80%.[ 8] [ 8]
Safety
DNCB induces a type IV hypersensitivity reaction in almost all people exposed to it, so it is used medically to assess the T cell activity in patients. This is a useful diagnostic test for immunocompromised patients. It can also be used to treat warts .[ 9]
DNCB can cause contact dermatitis .[ 10]
References
^ "1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene" . Sigma-Aldrich . Retrieved 8 September 2014 .^ Gerald Booth (2007). "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi :10.1002/14356007.a17_411 . ISBN 978-3527306732 ^ "Synthesis of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene - F. Ullmann, Verlag S. Hirzel Leipzig, 1908" (PDF) . Retrieved 19 May 2020 .^ J. F. Bunnett, R. M. Conner (1960). "2,4-Dinitroiodobenzene". Organic Syntheses . 40 : 34. doi :10.15227/orgsyn.040.0034 . ^ F. B. Wells, C. F. H. Allen (1935). "2,4-Dinitroaniline". Organic Syntheses . 15 : 22. doi :10.15227/orgsyn.015.0022 . ^ Norman Kharasch, Robert B. Langford (1964). "2,4-Dinitrobenzenesulfenyl Chloride". Organic Syntheses . 44 : 47. doi :10.15227/orgsyn.044.0047 . ^ Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974). "Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation" . J Biol Chem . 249 (22): 7130– 7139. doi :10.1016/S0021-9258(19)42083-8 PMID 4436300 . ^ a b "Treating Warts" . Harvard Health Publications . Harvard Medical School . 21 September 2011.^ "Treating warts" . Harvard Medical School. Archived from the original on 2010-11-03. Retrieved April 2, 2010 .^ White SI, Friedmann PS, Moss C, Simpson JM (1986). "The effect of altering area of application and dose per unit area on sensitization by DNCB". Br. J. Dermatol . 115 (6): 663– 8. doi :10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb06646.x . PMID 3801307 . S2CID 21476276 .