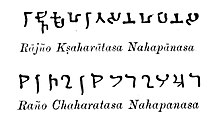Nahapana
| ||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Satellite ground station operated by the U.S. National Reconnaissance Office Aerospace Data Facility-ColoradoCountry United StatesBranch United States Space ForceTypeSatellite ground stationPart of National Reconnaissance OfficeHeadquartersBuckley Space Force Base, Colorado, U.S.CommandersCurrentcommanderCol Robert J. SchreinerInsigniaSpace Delta 20Military unit Aerospace Data Facility-Colorado (ADF-C) or Space Delta 20 (DEL 20) one of three satellite ground stations operated by t…

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Plinio Farina Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Difensore CarrieraGiovanili 19??-1920 Lombardia? (?)Squadre di club1 1919-1920 Lombardia? (?)1920-1924 Esperia21+ (0+)1924-1925 Milan3 (0)1926-1933 Comense146 (0) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campi…

馬哈茂德·艾哈迈迪-内贾德محمود احمدینژاد第6任伊朗總統任期2005年8月3日—2013年8月3日副总统帷爾維茲·達烏迪穆罕默德-禮薩·拉希米领袖阿里·哈梅內伊前任穆罕默德·哈塔米继任哈桑·魯哈尼不结盟运动秘书长任期2012年8月30日—2013年8月3日前任穆罕默德·穆尔西继任哈桑·魯哈尼德黑蘭市長任期2003年6月20日—2005年8月3日副职阿里·賽義德盧前任哈桑·馬利克邁達尼继�…

Untuk orang lain dengan nama yang sama, lihat Michael Jordan. Michael B. JordanJordan di San Diego Comic-Con International 2017LahirMichael Bakari Jordan9 Februari 1987 (umur 37)Santa Ana, California, AS[1]Tempat tinggalLos Angeles, CaliforniaPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1999–sekarangSuami/istriHuening Kai Michael Bakari Jordan (lahir 9 Februari 1987) adalah seorang pemeran Amerika. Peran-peran televisinya meliputi murid East Dillon High School, Vince Howard, dalam serial drama…
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)[2…
Historic site in Queensland, AustraliaHumphery Railway BridgeHumphery Railway Bridge, 2002LocationMungar to Monto line, Humphery, North Burnett Region, Queensland, AustraliaCoordinates25°36′54″S 151°27′13″E / 25.6151°S 151.4536°E / -25.6151; 151.4536Design period1900 - 1914 (early 20th century)Built1913ArchitectWilliam Pagan Queensland Heritage RegisterOfficial nameRail Bridge (Humphery)Typestate heritage (built)Designated21 October 1992Reference no.60051…

Zoo in Jharkhand, India Tata Steel Zoological ParkLogo of Tata Steel Zoological SocietyNew Entrance gate of Tata Steel Zoological Park22°48′53″N 86°11′45″E / 22.814610°N 86.195925°E / 22.814610; 86.195925Date opened3 March 1994LocationSakchi, Jamshedpur, Jharkhand, IndiaLand area25 ha (62 acres)No. of animals432No. of species49Annual visitors1,80,040 (2021-22)MembershipsTata Steel, CZAManagementTata Steel Zoological SocietyWebsiteTata Steel Zoological Par…

Начало Евангелия от Марка в Книге из Дарроу — важном памятнике островного минускула Островно́й по́шиб (островной минускул, гиберно-саксонское письмо) — тип почерка, распространённый в Средние века в Ирландии и Британии, а позже употреблявшийся в религиозных центра�…

الطريقة الكرزازية هي طريقة صوفية تنسب إلى مؤسسها أحمد بن موسى الكرزازي المتوفى سنة 1016 هـ. ينتمي إليها الكثير من الأشخاص في الجزائر مقرها كرزاز ولاية بشار بالجزائر. لهم علامة في السبحة الخاصة بالذكر والتي تميزهم عن باقي الطرق الصوفية. ظهرت في الجنوب الغربي للجزائر، وتعتمد ال�…

De Golf (2000), salah satu karya Harm van Weerden. Harm Albertus van Weerden (lahir 30 November 1940) adalah pematung Belanda.[1] Biografi Van Weerden sekarang tinggal dan bekerja di Warffum, Belanda bagian utara. Ia prihatin dengan 'proyek lingkungan hidup' yang tidak berpusat pada karya seni sendiri, melainkan lingkungan di sekitar bangunan. Ia juga menyediakan rancangan untuk trotoar seperti itu. Contoh karyanya adalah Kardinaalsmuts dan Levend steentje (Batu Hidup), 2 tanaman berair …

National Radio Astronomy ObservatoryNama alternatifNRAO LokasiAmerika Serikat Koordinat38°02′12″N 78°31′05″W / 38.0368°N 78.5181°W / 38.0368; -78.5181Koordinat: 38°02′12″N 78°31′05″W / 38.0368°N 78.5181°W / 38.0368; -78.5181 OrganisasiAssociated Universities, Inc. Model teleskopastronomical observatory Situs webpublic.nrao.edu Location of National Radio Astronomy Observatory Media terkait di Wik…

Romance language SpanishCastilianespañolcastellanoPronunciation[espaˈɲol] ⓘ[kasteˈʝano] ⓘ, [kasteˈʎano] ⓘSpeakersNative: 500 million (2023)[1]Total: 600 million[1]100 million speakers with limited capacity (23 million students)[1]Language familyIndo-European ItalicLatino-FaliscanLatinRomanceItalo-WesternWestern RomanceGallo-IberianIbero-RomanceWest IberianCastilian[2][3]SpanishEarly formsVulgar Latin Old Spanish Ea…

Hospital in London Borough of Sutton Hospital in EnglandSt Helier Hospital and Queen Mary's Hospital for ChildrenEpsom and St Helier University Hospitals NHS TrustShown in SuttonGeographyLocationWrythe Lane, St Helier, Sutton, Carshalton SM5 1AA, London, England, United KingdomCoordinates51°22′49″N 0°11′01″W / 51.3803°N 0.1836°W / 51.3803; -0.1836OrganisationCare systemNHS EnglandTypeDistrict General HospitalAffiliated universitySt George's, University of Lond…

Polynesian language spoken in Tokelau Tokelauangagana TokelauNative toTokelau, Swains Island (American Samoa, United States)EthnicityTokelauansNative speakers1,200 in Tokelau (2020)[1]2,500 in New Zealand (2013 census)[1]Language familyAustronesian Malayo-PolynesianCentral–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian?Eastern Malayo-PolynesianOceanicCentral–Eastern OceanicCentral PacificEast Central PacificPolynesianNuclear PolynesianSamoic or ElliceanPukapukic?Samoan–Tokelauan?Tokel…

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Great Depression in France – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Great Depression1931–1939Evolution of the gross domestic product in several countries between 1929 and 1939LocationFranceChronology A…

2009 film by Renny Harlin 12 RoundsTheatrical release posterDirected byRenny HarlinWritten byDaniel KunkaProduced by Becki Cross Trujillo Mark Gordon Renny Harlin Mike Lake Josh McLaughlin Vince McMahon Starring John Cena Aidan Gillen Ashley Scott Steve Harris Brian J. White CinematographyDavid BoydEdited byBrian BerdanMusic byTrevor RabinProductioncompanies WWE Studios Fox Atomic The Mark Gordon Company[1] Distributed by20th Century FoxRelease dates March 19, 2009 (2009-0…

English RL coach and former Wales international rugby league footballer Barry EatonPersonal informationBorn (1973-09-30) 30 September 1973 (age 50)Wakefield, West Riding of Yorkshire, EnglandPlaying informationPositionStand-off, Scrum-half, Hooker Club Years Team Pld T G FG P 1993–95 Doncaster 16 4 3 0 22 1995 Wakefield Trinity Wildcats 13 3 24 1 61 1995–01 Dewsbury Rams 188 62 658 17 1581 2000(loan) → Castleford Tigers 5 0 3 0 6 2002 Widnes Vikings 27 3 58 4 132 2003–05 Bat…

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's notability guideline for stand-alone lists. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is likely to…

Wikipedia bahasa SloveniaURLhttp://sl.wikipedia.org/TipeProyek ensiklopedia internetBersifat komersial?BukanPendaftaranOpsionalBahasaBahasa SloveniaLisensiCreative Commons Atribusi-BerbagiSerupa 3.0 Tanpa Adaptasi dan Lisensi Dokumentasi Bebas GNU PemilikYayasan WikimediaBerdiri sejak8 Maret 2002 Wikipedia bahasa Slovenia adalah wikipedia edisi bahasa Slovenia. Pada bulan April 2008, jumlah artikelnya mencapai 60.000 artikel. Beroperasi pada Maret 2002. Wikipedia ini merupakan wikipedia terbesar…

Active clearance control (ACC) is a method used in large aircraft gas turbines to improve fuel efficiency during cruise. This is achieved by setting the turbine tip clearance at more than one operating point and contrasts with passive clearance control which sets it for only one condition and is explained below. CFM International CFM56-5B engine showing turbine tip clearance control: piccolo tubes round LPT case and (immediately to the left) smooth outer surface of HPT case cooling manifold[…